he Role of Medical Biochemistry in the Analysis of Cellular Signaling Pathways Associated with Disease Progression Prof. Dr. Nasser Abdul-Hassan Nasser Head of the Department of Biochemistry Al-Mustaqbal Universit
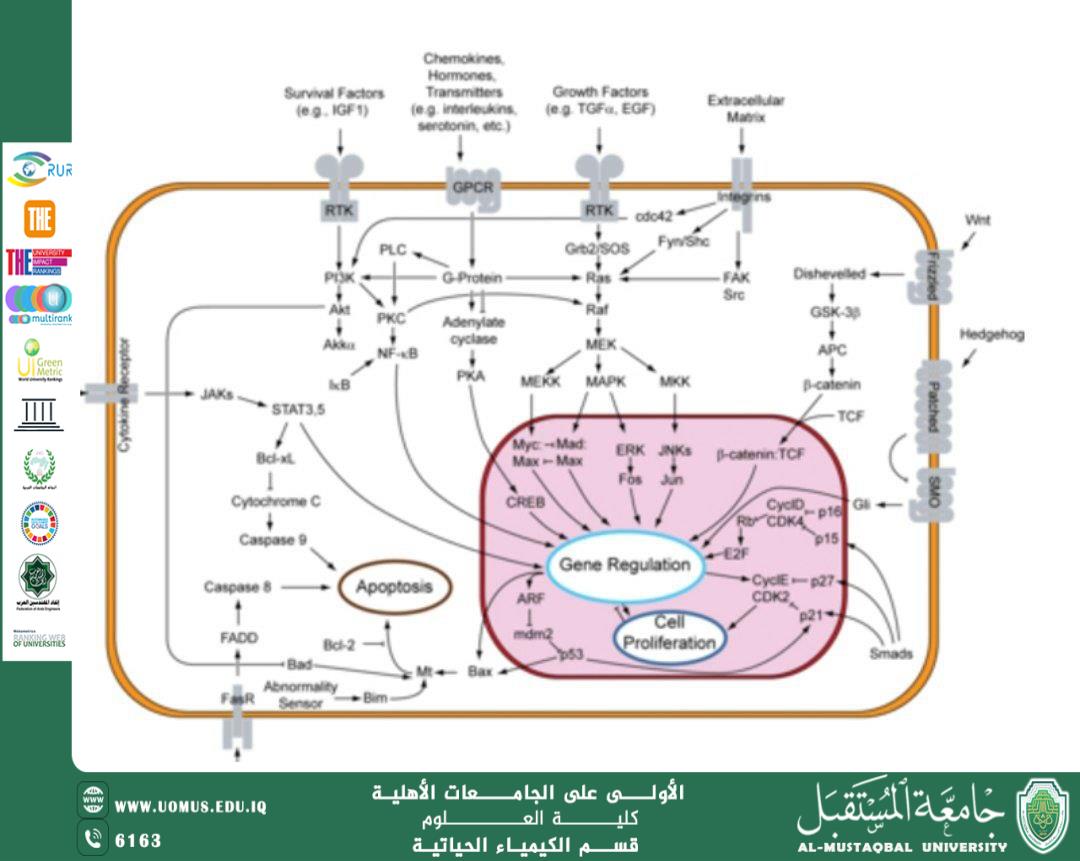
Cellular signaling pathways play a fundamental role in regulating cellular functions and maintaining homeostasis. Disruptions in these signaling mechanisms are closely associated with the development and progression of various chronic and cancerous diseases. Medical biochemistry provides essential tools and analytical approaches to understand, analyze, and interpret these complex molecular signaling events, thereby supporting both diagnostic and therapeutic advancements in modern medicine.
Concept of Cellular Signaling and Its Biochemical Importance
Cellular signaling refers to a series of biochemical reactions within the cell that begin with the reception of an external signal through specific receptors located on the cell membrane or within the cytoplasm. These signals are subsequently transmitted to the nucleus, where they regulate gene expression and other cellular behaviors. Such mechanisms are essential for maintaining cellular balance and enabling appropriate responses to environmental stimuli.
Analysis of Cellular Signaling from a Medical Biochemistry Perspective
Medical biochemistry plays a pivotal role in the study of cellular signaling pathways through:
Identification of proteins and enzymes involved in signal transduction pathways.
Application of advanced analytical techniques such as spectroscopic analysis, protein phosphorylation studies, and monitoring kinase activity.
Analysis of disease-related alterations in signaling pathways using omics-based approaches and proteomic profiling.
These analyses help clarify how cellular signaling differs between normal and diseased tissues, providing a scientific basis for identifying diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Cellular Signaling and Chronic Diseases
In chronic diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disorders, dysregulated cellular signaling is a major contributor to disease progression. Abnormal regulation of phosphorylation processes or inappropriate activation of signaling proteins can lead to:
Metabolic disturbances
Impaired hormonal responses
Persistent inflammatory processes
Medical biochemistry contributes to identifying these molecular alterations and classifying them as measurable laboratory indicators that can be used for diagnosis and disease monitoring.
Cellular Signaling and Cancer
In cancer, cellular signaling pathways represent a central mechanism driving tumor development. Alterations in signaling cascades can:
Promote uncontrolled cell proliferation
Inhibit programmed cell death (apoptosis)
Enhance invasion and metastasis
For example, dysregulation of specific pathways such as the Notch signaling pathway has been documented in various types of cancer. Analysis of these signaling abnormalities aids in understanding tumor progression and evaluating targeted therapeutic strategies.
Biochemical Techniques for the Analysis of Cellular Signaling
The study of cellular signaling relies on advanced biochemical techniques, including:
Chromatographic separation and spectroscopic analysis for identifying proteins and their modified forms
Immunological assays such as Western blotting and ELISA to quantify phosphorylated signaling proteins
Omics technologies, particularly proteomics, to detect large-scale changes in protein expression and modification
These tools enable the construction of detailed signaling maps and the identification of critical points of dysfunction in disease states.
Clinical Applications
Understanding cellular signaling pathways contributes significantly to:
The development of targeted therapeutic agents that inhibit cancer-related signaling pathways or modulate immune responses
The design of novel biomarkers for early detection of disease progression
Improved prediction of therapeutic response through monitoring changes in signaling pathways during treatment
Conclusion
The analysis of cellular signaling pathways from the perspective of medical biochemistry represents a vital link between molecular cell biology and clinical medicine. By elucidating signaling alterations associated with chronic and cancerous diseases, medical biochemistry enhances early diagnosis, supports the development of more precise therapies, and improves overall treatment outcomes for patients.
Al-Mustaqbal University
Ranked First among Iraqi Private Universities