مقاله بعنوان (Bioelectronics: The Intersection of Biology and Electronics)للأستاذ ماهر رحمن عبد الأمير
Bioelectronics, the integration of electronic devices with biological systems, is a rapidly growing field that offers new therapeutic and diagnostic options. Bioelectronic devices can interact directly with the nervous system, influencing biological functions with precision and minimal invasiveness.
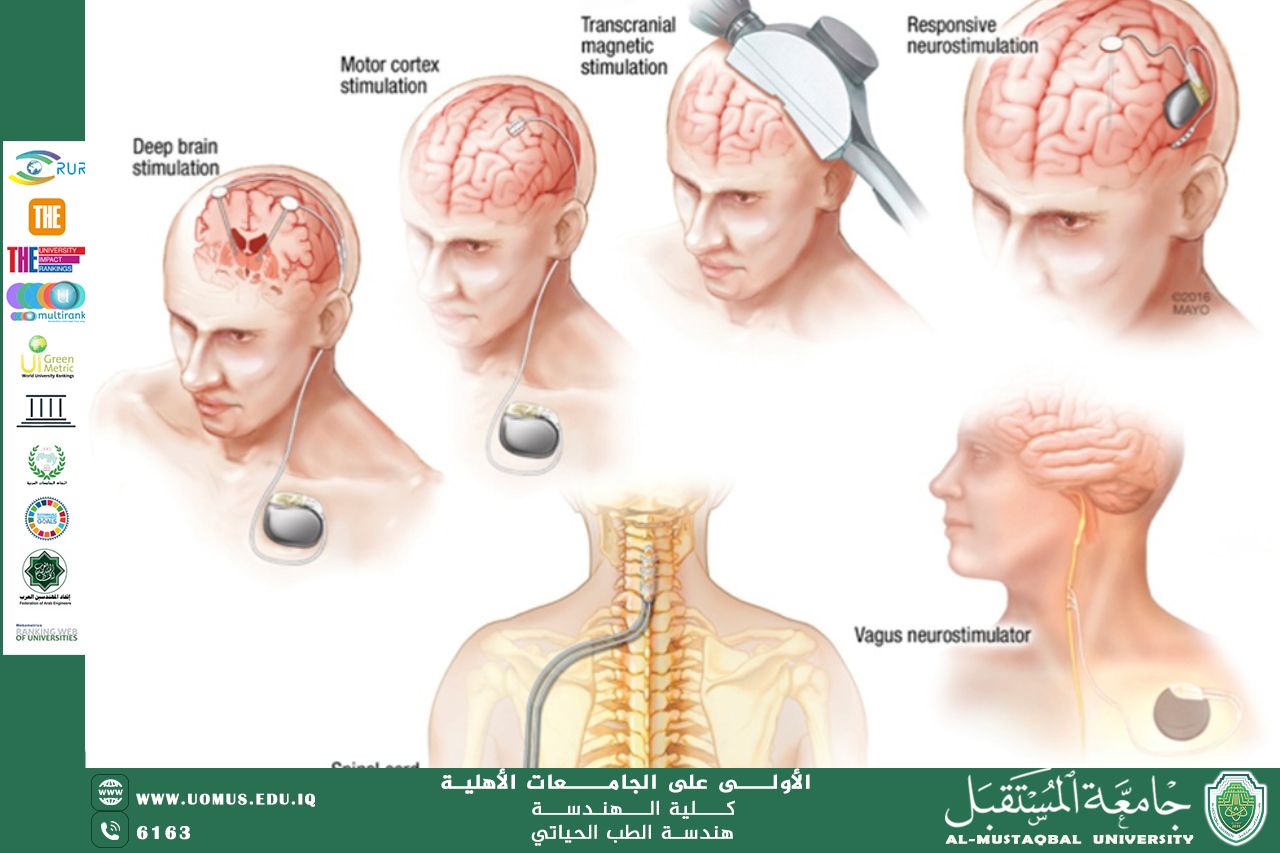
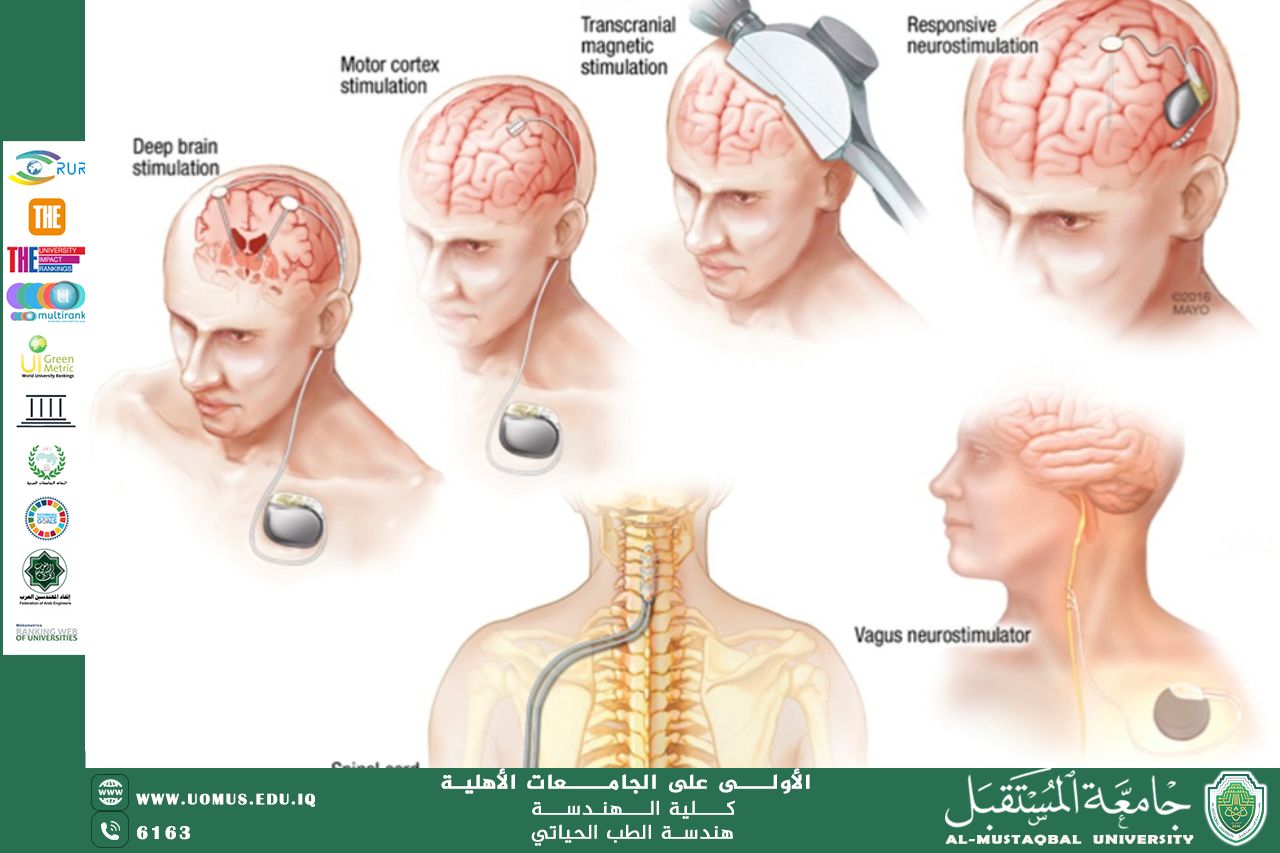
One of the most notable applications of bioelectronics is in neurostimulation. Devices such as deep brain stimulators and spinal cord stimulators are used to treat chronic pain, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy by sending electrical impulses to targeted areas of the nervous system. These technologies have reduced the need for traditional pharmaceuticals, providing patients with more localized and effective treatments.
Another significant area of bioelectronics is in biosensing, where electronic sensors detect and monitor physiological changes. For example, wearable biosensors are used to continuously monitor glucose levels in patients with diabetes or track heart function in individuals with cardiovascular disease. In diagnostics, bioelectronic devices can provide real-time feedback, enabling the early detection of disease and the development of personalized treatment plans. As research advances, bioelectronics is expected to lead to even more sophisticated devices that can not only treat diseases but also enhance human performance. The convergence of electronics with biology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare, offering patients more effective, customized, and less invasive treatment options.