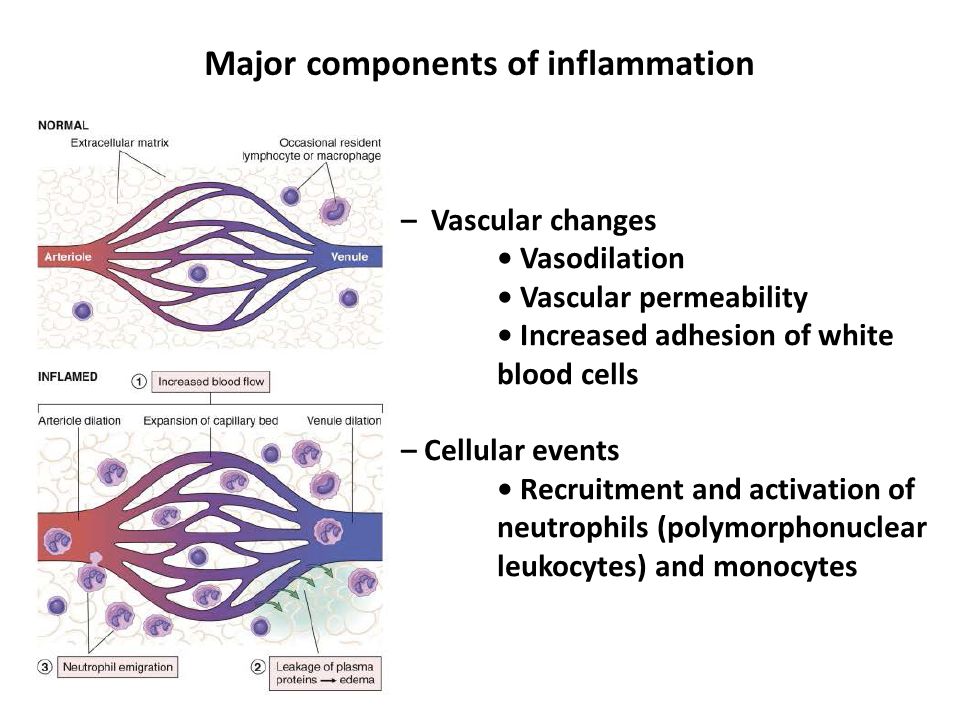
د. اثمارمحمد Inflammation:
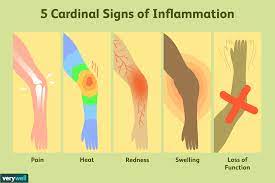
<br /><br />is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators.<br />Type of inflammation :<br />• Acute inflammation: The response to sudden body damage, such as cutting your finger. To heal the cut, your body sends inflammatory cells to the injury. ...<br />• Chronic inflammation: Your body continues sending inflammatory cells even when there is no outside danger<br /><br />Five cardinal sign of the inflammation: <br />1-rubor ( redness caused by dilation of vessels) <br />2-dolor (pain due to increased pressure exerted by the accumulation of interstitial fluid and to mediators such as bradykinin)<br />3-calor (heat caused by increased blood flow)<br />4-tumor ( swelling due to an extravascular accumulation of fluid <br />5-functiolaesa(loss of function) <br /><br /> <br /><br /><br /><br />Component of inflammation:<br />1- vascular changes <br />2- cellular events <br /> <br /><br /><br />The Three Stages of Inflammation:<br />• Phase 1: Inflammatory Response. Healing of acute injuries begins with the acute vascular inflammatory response. ...<br />• Phase 2: Repair and Regeneration. ...<br />• Phase 3: Remodelling and Maturation<br />