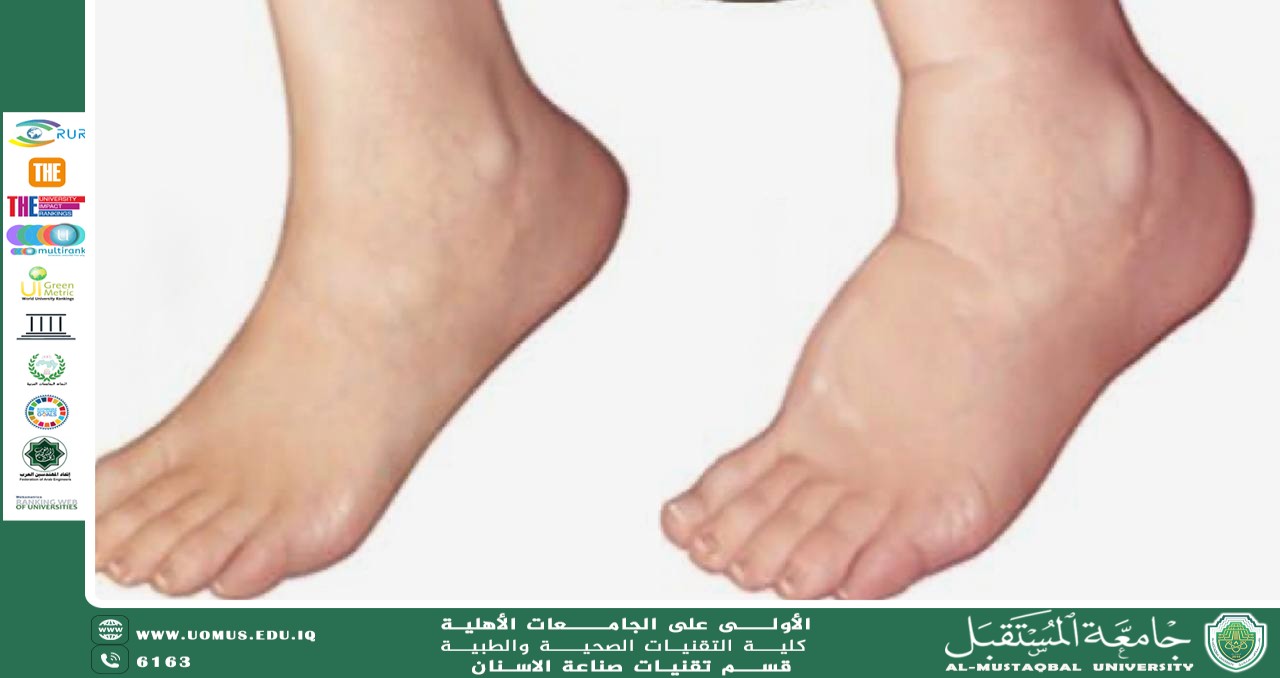
مقاله علمية للدكتوره نور مهند عباس بعنوان oedema
تحقيقا للهدف الثالث وهو الصحة الجيدة والرفاه قام قسم تقنيات صناعة الاسنان بنشر مقاله علمية للدكتوره نور مهند عباس بعنوان oedema وذلك يوم الاثنين الموافق 7/4/2025 وتضمنت المقالة:<br /><br />Oedema is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling. It can affect any part of the body but is most commonly observed in the feet, ankles, and legs. In some cases, it can also affect the hands, arms, face, or lungs.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Types of Oedema<br /> 1. Peripheral oedema: Swelling in the limbs, usually the legs and ankles.<br /> 2. Pulmonary oedema: Fluid accumulation in the lungs, which can be life-threatening.<br /> 3. Cerebral oedema: Swelling in the brain, often due to injury, infection, or stroke.<br /> 4. Macular oedema: Swelling in the retina of the eye, commonly linked to diabetic retinopathy.<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Causes of Oedema<br /><br />Oedema can result from various underlying health conditions or external factors, including:<br /> • Heart failure<br /> • Kidney disease<br /> • Liver cirrhosis<br /> • Chronic venous insufficiency<br /> • Infections and inflammation<br /> • Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs, corticosteroids, calcium channel blockers)<br /> • Pregnancy<br /> • Allergic reactions<br /> • Prolonged standing or sitting<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Common Symptoms<br /> • Swelling or puffiness of the skin<br /> • Skin that retains a dimple after being pressed (pitting)<br /> • Tight or shiny skin<br /> • Increased abdominal size (in cases of ascites)<br /> • Shortness of breath (in pulmonary oedema)<br /> • Reduced mobility and discomfort<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Diagnosis<br /><br />Doctors may use the following to diagnose oedema and its underlying cause:<br /> • Physical examination<br /> • Blood tests<br /> • Urinalysis<br /> • Chest X-ray or ultrasound<br /> • ECG or echocardiogram (for heart-related causes)<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Treatment Options<br /><br />Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the oedema:<br /> • Diuretics (“water pills”) to help the body remove excess fluid<br /> • Lifestyle changes, including reduced salt intake and elevating swollen limbs<br /> • Compression garments for limb oedema<br /> • Managing underlying conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease<br /> • Physical activity to improve circulation<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />When to See a Doctor<br /><br />Seek immediate medical attention if oedema is accompanied by:<br /> • Shortness of breath<br /> • Chest pain<br /> • Sudden or severe swelling<br /> • Signs of infection (e.g., redness, warmth, fever)<br /><br />⸻<br /><br />Conclusion<br /><br />Oedema is a common condition that can indicate an underlying health problem. While often manageable<br /><br />جامعة المستقبل الجامعة الاولى في العراق