The Role of Ultrasound in Detecting Thyroid Diseases
The Role of Ultrasound in the Detection of Thyroid Gland Diseases
The thyroid gland is one of the most important endocrine glands in the human body, playing a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and energy production through the secretion of thyroid hormones. Disorders of the thyroid gland can lead to various health problems, making early diagnosis essential.
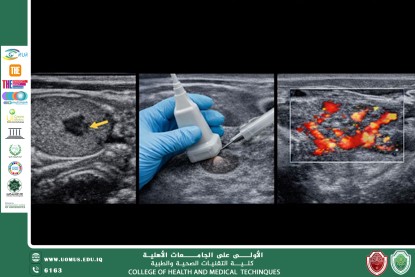
Ultrasound imaging is considered one of the most important and safe diagnostic tools for evaluating thyroid gland diseases. It uses high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the thyroid gland without exposing patients to ionizing radiation. Ultrasound is the preferred initial imaging modality for assessing thyroid size and morphology.
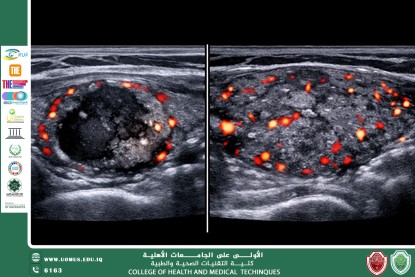
Ultrasound plays a key role in detecting thyroid nodules and evaluating their characteristics, such as size, shape, margins, and internal composition (solid, cystic, or mixed). It also helps differentiate between benign and malignant nodules based on specific imaging features, including microcalcifications and irregular borders.
Furthermore, ultrasound is valuable in diagnosing thyroiditis and thyroid enlargement, as well as in monitoring patients after medical or surgical treatment. It is also widely used to guide fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing procedural risks.
Due to its accessibility, low cost, and high diagnostic value, ultrasound remains an essential tool in the early detection of thyroid gland diseases and significantly contributes to improved patient management and outcomes.