Scientific Article by Dr. Gaith Ali Mahmoud Eyelid Ptosis (Blepharoptosis)
Ptosis is an abnormal drooping of the upper eyelid in which part or all of the pupil may be covered. It can be unilateral or bilateral. The severity of ptosis ranges from mild to severe, and it may be functional, affecting vision, or purely cosmetic. Ptosis is a common condition in ophthalmology and requires careful evaluation to determine the underlying cause and an appropriate management plan.
Classification
First: According to Age
Congenital Ptosis
• Present at birth or in early childhood
• Most commonly due to abnormal development of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle
• May be associated with:
• Amblyopia
• Abnormal head posture
Acquired Ptosis
• Develops later in life
• More common than congenital ptosis
Second: According to Etiology (in Acquired Ptosis)
Aponeurotic Ptosis
• The most common type
• Caused by stretching or dehiscence of the levator aponeurosis
• Common in elderly patients or following ocular surgery
Neurogenic Ptosis
• Results from neurological disorders (e.g., third cranial nerve palsy or Horner syndrome)
Myogenic Ptosis
• Caused by muscular diseases (e.g., myasthenia gravis)
Mechanical Ptosis
• Due to increased eyelid weight (tumor, edema, excess skin)
Traumatic Ptosis
• Occurs after trauma or surgical procedures
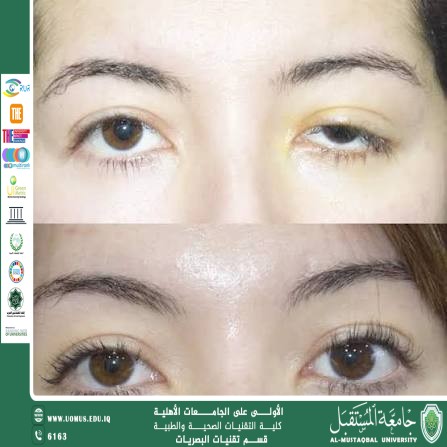
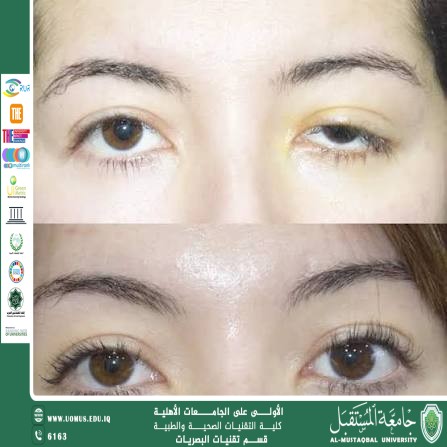
Clinical Features
• Decreased palpebral fissure height
• Partial or complete coverage of the pupil
• Frontalis muscle overaction with eyebrow elevation
• Compensatory head posture (chin elevation)
• May be associated with superior visual field defect
Clinical Evaluation
Includes:
• Measurement of the margin reflex distance 1 (MRD1)
• Assessment of levator muscle function
• Examination of the eyebrows and frontalis muscle
• Visual field testing when functional impairment is suspected
Indications for Treatment
Ptosis should be treated when it:
• Affects visual acuity or visual field
• Causes ocular fatigue or abnormal head posture
• Poses a risk of amblyopia (in children)
• Is treated for cosmetic reasons in adult patients
Conclusion
Ptosis is a condition with multiple etiologies that requires accurate diagnosis to determine its type and underlying mechanism. Management depends on the cause, severity, and functional impact of the ptosis. Proper differentiation between the various types is essential to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes.
University of Al-Mustaqbal – The First and Leading Private University