Rheumatism in the Elderly: Health Challenges and How to Manage Them
As people age, many face a range of health challenges that directly impact their quality of life. One of the most common of these challenges is rheumatic diseases, which cause joint inflammation and persistent pain, and are a leading cause of disability among older adults. Rheumatic diseases are diverse and affect people differently, but their impact on older adults can be more severe due to the natural changes that occur in the body with age. In this article, we will explore how rheumatism affects older adults, its most common types, and how to effectively manage and cope with the disease to improve quality of life.
1. What is Rheumatism?
Rheumatism is an umbrella term used to refer to a group of diseases that affect the joints and surrounding tissues. This includes inflammation that leads to pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the joints. Rheumatic diseases are among the most common chronic diseases affecting older adults and significantly impact their ability to perform daily activities.
There are different types of rheumatic diseases, but the most common among older adults are:
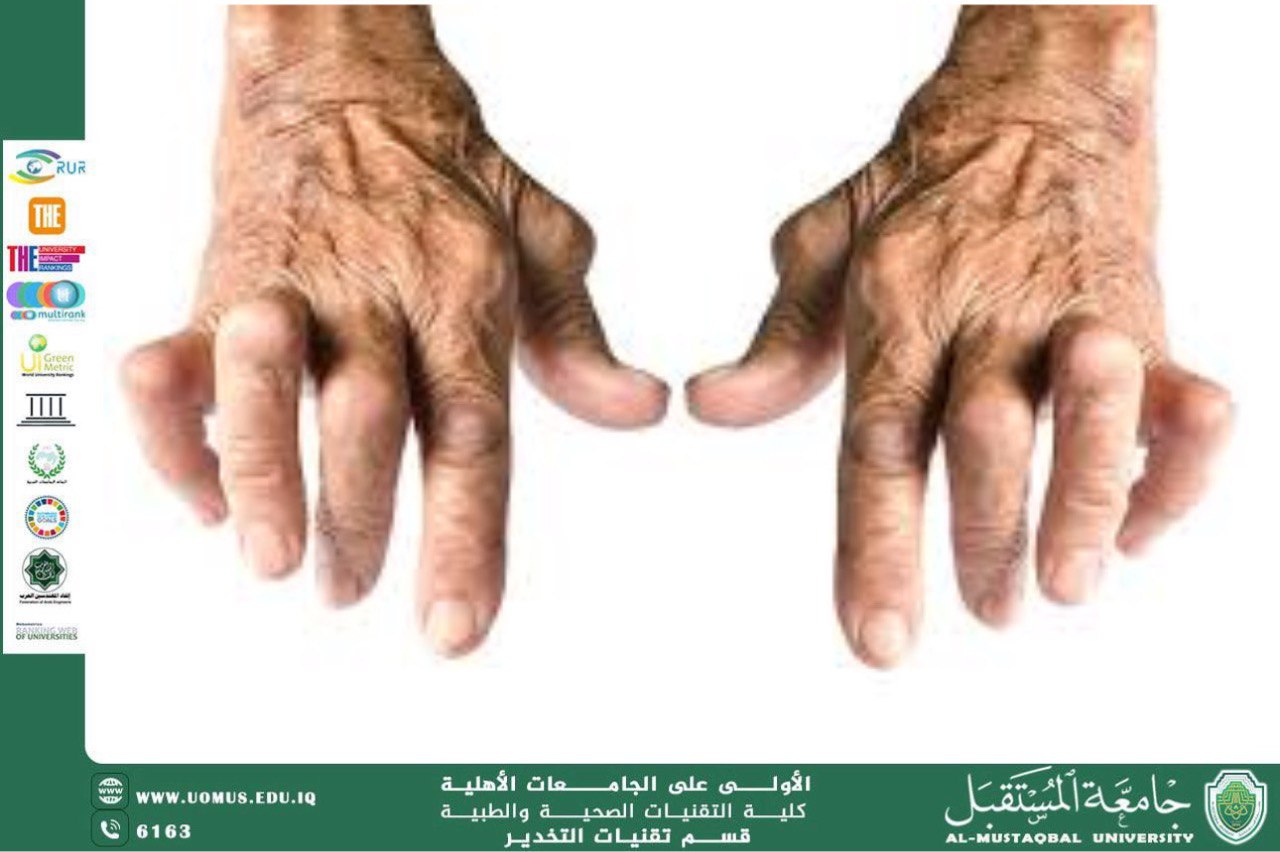
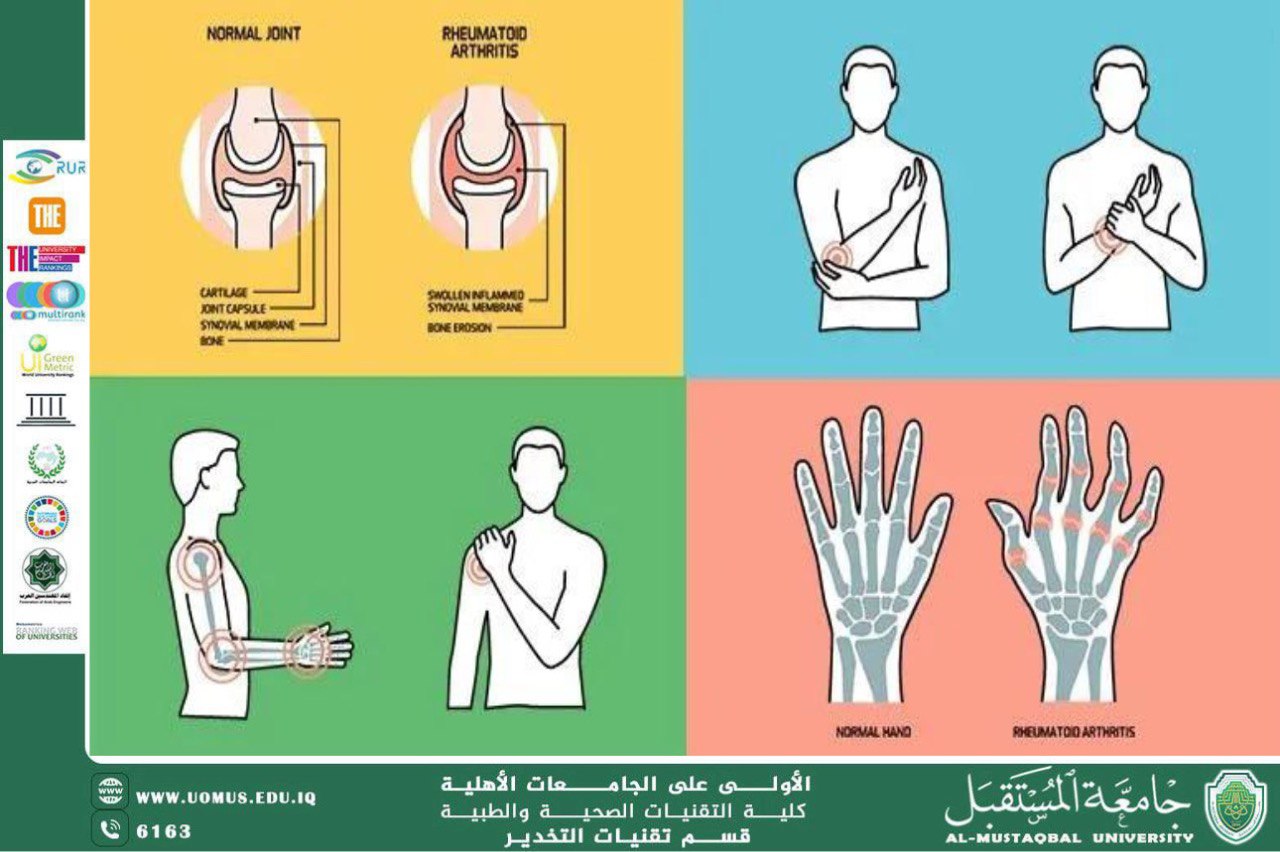
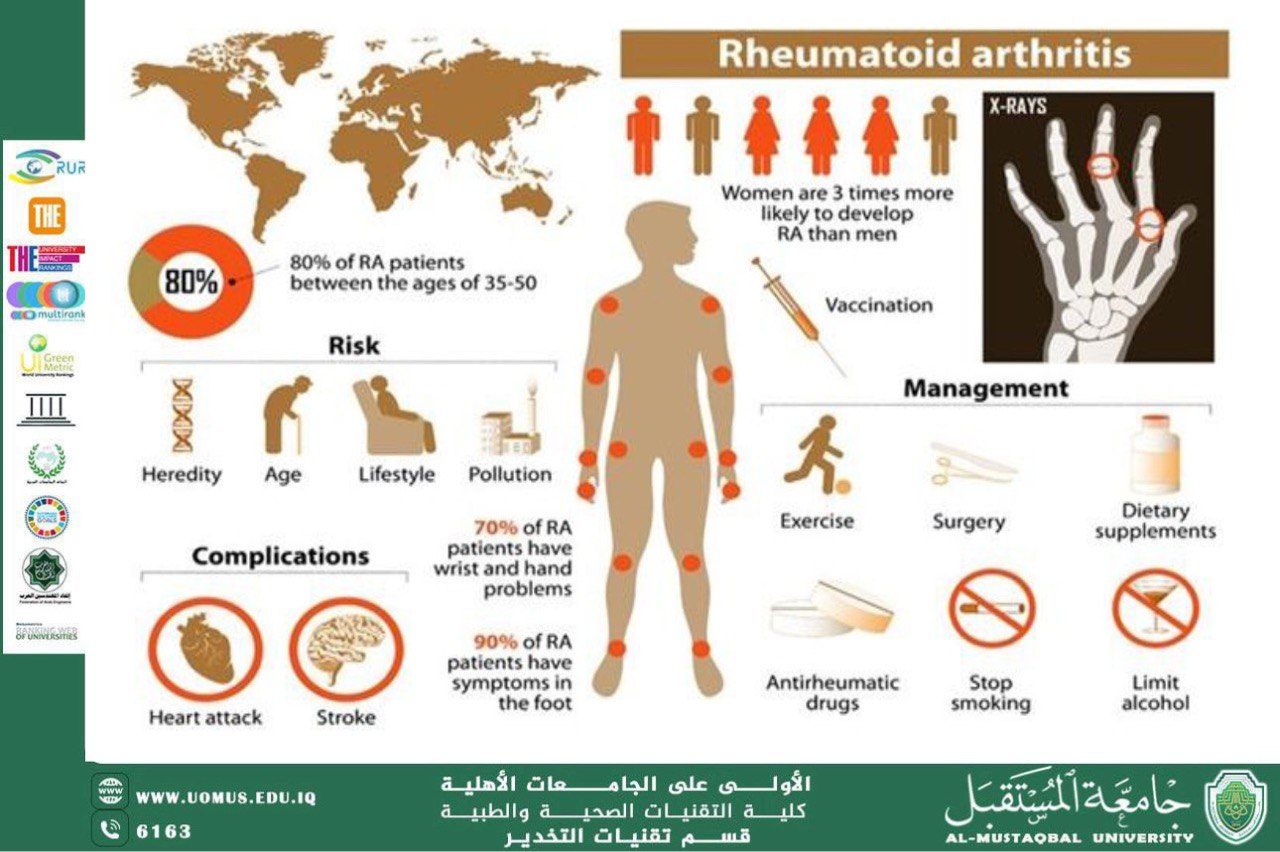
Rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune disease that leads to chronic inflammation in the joints. It can affect the small joints of the hands and feet, and in severe cases, it can lead to permanent joint deformities.
Osteoarthritis: This is one of the most common types of rheumatic diseases among older adults. It occurs as a result of cartilage erosion in the joints, leading to pain and difficulty in movement.
Gout: This is another type of arthritis that occurs as a result of the accumulation of uric acid in the joints. It causes sudden attacks of severe pain, especially in the large joint of the thumb.
2. The Impact of Rheumatism on Older Adults:
2.1. Persistent Pain and Movement Restrictions: Rheumatism in older adults is often associated with persistent pain, especially in large joints such as the knees, hips, and spine. This pain can hinder daily movement and make it difficult to perform simple activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or even getting dressed. Over time, this can lead to general muscle weakness due to reduced mobility, increasing health risks such as falls or injuries.
2.2. Psychosocial Impact:
Persistent pain and limited mobility can lead to feelings of depression and social isolation. Older adults with rheumatism may avoid social activities or hobbies they previously enjoyed, increasing their risk of depression and anxiety. Social isolation, in turn, affects overall health, as research shows that social interaction is important for maintaining both mental and physical well-being.
2.3. Impact on Independence:
Rheumatism can lead to a loss of the ability to perform daily activities independently. Some older adults with rheumatism may need assistance with tasks such as eating, bathing, or even getting around. Loss of independence can lead to feelings of frustration and low self-esteem.
3. How to Manage and Cope with Rheumatism:
3.1. Drug Therapy:
Several medications can help reduce the symptoms associated with rheumatism, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for rheumatoid arthritis. These medications help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. In some more severe cases, biologic drugs that modulate the immune system may be used.
3.2. Physical Therapy and Exercise:
One of the most important ways to manage rheumatism, especially in older adults, is through physical therapy. Exercises that focus on improving flexibility and strengthening muscles can help reduce pain and improve mobility. These can include simple exercises such as walking, swimming, or stretching. Physical therapy helps maintain range of motion in the joints and reduces joint stiffness.
3.3. Weight Management: Excess weight puts extra strain on the joints, especially weight-bearing joints like the knees.
Therefore, it is important for older adults to carefully monitor their weight and work to reduce excess weight, which can significantly improve the symptoms associated with rheumatism.
3.4. Psychosocial Support:
Older adults need to receive psychosocial support when dealing with rheumatism. Support from family and friends can help them cope with their condition and improve their quality of life. Additionally, support groups or psychological counseling can help reduce feelings of depression and isolation.
3.5. Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes:
Using Assistive Devices: Such as canes or wheelchairs to help with daily mobility.
Home Modifications: Such as installing resting chairs or handrails to provide support while moving.
Focusing on a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help improve joint health and reduce inflammation.
4. Finally:
Rheumatism is a common disease among older adults and significantly impacts their quality of life, causing chronic pain, limited mobility, and psychological and social effects. However, this disease can be effectively managed through medical care, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and psychological support. By following these measures, older adults can improve their quality of life and live more independently and healthily. Most importantly, raising awareness about the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate treatment is crucial for improving the lives of patients with rheumatism.
Ali Rasool
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.