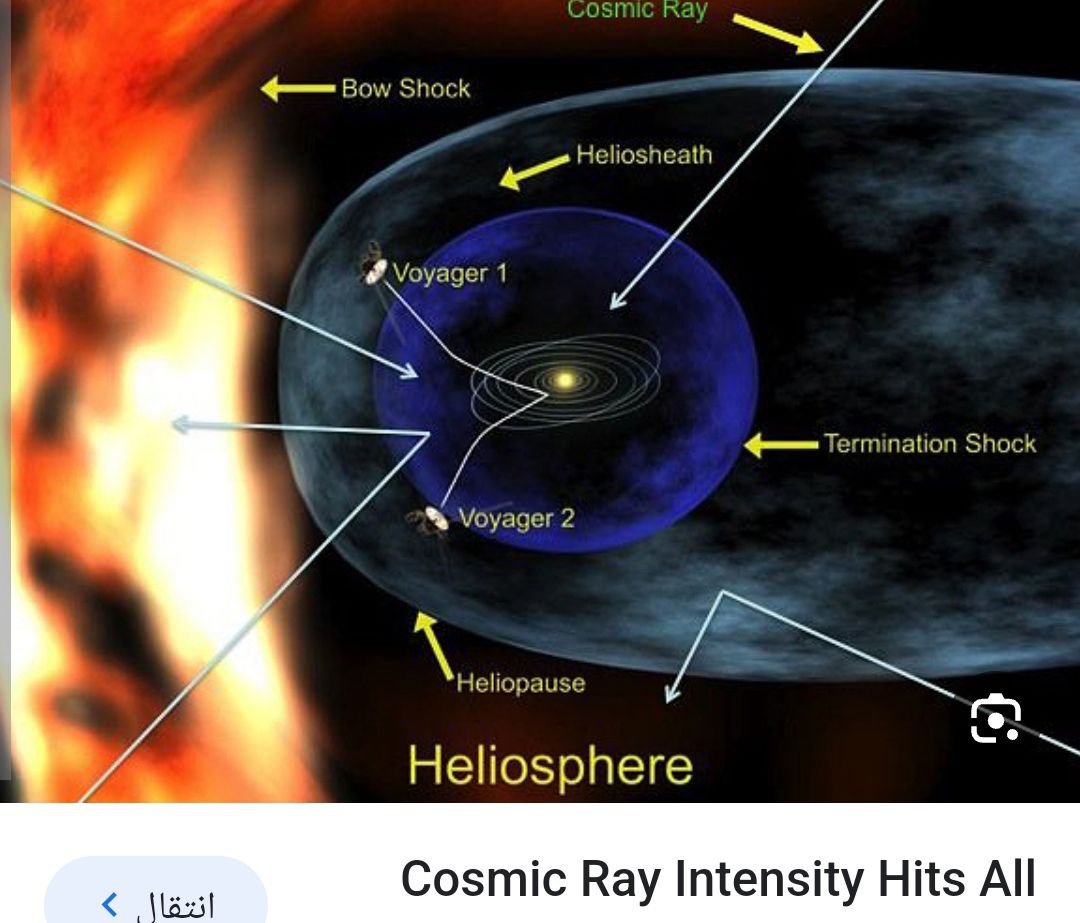
Effects of the Cosmic X ray on Humans and their environment
by Prof. Dr. Raad Shaker Alnayli <br /><br />Introduction<br />Cosmic X-rays have limited direct impact on human health due to their relatively low intensity and the Earth's protective atmosphere. The Earth's atmosphere shields us from most cosmic X-rays, preventing them from reaching the surface. However, astronauts and space travelers outside the Earth's protective atmosphere may be exposed to higher levels of cosmic X-rays, which can pose health risks such as increased cancer risk or radiation sickness over prolonged exposure.<br />1-Effects on the Environment:<br />Cosmic X-rays do not have any significant direct effects on the environment. As mentioned earlier, the Earth's atmosphere acts as a shield, absorbing the majority of cosmic X-rays and preventing them from reaching the surface. Therefore, the impact of cosmic X-rays on the environment is negligible compared to other sources of radiation, such as natural radioactivity or human activities like nuclear power generation.<br />It's worth noting that while cosmic X-rays have minimal direct effects on humans and the environment, studying them helps scientists gain insights into fundamental astrophysical processes, the formation of celestial objects, and the evolution of the universe as a whole.<br /><br />3-How do scientists study cosmic X-ray<br />and what have they discovered so far?<br />Scientists study cosmic X-rays using specialized telescopes and detectors designed to detect and measure the high-energy X-ray photons coming from celestial sources. The most common instrument for studying cosmic X-rays is the X-ray telescope, which operates outside the Earth's atmosphere, either on satellites or high-altitude balloons. By observing X-rays from various cosmic sources, scientists have made several significant discoveries. Here are a few examples:<br />3.1. Black Holes: X-ray observations have provided compelling evidence for the existence of black holes. By studying X-rays emitted from accretion disks around black holes or from matter falling into them, scientists have been able to characterize their properties, such as their mass, spin, and accretion processes.<br />3.2. Neutron Stars and Pulsars: X-ray observations have revealed the presence of highly magnetized and rapidly rotating neutron stars known as pulsars. These observations have helped scientists understand the emission mechanisms and energy release processes occurring in these extreme objects.<br />3.3. Supernova Remnants: X-ray studies of supernova remnants have provided insights into the mechanisms behind the explosion of massive stars. These observations have helped scientists understand the dynamics of shockwaves, the acceleration of high-energy particles, and the subsequent emission of X-rays.<br />3.4. Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): X-ray observations have been instrumental in studying the central regions of active galaxies, where supermassive black holes reside. By analyzing X-ray emissions from AGN, scient