An article titled "Sustainable Bioactive Coatings for Medical Implants" by Lecturer M.M. Abdullah Qais Hashim
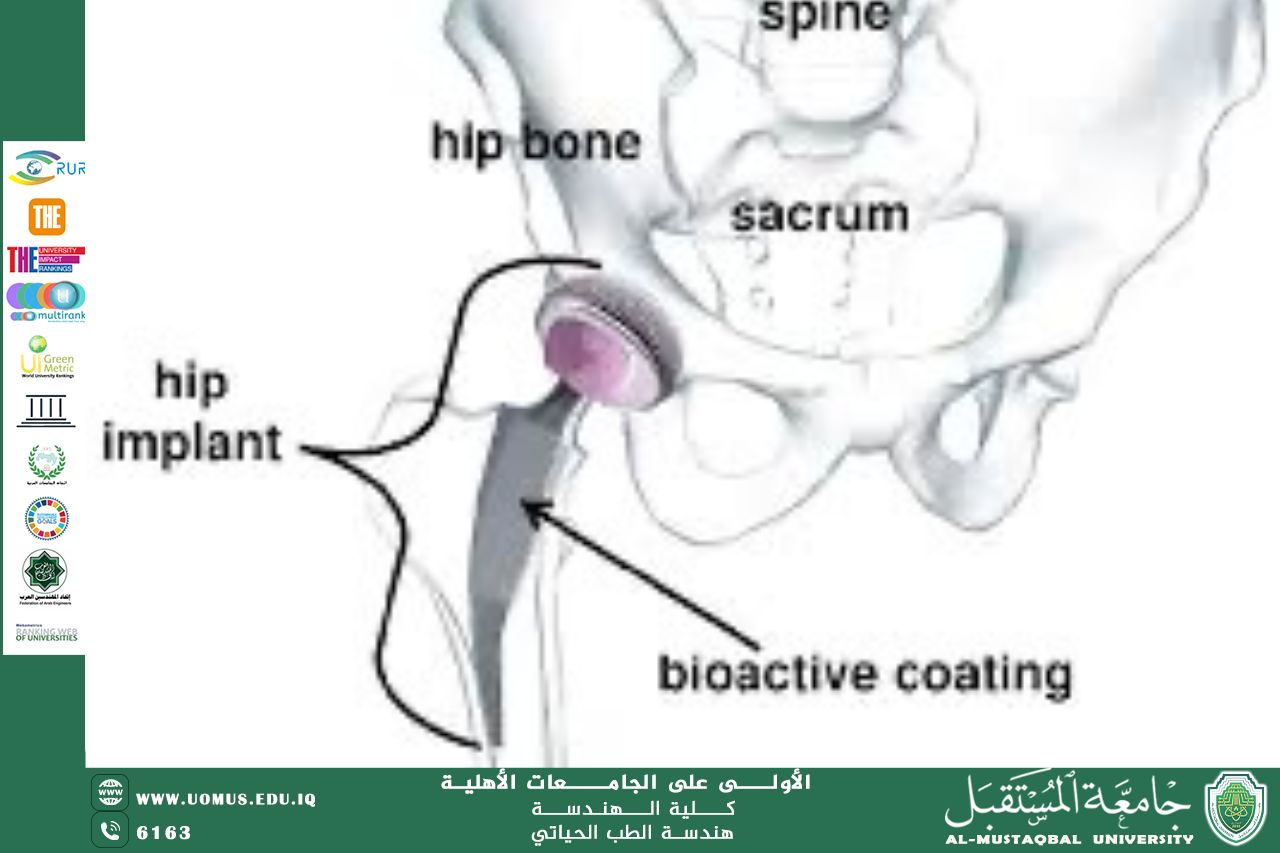
Metallic implants such as titanium-based materials are widely used in orthopedic and dental applications due to their excellent mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. However, their biological performance is largely determined by surface properties rather than bulk characteristics. For this reason, bioactive surface coatings have become an important and sustainable approach to improving implant performance.
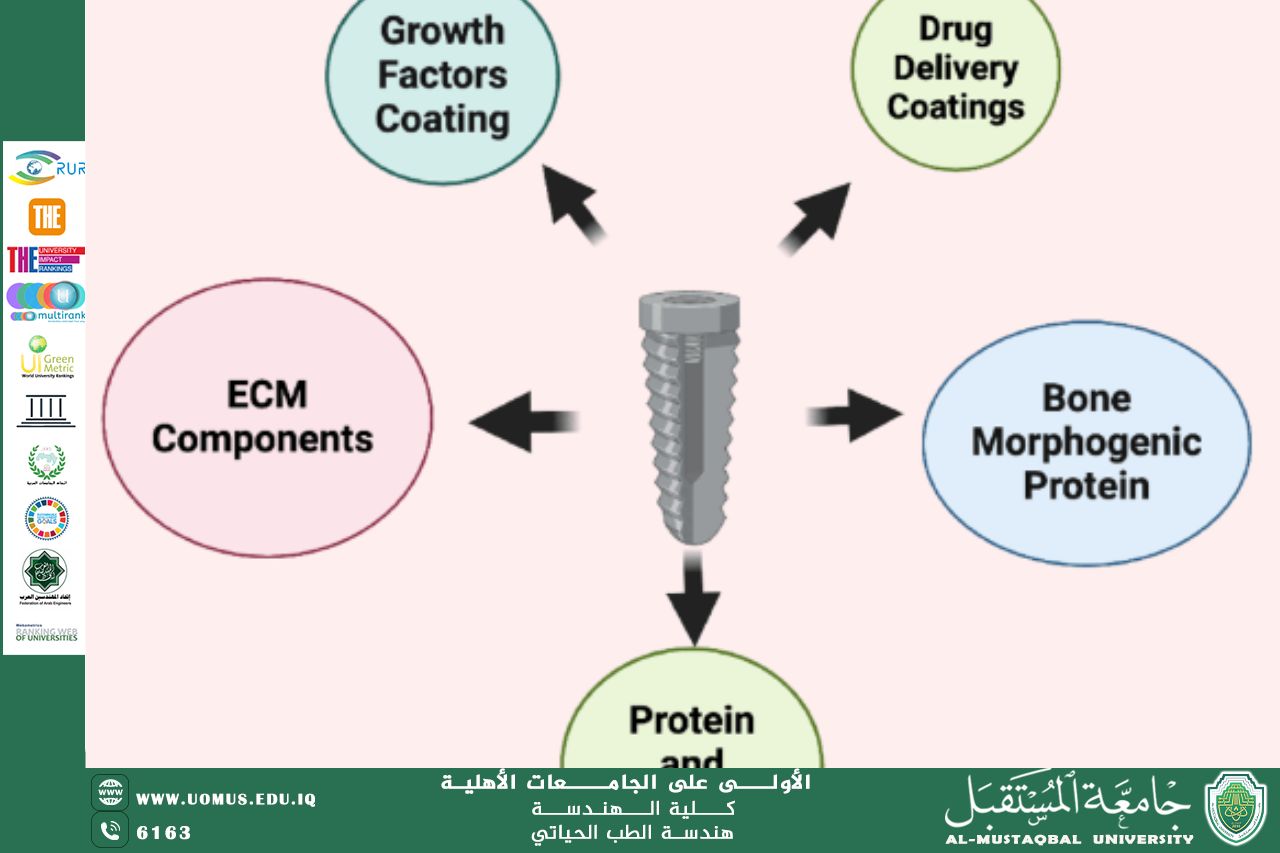
Bioactive coatings are thin layers applied to the implant surface to enhance biocompatibility, promote bone integration, and reduce the risk of bacterial infection. Common coating materials include bioceramics such as hydroxyapatite, as well as biodegradable polymer-based coatings that can release therapeutic agents locally. These coatings improve the interaction between the implant and surrounding tissue without increasing material usage or implant weight.
From a sustainability standpoint, surface coating technologies offer several advantages. By extending implant lifetime and reducing the need for revision surgeries, they help minimize medical waste and resource consumption. Additionally, many coating techniques, such as sol–gel and dip coating, are low-energy and low-waste processes, aligning well with sustainable manufacturing principles.
In conclusion, sustainable bioactive coatings play a crucial role in modern biomedical engineering by improving implant functionality while supporting environmentally responsible healthcare solutions.