Scientific article by Assist lecturer Reyam.abdulkhuder Mohammed Titled AS:-Tuberculosis
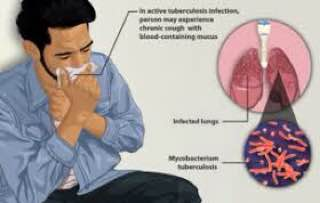
Tuberculosis (TB) is a common and often deadly infectious disease caused by mycobacterium; in humans it is mainly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but they can also damage other parts of the body. It is a great problem for most developing countries because of the weak diagnostic and treatment opportunities. Tuberculosis has the highest mortality rate among the diseases caused by a single type of microorganism. Thus, tuberculosis has a great health concern all over the world<br />.<br />TB spreads through the air when a person affected with the lung or throat coughs, sneezes, or talks. If you have been exposed, you should go to your doctor for testing. You are more likely to get TB if you have a weak immune system.<br />Symptoms of TB in the lungs may include<br /> • A bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer<br /> • Weight loss<br /> • Loss of appetite<br /> • Coughing of bloody mucus<br /> • Weakness or fatigue<br /> • Fever<br /> • Night sweats<br />Skin test, blood test, x-ray, and other tests can prove if you have TB. If dose not treated properly, TB can be deadly. You can usually cure active TB by taking several medicines for a long period of time..<br /><br /><br /><br />TB disease can be treated<br />There are some drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB, that form the core of treatment regimens are:<br />• isoniazid (INH)<br />• rifampin (RIF)<br />• ethambutol (EMB)<br />• pyrazinamide (PZA)<br /><br />TB Prevention and precautions:<br /> •Treatment of Latent TB<br /> • Infection prevention and control<br /> • WHO 3 pillars of TB IPC <br />Administrative , Environmental , Respiratory (PPE)<br /> • Core components<br /> •.TB Vaccines<br />