An article titled "Medical Imaging in Biomedical Engineering" by Lecturer M.M. Hiba Dhiaa Abdul-Amir
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in modern healthcare by enabling non-invasive visualization of internal anatomical structures and physiological processes. Advances in biomedical engineering have significantly improved imaging modalities in terms of resolution, speed, safety, and diagnostic accuracy. This article reviews the fundamental principles of medical imaging, common imaging techniques, methodological approaches, and their clinical applications. Emphasis is placed on the integration of engineering concepts with medical diagnostics to enhance patient care.
Introduction
Medical imaging is a cornerstone of diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease monitoring. Biomedical engineers contribute to the development and optimization of imaging systems by applying principles from physics, electronics, signal processing, and computer science. Imaging modalities such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, and nuclear imaging have transformed clinical practice by enabling early detection and accurate assessment of disease.
Methods
Medical imaging methods rely on different physical principles:
• X-ray and CT Imaging: Based on differential attenuation of ionizing radiation as it passes through tissues of varying densities.
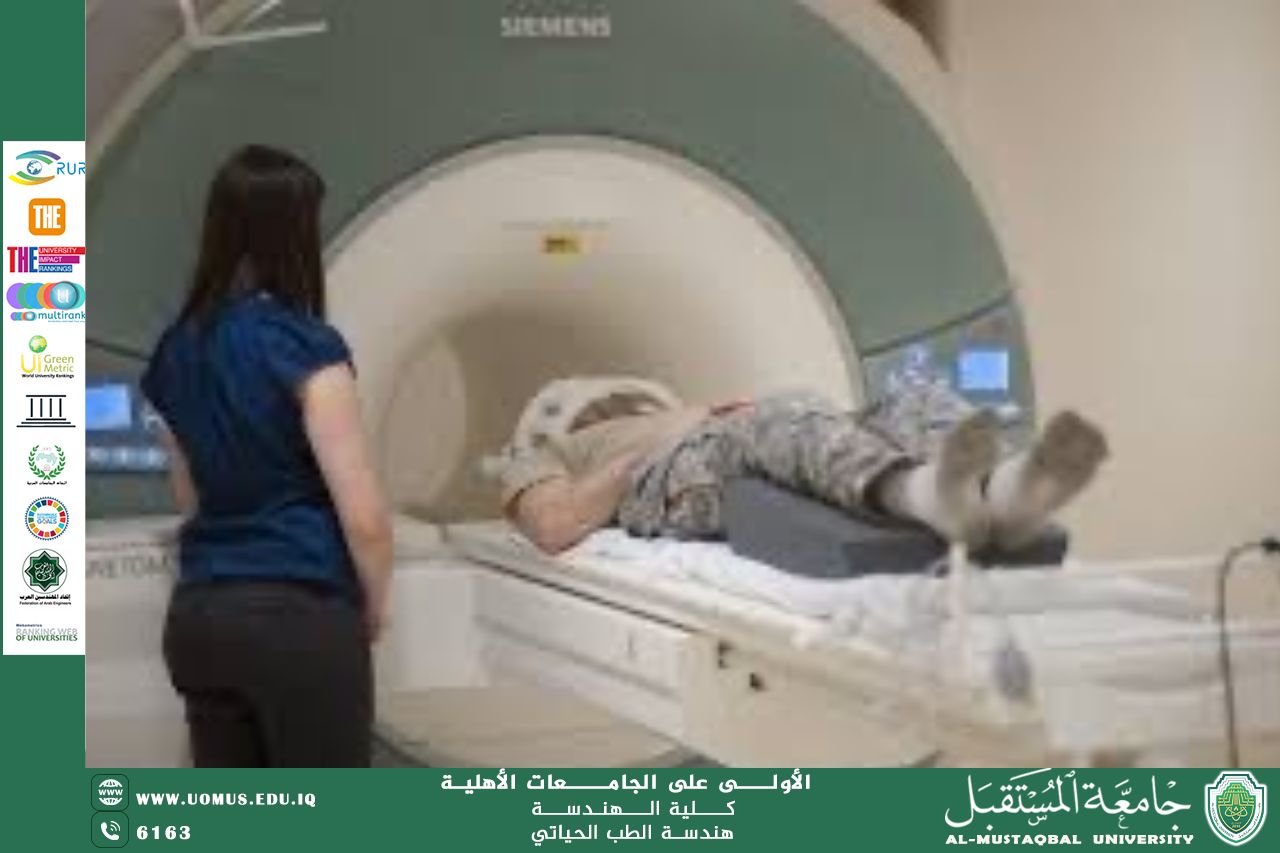
• Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Utilizes nuclear magnetic resonance of hydrogen protons in a strong magnetic field to produce high-contrast soft tissue images.
• Ultrasound Imaging: Employs high-frequency sound waves and their reflections from tissue interfaces.
• Nuclear Imaging (PET/SPECT): Uses radiotracers to visualize metabolic and functional processes.
Signal acquisition, image reconstruction algorithms, noise reduction, and contrast enhancement are key engineering aspects in these methods.
Applications
Medical imaging is widely used in:
• Disease diagnosis (e.g., cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders)
• Image-guided interventions and surgery
• Monitoring disease progression and treatment response
• Biomedical research and clinical trials
Advanced applications include 3D imaging, functional imaging, and image fusion techniques.
Conclusion
Medical imaging continues to evolve through innovations in biomedical engineering. Improvements in hardware design, computational algorithms, and artificial intelligence integration are expanding diagnostic capabilities while reducing risks to patients. Ongoing research aims to achieve higher resolution, faster imaging, and personalized diagnostic solutions.