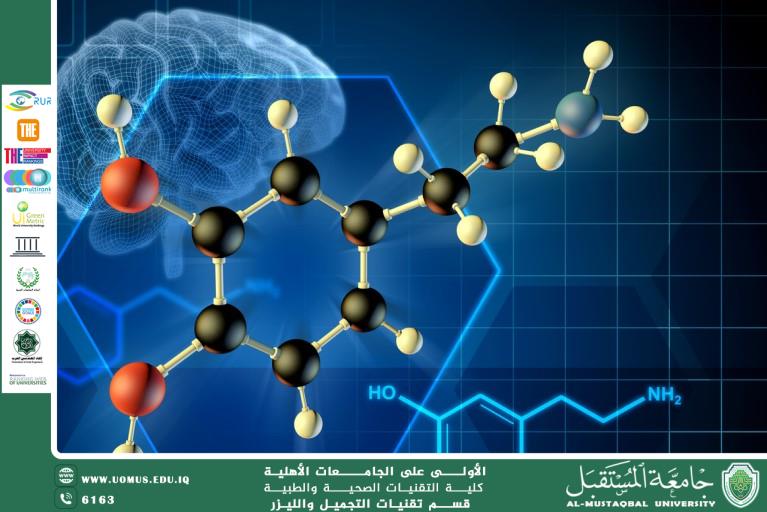
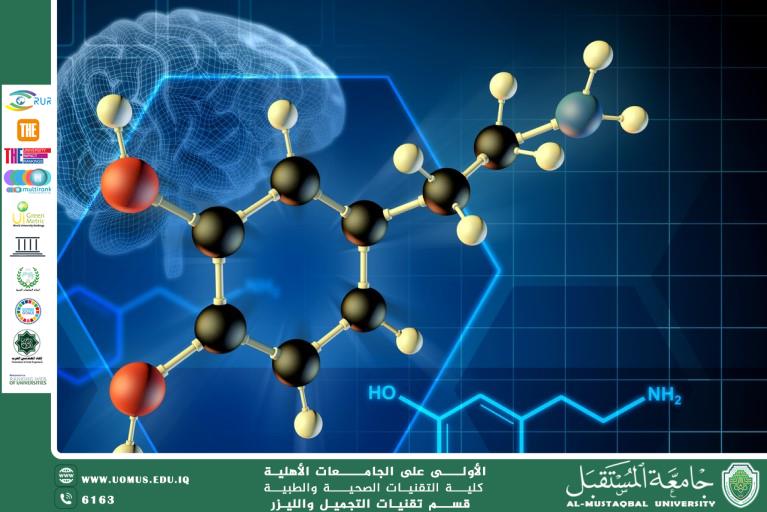
Dopamine and the Brain: Its Role in Mood, Learning, and Behavior
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a chemical substance that functions primarily as a neurotransmitter in the brain, rather than only as a hormone in the traditional sense. It is produced in brain regions such as the substantia nigra and the limbic system, and it plays a key role in:
Control of movement
Motivation and goal-directed behavior
The reward and pleasure system
Attention and learning
Regulation of mood and energy
In the body, it is also released through the endocrine system and can influence blood pressure and kidney function.
Dopamine and the Reward System
Dopamine levels increase when we:
Achieve a goal
Learn a new skill
Engage in enjoyable activities
Receive appreciation or a reward
For this reason, dopamine is often called the “motivation chemical” rather than simply a “happiness hormone.”
Happiness also involves other neurotransmitters such as serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins.
Dopamine Imbalance
Low dopamine may be associated with:
Lack of motivation and apathy
Depression or loss of pleasure
Poor concentration
Parkinson’s disease (in cases of severe deficiency in motor pathways)
Excessive dopamine activity may be associated with:
Anxiety or impulsivity
Certain psychotic disorders
Compulsive or addictive behaviors
Important: These are medical conditions that must be diagnosed by specialists — symptoms alone are not enough.
How to Support Healthy Dopamine Levels Naturally
Research suggests that the following habits may help improve dopamine function:
Adequate, regular sleep
Physical activity and exercise
Balanced nutrition (especially foods rich in tyrosine, such as eggs, fish, and legumes)
Moderate sun exposure
Stress reduction
Avoiding excessive sugar, stimulants, and digital overuse
Medications and Dopamine
Some medications act on dopamine pathways, including:
Parkinson’s disease medications
Certain ADHD medications
Some antipsychotic drugs (which reduce dopamine activity)
These should only be used under medical supervision.
Conclusion
Dopamine is not simply a “happiness hormone,” but rather a central factor in:
motivation — learning — movement — the sense of reward.
Its balance depends on a complex interaction between the brain, lifestyle, and psychological factors
AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq