The Role of Molecular Docking Techniques in the Development of Medical Biochemistry–Based Therapies Prof. Dr. Nasser Abdul-Hassan Nasser Head of the Department of Biochemistry Al-Mustaqbal University
Medical biochemistry has witnessed remarkable progress in recent decades due to its integration with modern computational technologies. Among the most prominent of these technologies is molecular docking, which has become a fundamental tool in drug discovery and design. Molecular docking contributes significantly to understanding molecular interactions between drug compounds and biological targets such as proteins and enzymes, enabling the development of more precise, effective therapies with fewer side effects.
Concept of Molecular Docking
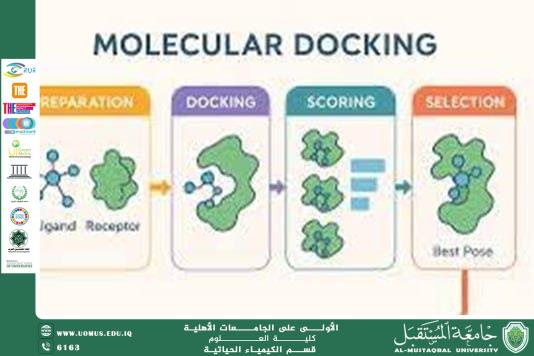
Molecular docking refers to a computational technique used to predict how a small molecule (ligand) binds to the active site of a larger biological molecule such as a protein or enzyme. This technique relies on the principles of medical biochemistry to understand:
Hydrogen bonding
Electrostatic interactions
Van der Waals forces
Hydrophobic interactions
All of these factors play a critical role in determining the stability and feasibility of molecular binding.
Importance of Molecular Docking in Medical Biochemistry
Molecular docking techniques play a pivotal role in medical biochemistry by:
Analyzing the three-dimensional structure of disease-related proteins
Identifying active binding sites
Evaluating the binding affinity of drug candidates to biological targets
Reducing the need for costly and time-consuming laboratory experiments in early drug development stages
Role of Molecular Docking in Therapy Development
1. Targeted Drug Design
Docking techniques assist in designing drugs that specifically target proteins responsible for disease progression, such as:
Cancer-related enzymes
Cellular signaling receptors
Viral proteins
This targeted approach enhances therapeutic precision while minimizing effects on healthy cells.
2. Accelerating Drug Discovery
Instead of experimentally testing thousands of compounds, molecular docking enables the virtual screening of large compound libraries within a short time frame, allowing researchers to select the most promising candidates for experimental validation.
3. Predicting Drug Efficacy
Docking results provide estimates of binding free energy, which are used as indicators of the strength and potential effectiveness of drug candidates.
Integration of Molecular Docking and Medical Biochemistry
The success of molecular docking depends on a deep understanding of medical biochemistry, particularly:
Enzyme mechanisms of action
Metabolic pathways
Molecular regulation of cellular signaling
This integration allows for accurate interpretation of docking results and their correlation with biological function at the cellular level.
Recent Applications
Molecular docking techniques are currently applied in:
Cancer drug development
Discovery of enzyme inhibitors for neurological diseases
Design of antiviral agents
Investigation of drug resistance at the molecular level
Their effectiveness has been further enhanced when combined with artificial intelligence and molecular dynamics simulations.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Despite their importance, molecular docking techniques face several challenges, including:
Limited accuracy of structural models
Difficulty in simulating the true cellular environment
The need for better integration with experimental data
Nevertheless, continuous advancements in computational algorithms and artificial intelligence promise an expanded role for molecular docking in the future of medical biochemistry.
Conclusion
Molecular docking techniques represent one of the most powerful modern tools in medical biochemistry, contributing effectively to the development of targeted therapies and accelerating drug discovery. Their impact is expected to grow further with advancements in computational technologies and integration with nanotechnology and artificial intelligence, thereby enhancing the precision and efficiency of modern medicine.
Al-Mustaqbal University
Ranked First among Iraqi Private Universities