An article by teaching assistant Hawraa Ali entitled Genetic Mutation and Its Importance in Biology
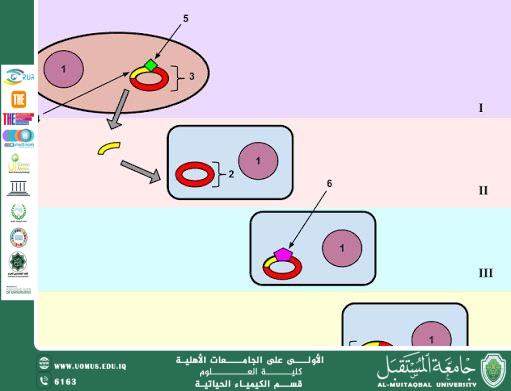
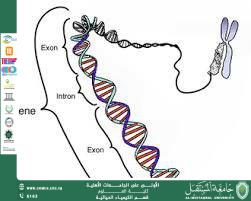
A genetic mutation is defined as a permanent change in the DNA sequence of an organism, resulting in differences in genetic traits compared to the original form. Genetic mutations are considered a fundamental concept in genetics and biological evolution.
Genetic mutations may occur spontaneously during DNA replication within the cell, or as a result of exposure to external factors known as mutagens, such as ionizing radiation, chemical substances, and certain viruses. These mutations may affect a single gene or larger segments of chromosomes.
Mutations are classified into beneficial, harmful, or neutral mutations, depending on their effects on the organism. Beneficial mutations may enhance an organism’s ability to adapt to its environment, while harmful mutations can lead to genetic diseases or functional disorders. Neutral mutations, on the other hand, do not produce noticeable effects.
Genetic mutations play a crucial role in genetic diversity and evolution, as they are the primary source of new traits in living organisms. Moreover, they are of great importance in the medical field, where studying mutations helps in understanding the causes of genetic diseases and cancers, as well as in developing diagnostic methods and gene-based therapies.
In conclusion, genetic mutation is a significant biological phenomenon with both positive and negative effects, and understanding it contributes greatly to advances in genetics and medical sciences.
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First among Iraqi Private Universities