Preprosthetic Surgery
Author: Mohammed Ali Shalan
Introduction
Preprosthetic surgery refers to a group of surgical procedures performed on the oral and maxillofacial structures to improve the foundation for prosthetic rehabilitation. The main objective is to create optimal anatomical conditions for the placement, retention, stability, and function of dental prostheses such as complete dentures, removable partial dentures, fixed prostheses, or implant-supported restorations. These procedures are commonly indicated in patients with unfavorable ridge anatomy, soft tissue abnormalities, or bony irregularities that compromise prosthetic success.
With the increasing life expectancy and demand for oral rehabilitation, preprosthetic surgery plays a crucial role in restoring oral function, esthetics, and patient comfort.
Objectives of Preprosthetic Surgery
The primary goals of preprosthetic surgery include:
• Improving the shape, height, and contour of the alveolar ridges
• Eliminating anatomical obstacles to prosthesis placement
• Enhancing denture stability and retention
• Creating adequate space for prosthetic components
• Preserving vital anatomical structures
• Improving patient comfort and oral hygiene
Indications for Preprosthetic Surgery
Preprosthetic surgery is indicated in patients presenting with:
• Irregular or sharp alveolar ridges
• Bony undercuts interfering with denture insertion
• Excessive alveolar ridge resorption
• Enlarged tuberosities or tori
• Hyperplastic or mobile soft tissues
• High frenum attachments
• Inadequate vestibular depth
Classification of Preprosthetic Surgical Procedures
1. Soft Tissue Procedures
Soft tissue surgeries aim to improve the mucosal environment for denture support and stability.
a. Frenectomy and Frenotomy
Abnormally positioned or thick labial, buccal, or lingual frena may compromise denture stability. Frenectomy involves complete removal of the frenum, while frenotomy is its repositioning.
b. Vestibuloplasty
Vestibuloplasty is performed to deepen the oral vestibule, thereby increasing the denture-bearing area. Techniques include mucosal advancement procedures, secondary epithelialization methods, and graft-assisted vestibuloplasty.
c. Excision of Hyperplastic Tissue
Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia (epulis fissuratum) caused by ill-fitting dentures must be surgically excised to allow proper denture adaptation.
2. Hard Tissue Procedures
Hard tissue procedures focus on modifying the alveolar bone to achieve a smooth and favorable ridge contour.
a. Alveoloplasty
Alveoloplasty involves reshaping the alveolar ridge by removing sharp bony projections or irregularities. It may be performed at the time of tooth extraction (primary alveoloplasty) or after healing (secondary alveoloplasty).
b. Removal of Tori and Exostoses
Torus palatinus and torus mandibularis may interfere with denture construction and require surgical removal when symptomatic or obstructive.
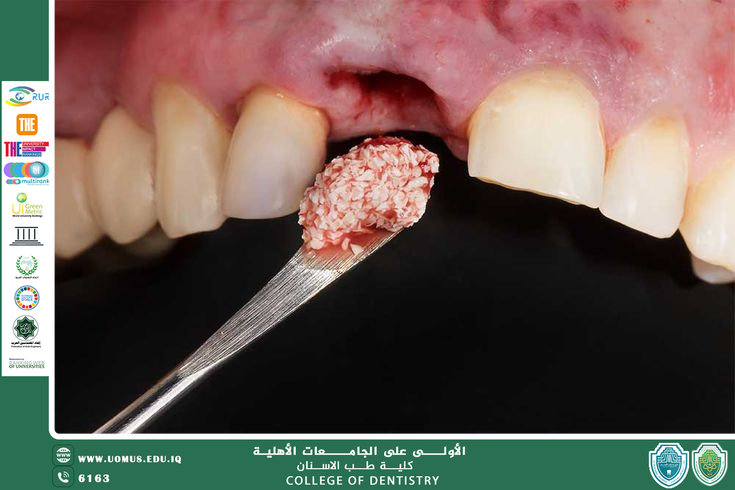
c. Ridge Augmentation
In cases of severe ridge resorption, augmentation procedures using bone grafts or biomaterials may be required to improve ridge height and width, especially for implant-supported prostheses.
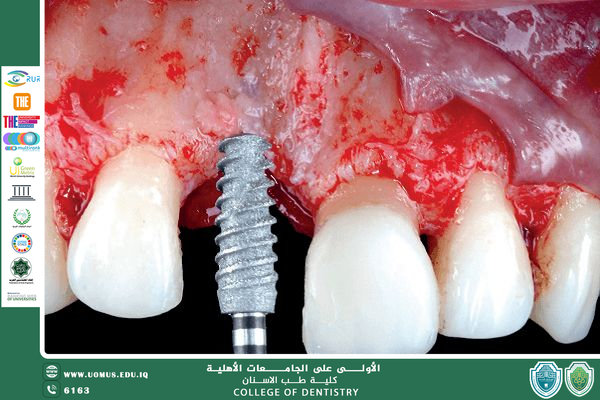
3. Preprosthetic Implant Surgery
Dental implants have significantly reduced the need for extensive preprosthetic surgery; however, preparatory procedures such as ridge augmentation, sinus lift, or soft tissue management may be necessary prior to implant placement.
Contraindications
Preprosthetic surgery may be contraindicated in:
• Medically compromised patients with poor healing potential
• Patients with unrealistic expectations
• Poor oral hygiene and non-compliant patients
• Severe systemic diseases without medical clearance
Complications
Possible complications include:
• Postoperative pain and swelling
• Infection
• Hemorrhage
• Delayed wound healing
• Excessive bone removal leading to ridge weakening
Careful case selection, proper surgical planning, and close collaboration between the surgeon and prosthodontist are essential to minimize complications.
Conclusion
Preprosthetic surgery is an integral part of comprehensive oral rehabilitation. When properly indicated and executed, it significantly enhances the success of prosthetic treatment by improving the anatomical foundation. Advances in surgical techniques and the integration of implant dentistry have expanded treatment options, allowing for more predictable functional and esthetic outcomes. A multidisciplinary approach ensures optimal patient satisfaction and long-term prosthetic success.