A Scientific Article by Dr. Zaid Abd Al-Hadi Entitled: Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is an endocrine disorder characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormones (thyroxine [T4] and triiodothyronine [T3]) from the thyroid gland.
These hormones regulate metabolism, and their excess leads to an increased metabolic rate. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune condition.
Other causes include toxic multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, and thyroiditis. Excess iodine intake and certain medications can also trigger the condition. Patients often present with weight loss despite increased appetite.
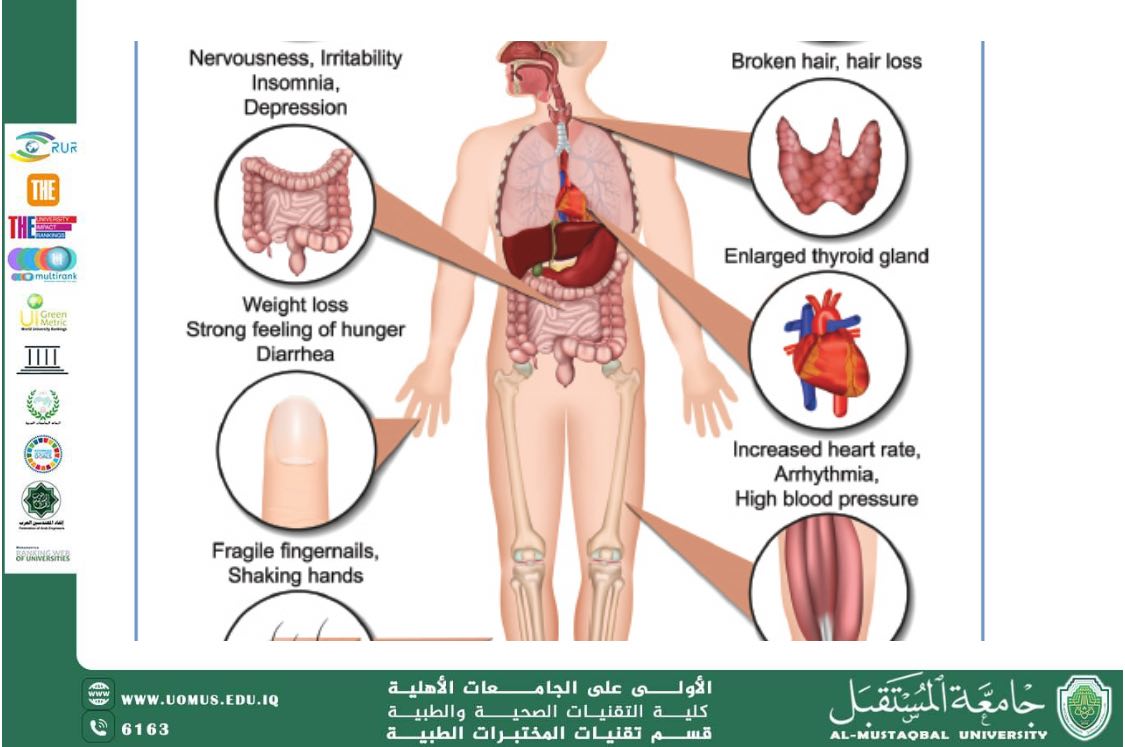
Common Symptoms include heat intolerance, excessive sweating, and palpitations. Neuropsychiatric features such as anxiety, irritability, and tremors are frequent.Cardiovascular effects include tachycardia and atrial fibrillation. Women are affected more commonly than men.
Diagnosis is based on clinical features and laboratory tests.
Typically, serum TSH levels are suppressed.
Free T4 and/or T3 levels are elevated.
Thyroid autoantibodies may help identify autoimmune causes.
Imaging studies such as radioactive iodine uptake can determine etiology.
Treatment include antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery. Beta-blockers are often used for symptomatic relief. If untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to serious complications.
These include osteoporosis, cardiac arrhythmias, and thyroid storm. Early diagnosis and appropriate management improve outcomes significantly.
Al-Mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq
Department of Medical Laboratory Techniques – First in the Iraqi National Ranking.