مقالة علمية للتدريسي ذوالفقار عباس اسود بعنوان الفرق بين البروبيوتيك والبريبايوتكس من حيث فوائدهما الصحية ومصادرهما الشائعة
This article explains in detail the difference between probiotics and prebiotics, how they work, their sources, benefits, side effects, and how to include them in your diet effectively.
Gut health is one of the foundations of overall well-being, influencing digestion, immunity, mood, and even metabolism. Two terms that often appear together in discussions about gut health are probiotics and prebiotics. Although they sound similar, they play distinct yet complementary roles in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
Probiotics are live beneficial microorganisms that help maintain or restore healthy gut flora, while prebiotics are non-digestible food components that serve as nourishment for these beneficial microbes. Together, they form a powerful duo that supports optimal digestive and immune function.
What Are Probiotics?
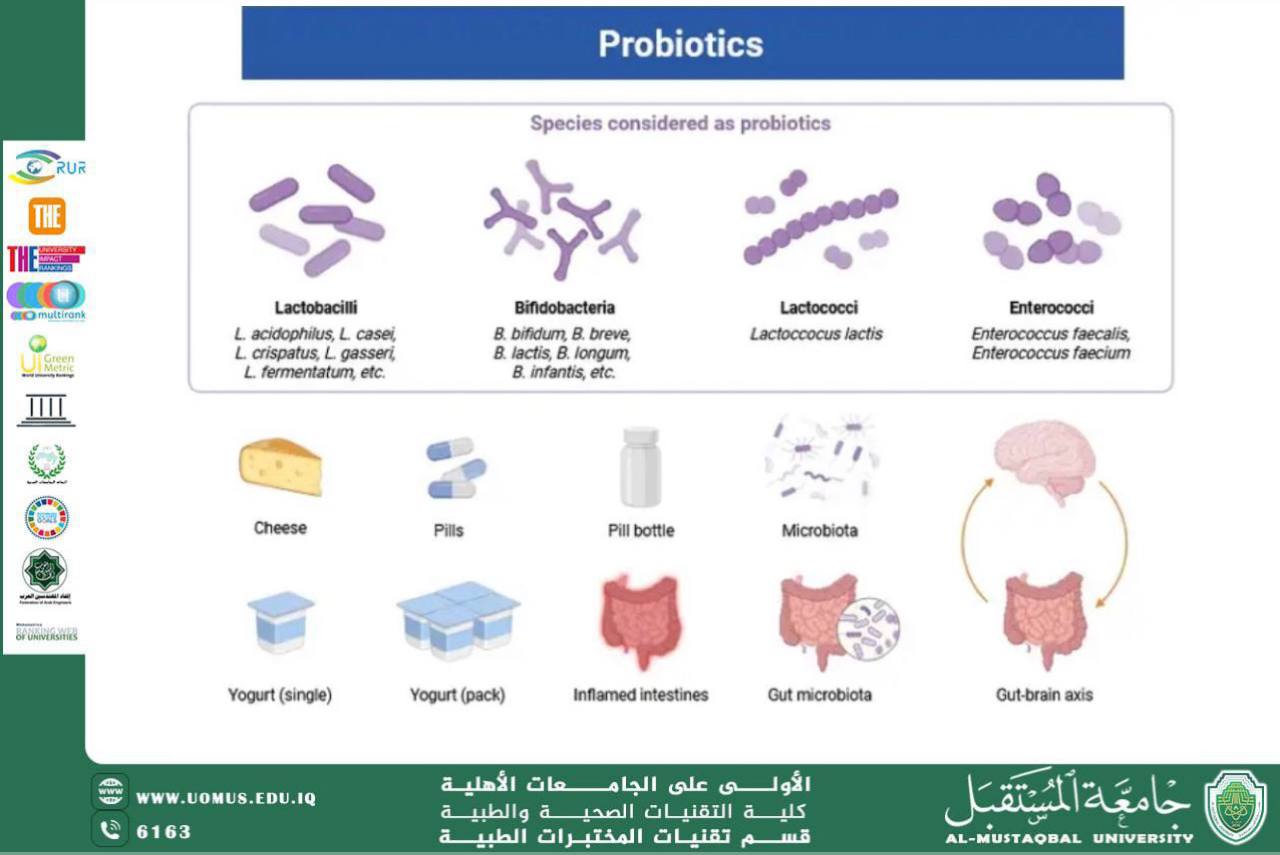
Probiotics are live microorganisms, mainly beneficial bacteria and yeasts, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They are similar to the “good bacteria” naturally found in the human gut.
Common Probiotic Microorganisms:
• Lactobacillus species – found in yogurt and fermented milk.
• Bifidobacterium species – present in some dairy products.
• Saccharomyces boulardii – a probiotic yeast used in supplements.
• Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactococcus lactis – used in dairy fermentation.
How Probiotics Work?
Probiotics colonize the gut and:
• Restore microbial balance after antibiotic use.
• Compete with harmful microbes for nutrients and adhesion sites.
• Strengthen the gut barrier function.
• Regulate immune responses.
• Produce substances (like lactic acid) that inhibit pathogen growth.
Sources of Probiotics
• Yogurt and fermented milk
• Kefir (fermented milk drink)
• Sauerkraut and kimchi
• Miso and tempeh
• Kombucha (fermented tea)
• Probiotic supplements (capsules, powders, or tablets)
What Are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers or carbohydrates that promote the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria. Unlike probiotics, prebiotics are not alive—they act as “food” for probiotics.
Common Prebiotic Substances:
• Inulin
• Fructooligosaccharides (FOS)
• Galactooligosaccharides (GOS)
• Resistant starch
How Prebiotics Work?
When consumed, prebiotics pass undigested through the upper gastrointestinal tract and reach the colon, where beneficial bacteria ferment them. This fermentation produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate, which:
• Nourish colon cells
• Reduce inflammation
• Improve mineral absorption (especially calcium and magnesium)
• Support immune and metabolic health
Sources of Prebiotics
• Fruits: Bananas, apples
• Vegetables: Onions, garlic, asparagus, leeks
• Whole grains: Oats, barley, wheat bran
• Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas
• Root vegetables: Chicory root, Jerusalem artichoke