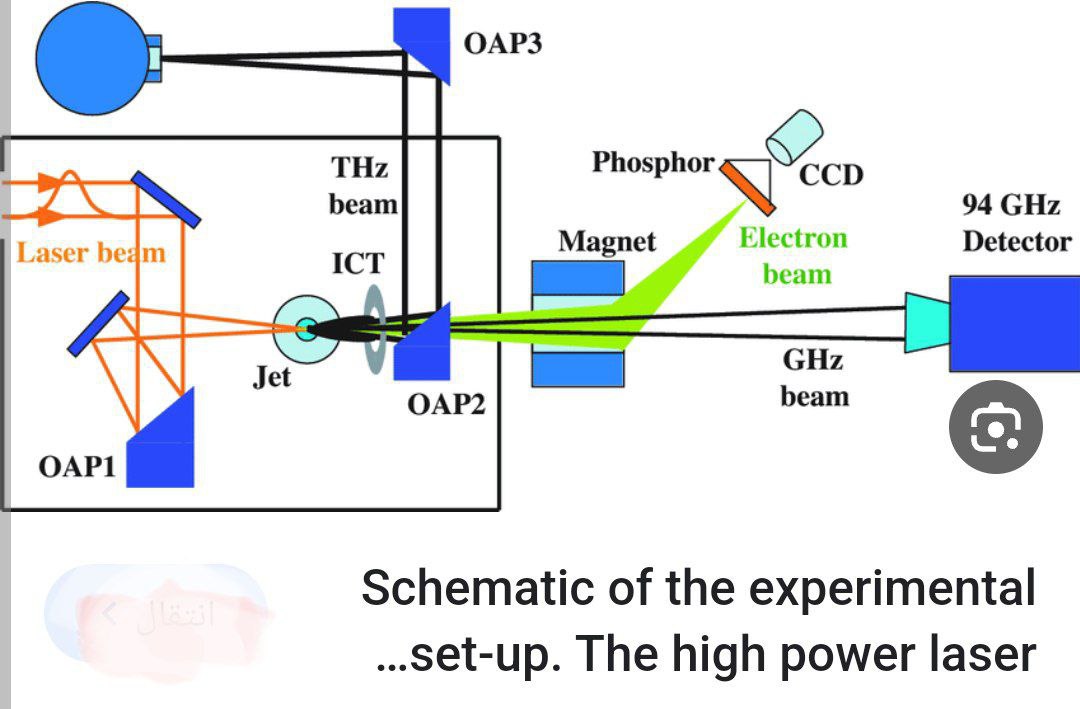
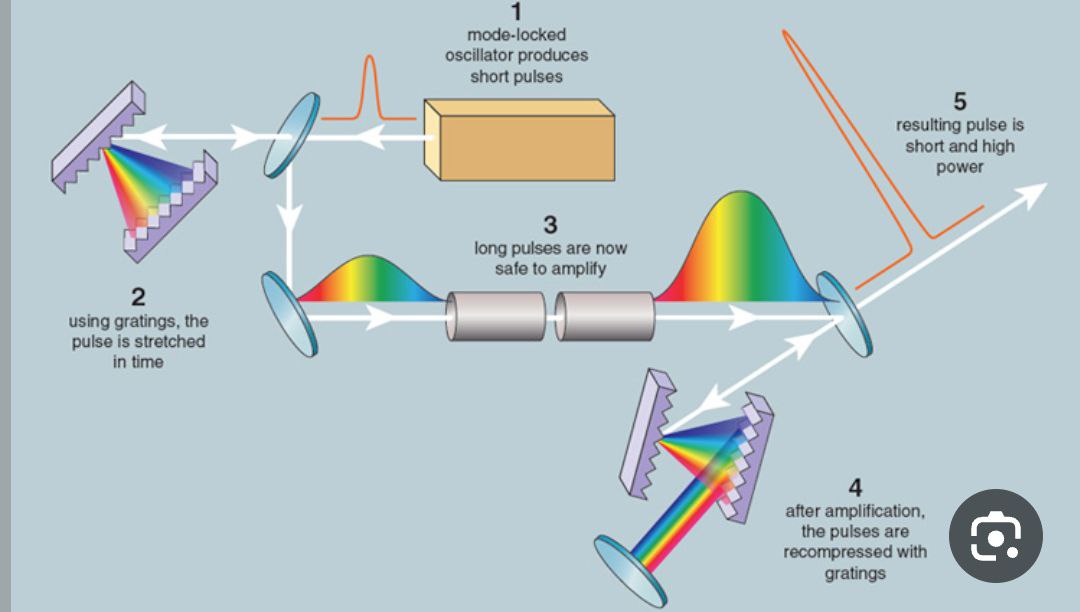
Giant Pulses laser and its application in differences Field by Prof . Dr. Raad Shaker Alnayli
Giant laser pulses, also known as high-intensity laser pulses or ultrafast laser pulses, refer to extremely powerful laser beams with high energy and short duration. These pulses have unique characteristics that make them suitable for various applications in science, technology, and industry. Here are some examples of the applications of giant laser pulses:<br /><br />1. Laser-induced fusion: Giant laser pulses can be used in fusion research to create conditions similar to those found in the core of the Sun. By focusing intense laser beams on a small target containing fusion fuel, such as hydrogen isotopes, scientists aim to trigger a controlled fusion reaction. This research has the potential to provide a clean and virtually limitless source of energy.<br /><br />2. Particle acceleration: Giant laser pulses can generate extremely high electric fields, capable of accelerating charged particles to high energies over short distances. This technique, known as laser wakefield acceleration, has the potential to revolutionize particle accelerators and enable compact, tabletop devices for medical and scientific applications.<br /><br />3. High-energy physics: In addition to particle acceleration, giant laser pulses can be used to study fundamental particles and their interactions. By focusing intense laser beams onto solid or gaseous targets, researchers can generate high-energy gamma rays, positrons, or other particles, which can be used to investigate the properties of matter and the fundamental forces of nature.<br /><br />4. Material science: The intense and short-duration nature of giant laser pulses allows for the study of materials under extreme conditions. By subjecting materials to ultrafast laser pulses, researchers can induce high pressures, temperatures, and strain rates, enabling the investigation of material properties at the atomic and molecular scale. This research is crucial for developing new materials with unique properties and understanding the behavior of matter under extreme environments.<br /><br />5. Laser micromachining: Giant laser pulses can be used for precision micromachining and material processing applications. The high peak power and short pulse duration enable the precise ablation, cutting, and drilling of various materials, including metals, ceramics, and semiconductors. This technique finds applications in industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace for manufacturing microstructures, circuit boards, and medical devices.<br /><br />6. Laser spectroscopy: Giant laser pulses can be used in ultrafast spectroscopy techniques to investigate the dynamics of chemical reactions and molecular processes. By using ultrafast laser pulses to probe the interaction between light and matter on femtosecond timescales, researchers can obtain detailed information about molecular structure, energy transfer, and reaction kinetics. This knowledge is essential for understanding chemical reactions and designing new materials and drugs.<br /><br />These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of giant laser pulses. The field of laser science and technology continues to advance rapidly, opening up new possibilities for research and practical applications in various disciplines.