Scientific article by Ms. Tamara Nihad Abbas entitled “Lenses: Their Types and Applications in Optical Systems.”
Lenses are among the most important optical elements used to direct light and form images. They play a fundamental role in many modern optical devices such as eyeglasses, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes. The operation of lenses is based on the principle of light refraction when it passes between different transparent media, which leads to the convergence or divergence of light rays. This article aims to explain the concept of lenses, their types, and their most important applications.
Concept of Lenses
A lens is a transparent medium bounded by two polished surfaces, which are often spherical, or one spherical and the other plane. When light falls on a lens, it is refracted according to the laws of refraction, causing a change in its direction and the formation of images. Thin lenses are considered the simplest type of lenses and are the most commonly used in optical analysis.
Types of Lenses
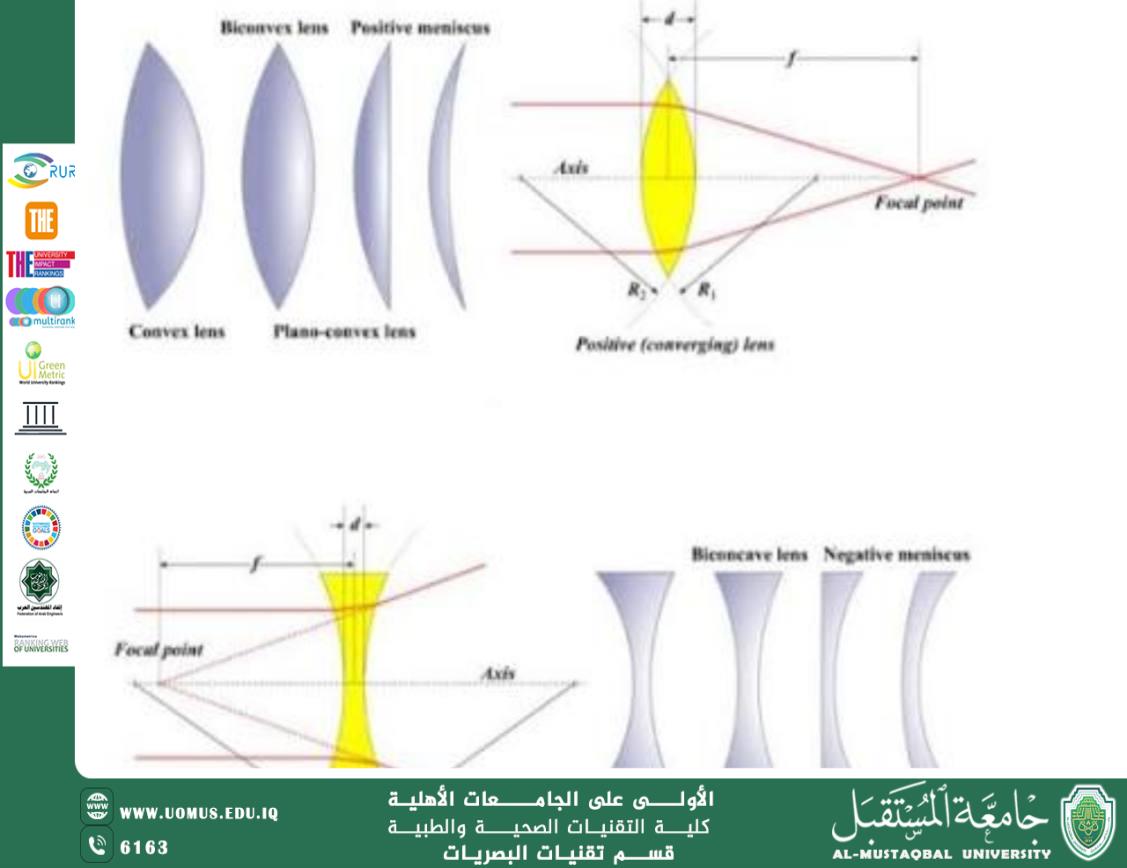
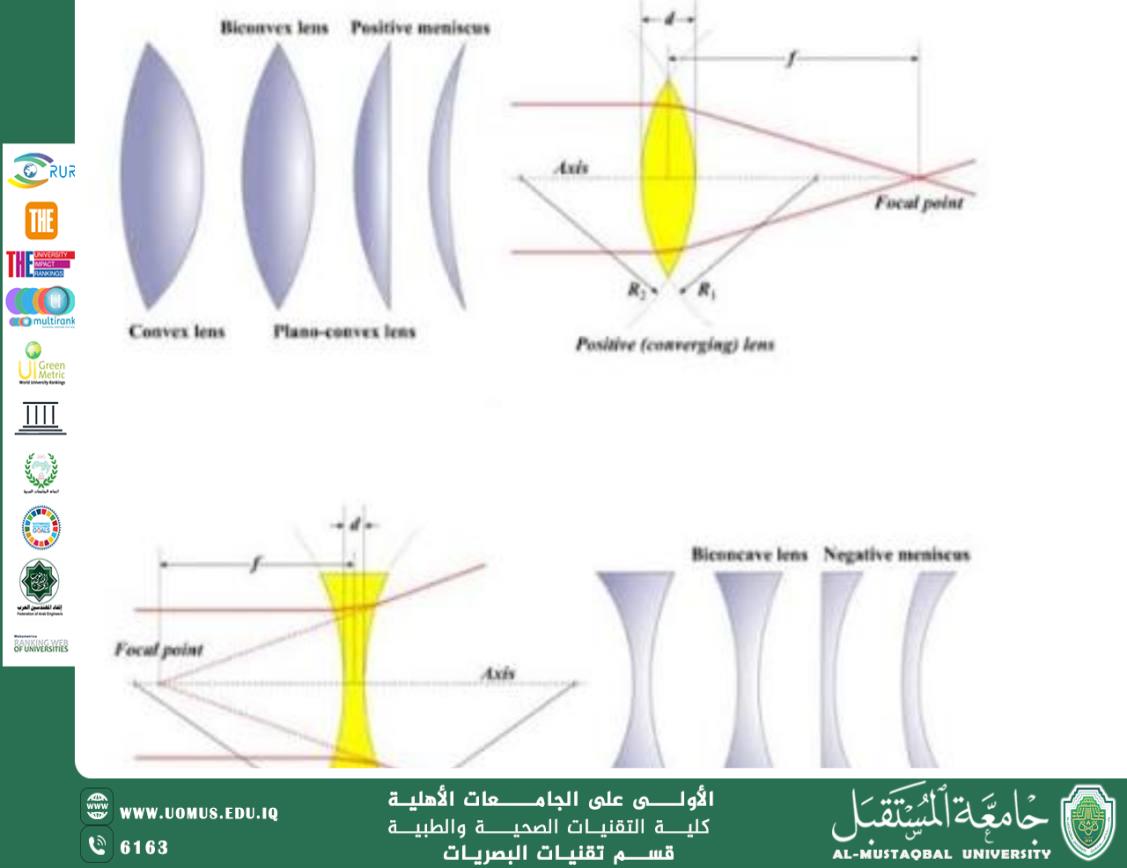
1. Convex (Converging) Lenses
A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges. It converges parallel incident rays to a point called the focal point. These lenses are used in magnifying glasses, cameras, and microscopes.
2. Concave (Diverging) Lenses
A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges. It diverges parallel rays so that they appear to originate from a virtual focal point. These lenses are commonly used to correct myopia (short-sightedness).
Basic Elements of a Lens
• Principal axis
• Optical center
• Focal point
• Focal length
These elements are essential for understanding how images are formed by lenses.
Conclusion
Lenses are a fundamental component of optics and are indispensable in modern scientific and technological applications. Understanding the types of lenses and their properties helps in the development of optical devices and the improvement of their performance.
University of Al-Mustaqbal – The First and Leading Private University