مقالة علمية جديدة للدكتورة هنادي هادي بعنوان "Pericoronitis"
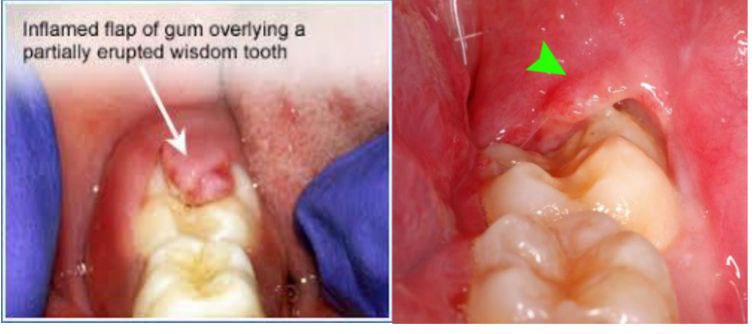
Pericoronitis<br />Pericoronitis is a term used to describe the localized inflammation of the soft tissues <br />surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth (most common lower third molar).<br />It occurs due to accumulation of the bacterial plaque in the pseudo-pocket formed <br />around the lower third molar. In early stages of pericoronitis, the patient suffers from <br />pain, swelling of the peicoronal tissues, redness, mucosal ulceration, and loss of <br />function. Local therapy is recommended in the initial stage by irrigation with sterile <br />saline, chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, debridement of plaque and food debris and <br />removal of the occlusal trauma. No antibiotic is indicated in the initial stage of <br />pericoronitis. Antibiotic therapy is recommended only when there is systemic <br />symptoms in severe cases like lymphadenopathy, pyrexia, malaise, difficulty in<br />swallowing and trismus. These severe cases may lead to a life-threatening Ludwig’s <br />angina. The use of antibiotics in the severe cases is an adjunct therapy and should not <br />be considered as a first-line treatment.<br />Oral amoxicillin (500 mg every 8 hours for five days) or oral metronidazole (400 mg<br />every 8 hours for five days) are recommended for predominant anaerobic microflora <br />found in pericoronitis. Erythromycin is used in case of penicillin allergy.<br />Surgical treatment is done in some conditions by doing operculectomy (if the lower<br />third molar with a favorable eruption position) or pericoronal ostectomy (If a tooth is <br />in a favorable position to erupt into functional occlusion with adequate space, <br />removing the bone that is covering the coronal portion of the erupting tooth can help <br />accelerate the eruption). Extraction of the involved tooth is recommended by dentists <br />if the tooth does not have a favorable eruption position. If a mechanical trauma is <br />caused by the opposing tooth, extraction of the opposing tooth should be considere