Enhancing heat transfer using porous media (gravel)
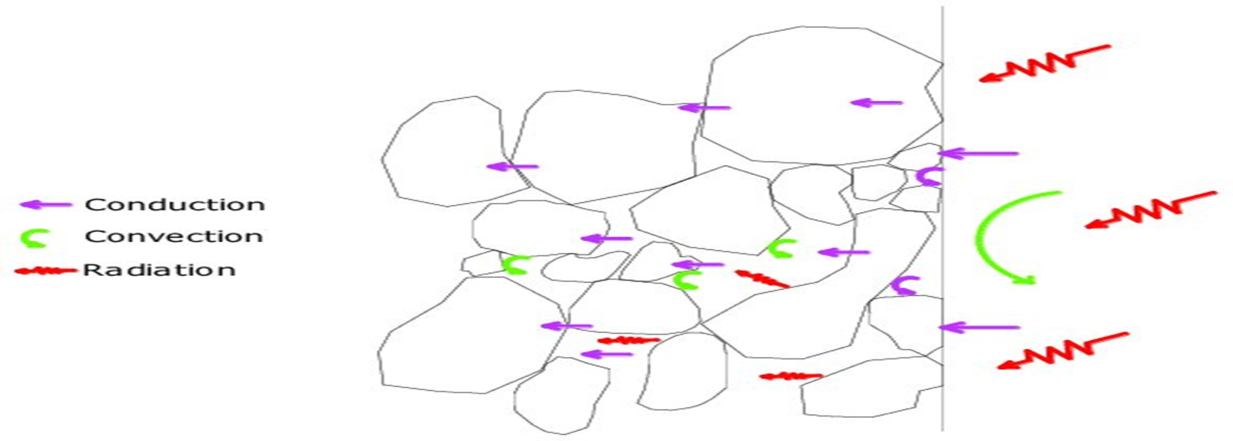
Enhancing heat transfer using porous media (gravel)<br />Improving heat transfer is a vital topic in thermal engineering, as it plays a major role in the design of thermal systems, such as heat exchangers, solar systems, and refrigeration systems. One of the modern techniques used to enhance heat transfer is the use of porous media, such as gravel, which can enhance the efficiency of heat exchange between different fluids.<br /><br /> <br />The concept of porous media<br />A porous medium is a material that contains small pores or spaces that allow liquids or gases to pass through it. Porous materials include many types, such as rocks, gravel, sponges, and minerals with a cellular structure. Porous materials are used in thermal applications to increase the heat exchange surface and improve heat transfer between fluids.<br />When gravel is used as a porous medium, it provides a relatively large surface area exposed to the flowing fluid, which increases the interaction between the fluid and the surrounding medium, thus enhancing the heat transfer process. Gravel is used in various systems, such as heat exchangers, solar reactors, and in ground cooling systems (such as underground systems).<br />. Heat transfer improvement mechanism<br />The process of improving heat transfer using porous media (gravel) can be explained by several mechanisms:<br />• Increased surface area: The rough and irregular nature of gravel contributes to increasing the surface area available for heat exchange. This means that there is more surface area exposed to the fluid (liquid or gas) flowing through the medium, enhancing heat transfer.<br />• Improved mixing and turbulence: Flow through an irregular porous medium leads to fluid turbulence, which increases the mixing process and enhances heat exchange between the fluid and the medium. This helps improve heat transfer efficiency compared to traditional systems.<br /> <br />• Reduced thermal resistance: In porous media, heat is transferred directly between the fluid and solid materials (gravel). Thus, the thermal resistance found in systems that rely solely on heat transfer in fluids is reduced.<br />) Applications of using porous media gravel(<br />The use of porous media to improve heat transfer extends to many industrial and engineering applications, such as:<br />• Heat exchangers: Gravel is placed inside the heat exchangers to provide more space for heat transfer and increase thermal efficiency. For example, in air heating or cooling systems, gravel can be used to improve heat exchange between the two fluids.<br />• Solar energy systems: Gravel is used in some solar reactors to store heat. Gravel acts as a medium to store thermal energy that is generated from sunlight, and then transfers it to another fluid in the process of thermal storage.<br />• Geothermal cooling: Gravel is buried underground as part of geothermal cooling systems. Where air or water flows through gravel buried in the ground, which improves heat transfer between the fluid and the soil and thus achieves higher cooling efficiency.<br />)Advantages and disadvantages of using porous media gravel)<br />Advantages:<br />• Improving thermal efficiency: The porous medium contributes to significantly improving the heat transfer rate.<br />• Low cost: Gravel is a natural material and relatively inexpensive, making it an economical option.<br />• Ease of application: This technology can be easily applied in many systems without requiring major design changes.<br />Disadvantages:<br /> <br />• Pressure problem: Fluid flow through a porous medium may cause an increase in pressure, requiring stronger pumps to push the fluid.<br />• Erosion and sedimentation: Over time, dirt or sediment may accumulate between the pores of the gravel, reducing its effectiveness and requiring regular maintenance.<br />Challenges and considerations<br />Despite the great benefits of using gravel as a porous medium to improve heat transfer, there are some challenges that must be considered. Among these challenges:<br /> <br />• Proper design: Engineers need to carefully design the system to ensure optimal fluid flow and minimize pressure losses.<br />• Choosing the appropriate materials: The type of gravel that can withstand different environmental conditions (such as high temperatures or chemical corrosion) must be chosen.<br />• Maintenance: Systems that use gravel require regular maintenance to remove deposits that may affect the effectiveness of the system.<br /> <br /> <br />Conclusion<br />The use of porous media, such as gravel, is an effective solution for improving heat transfer in many industrial and engineering applications. Gravel contributes to increasing the efficiency of thermal systems by increasing the surface area, improving the mixing process, and reducing thermal resistance. Although there are some challenges, the benefits of improved thermal efficiency and reduced cost make it an <br />attractive option in the design of modern thermal systems.<br /> <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br />Article by M.SC. Ali Baqer Hussein