تم نشر مقاله علمية للتدريسي في قسم تقنيات التخدير (م.م احمد بسيم مهدي ) بعنوان Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater Using Low-cost Adsorbents
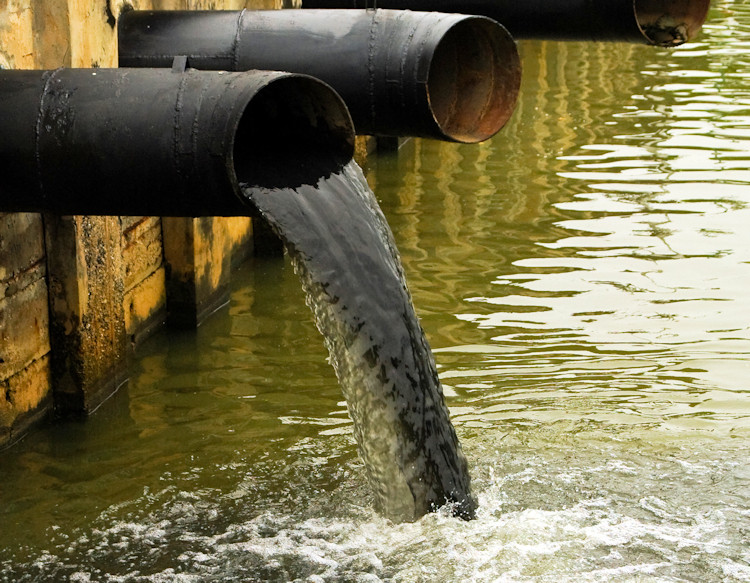
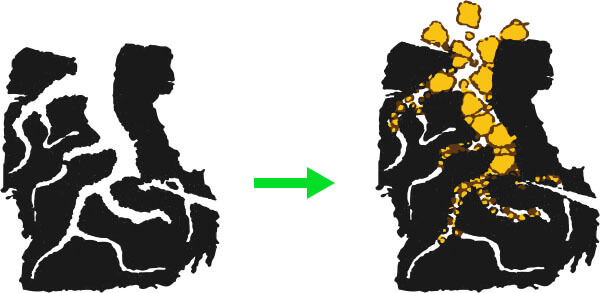
Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater Using Low-cost Adsorbents<br />Discharge of lab or dyes wastewater from various industries like textile, leather, paint, cosmetics etc. industries contributes to large amounts of pollution, leading to serious environmental problems such as quality deterioration of fresh water and endangering ecosystems health. One of the conventional anti-fungal agent in aquaculture which should be eliminated from wastewaters prior to releasing it into natural water resources. Tremendous volumes of colored wastewater are generated in textile, leather, paint, cosmetics etc. industries, causing eternal damage to the water resources. Wastewaters released from dye production and application industries are responsible for water pollution. Untreated disposal of the colored water into receiving water body causes damage to aquatic life and human bodies. they must be treated before being discharged into the receiving body of water.<br /><br />Figure 1 : A real picture of the pollution of natural waters with pollutants.<br /><br /><br /><br />The adsorption process: Are one of the potential and efficient methods among all the possible techniques for colored effluent treatment due to its low initial investment, design simplicity, and availability of low-cost adsorbents.<br /><br /> <br />Figure 2 : Adsorption process.<br /><br /><br />Active carbon (AC) is a special type of porous carbon material that is processed to obtain small, low-volume pores that expand the surface area. Activated carbon is suitable for small particles used in the purification of gases and liquids. It alone gives good results in the treatment of water pollution, but when an adsorbent compound consisting of activated carbon and any second material such as ZnO or TiO2 is prepared, an adsorbent material is formed that is very effective, low in cost, and capable of being reactivated in the continuous removal of polluting compounds from water.<br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> <br />Figure 3 : Demonstrates the porosity of activated carbon to adsorb pollutants.<br /><br />By: Asst. Lec. Ahmed B. Mahdi<br />Email: [email protected] <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br />