Asst. Lecturer Zainab Ali Mohsen: The Role of Gut Microbiota in Human Health
The gut microbiota refers to a complex community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that reside in the human gastrointestinal tract. Recent scientific studies have shown that the gut microbiota plays a vital role in maintaining human health by aiding digestion, producing essential vitamins such as vitamin K and B-complex vitamins, and regulating nutrient absorption.
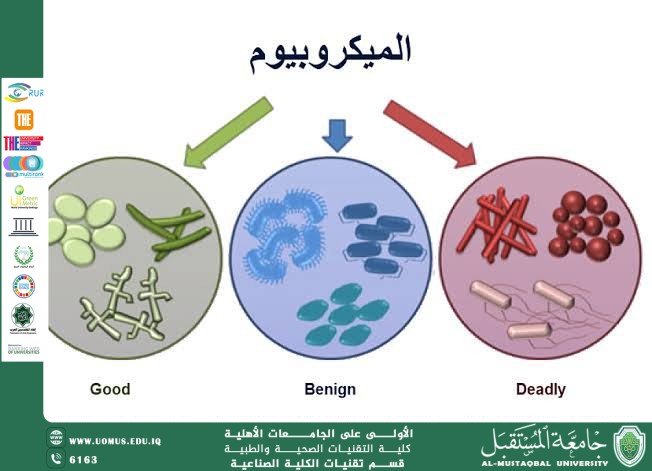
In addition, the gut microbiota has a significant influence on the immune system. It helps train immune cells to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances and prevents the colonization of pathogenic microorganisms. Imbalance in gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, has been associated with several chronic diseases, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain mental health disorders.
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in dietary fiber and probiotics supports gut microbiota balance and contributes to overall health and disease prevention.
Al-Mustaqbal University the First in Iraq