Genetic Analysis and Its Role in Disease Prevention Prepared by: Lecturer M.Sc. Abbas Hamza Khudair Department of Biochemistry – College of Science – Al-Mustaqbal University
Introduction
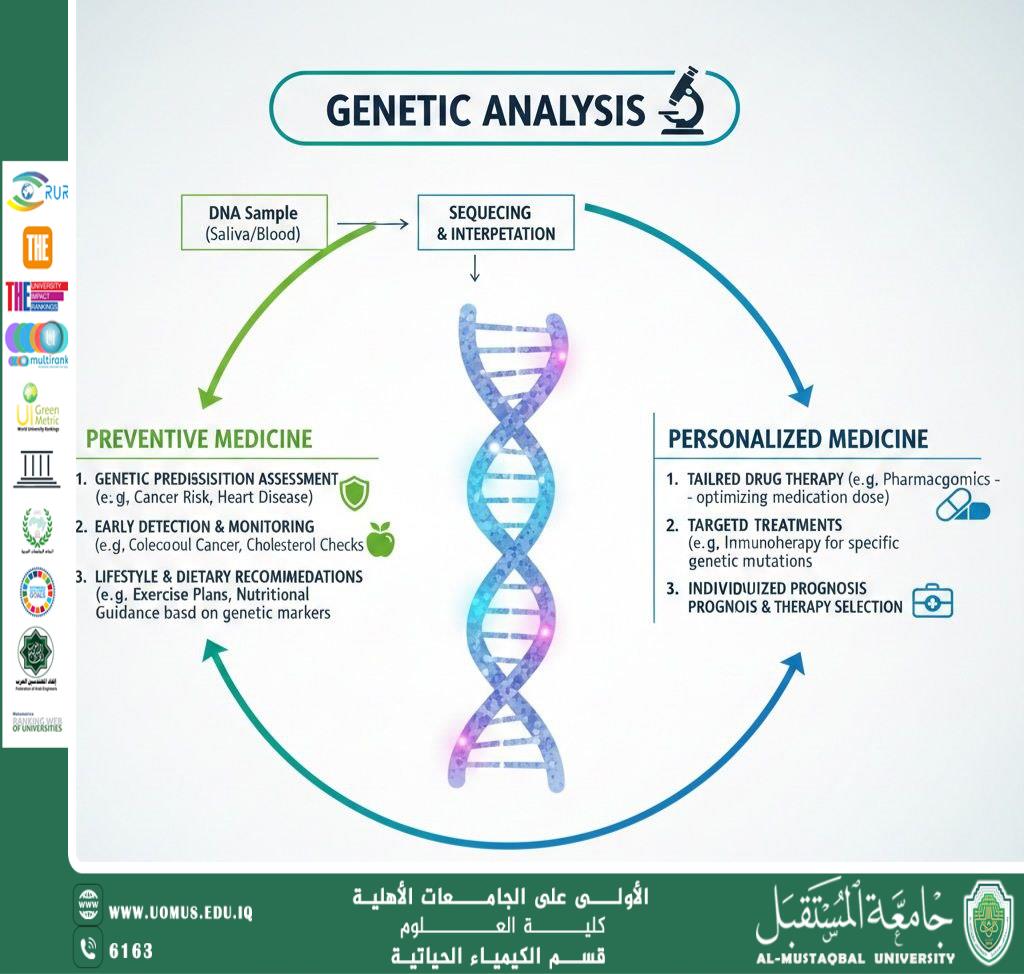
Genetic analysis represents one of the most significant modern advancements in medical and life sciences, as it provides a precise understanding of the human genetic structure and enables early detection of susceptibility to various diseases. This field is based on studying DNA sequences and analyzing genetic mutations and variations that influence health, as well as individual responses to environmental and therapeutic factors.
Concept of Genetic Analysis
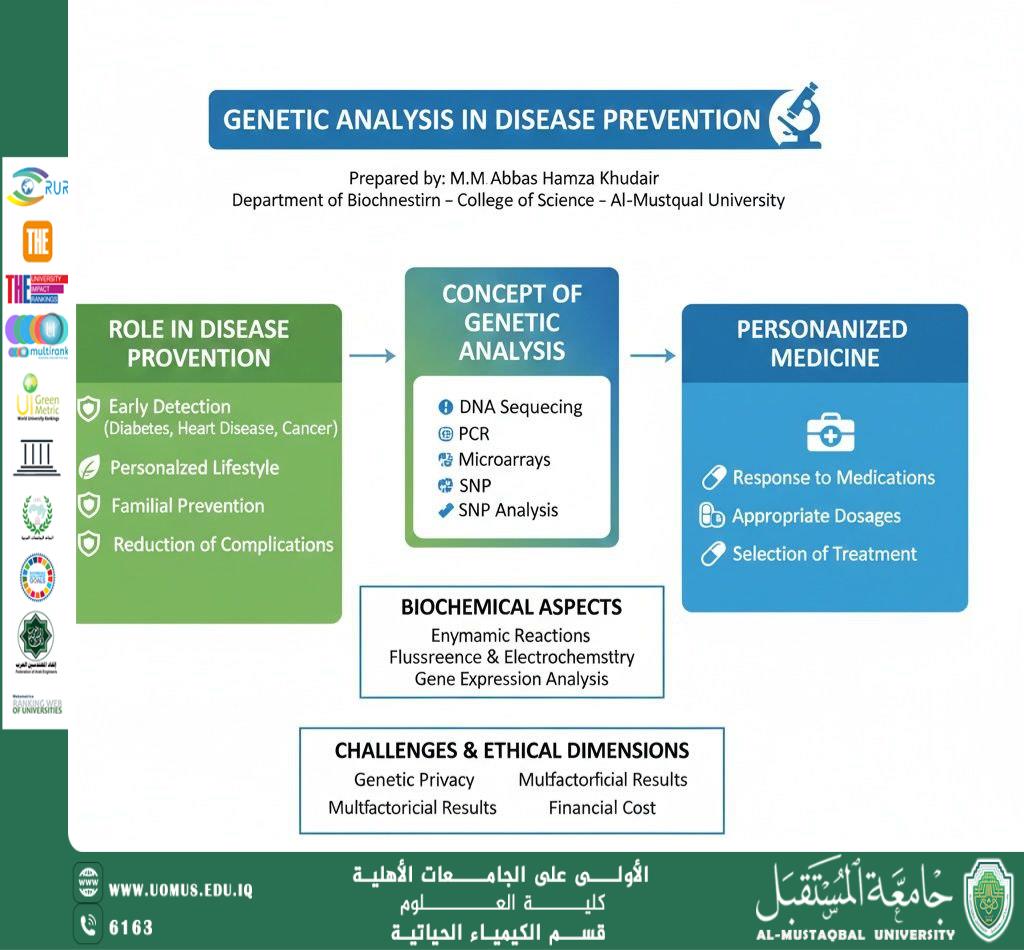
Genetic analysis refers to the study of genes or specific regions of DNA using advanced laboratory techniques, including:
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
DNA Sequencing
Genetic Microarray Technologies
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Analysis
These analyses aim to identify genetic mutations associated with hereditary or chronic diseases.
The Role of Genetic Analysis in Disease Prevention
Genetic analysis contributes to disease prevention through:
Early detection of genetic predisposition to diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and autoimmune disorders
Personalizing lifestyle patterns based on an individual’s genetic profile, including nutrition and physical activity
Family-based prevention through screening relatives in cases of inherited diseases
Reducing complications by enabling early monitoring and appropriate medical intervention
Personalized Medicine and Genetic Diagnosis
Advances in genetic analysis have led to the emergence of personalized medicine, which relies on genetic characteristics to determine:
Drug responsiveness
Appropriate dosages to minimize side effects
The most effective treatment options for each patient
Biochemical Aspects of Genetic Analysis
The accuracy of genetic analysis depends on several biochemical factors, including:
Enzyme-specific reactions involved in DNA replication and amplification
Fluorescent and electrochemical detection techniques
Analysis of gene expression and its relationship with cellular pathways
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its significant benefits, genetic analysis faces several challenges, such as:
Protection of genetic privacy
Interpretation of multifactorial genetic results
High costs associated with some advanced technologies
Conclusion
Genetic analysis is a pivotal tool in modern preventive medicine, contributing to the shift from reactive treatment to proactive prevention. Integrating genetic analysis into healthcare programs enhances early detection, reduces the burden of chronic diseases, and supports the improvement of overall quality of life.
Al-Mustaqbal University
Ranked First among Iraqi Private Universities