Urinary Tract Diseases and Their Treatment
Urinary tract diseases are among the most common conditions affecting people of all age groups. They include disorders involving the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. These diseases directly affect quality of life and may lead to serious complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Brief Anatomy of the Urinary Tract
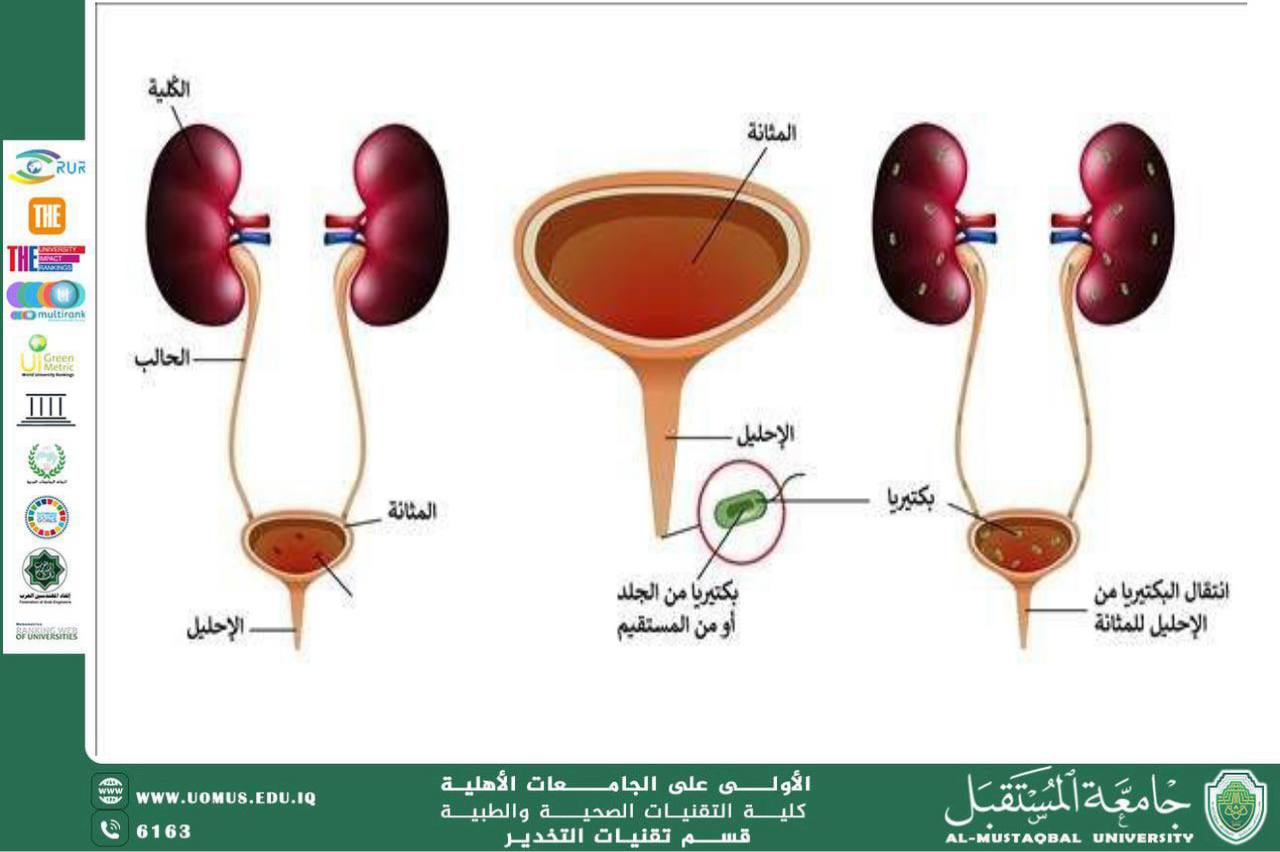
The urinary system consists of:
• Kidneys
• Ureters
• Urinary bladder
• Urethra
Its primary function is to filter waste products from the blood and regulate fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
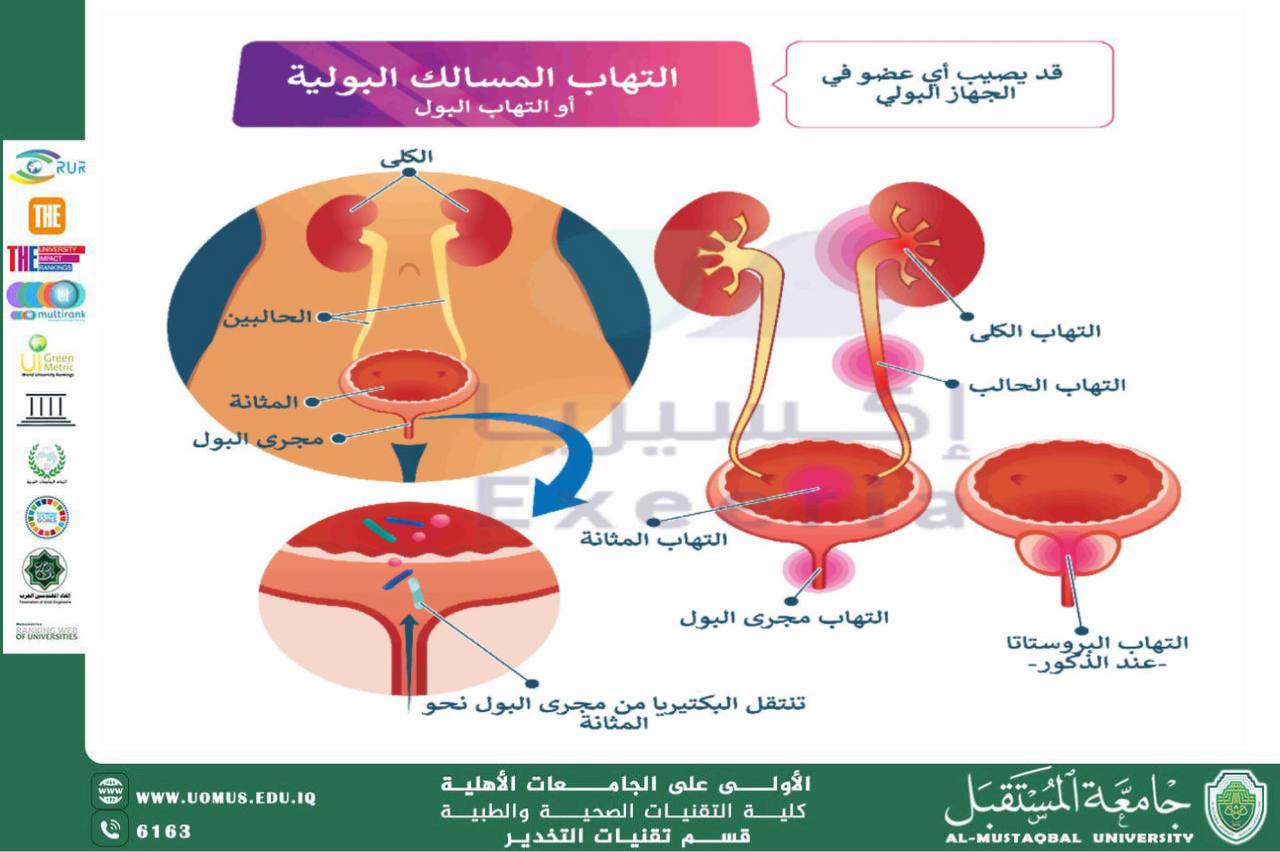
Common Urinary Tract Diseases
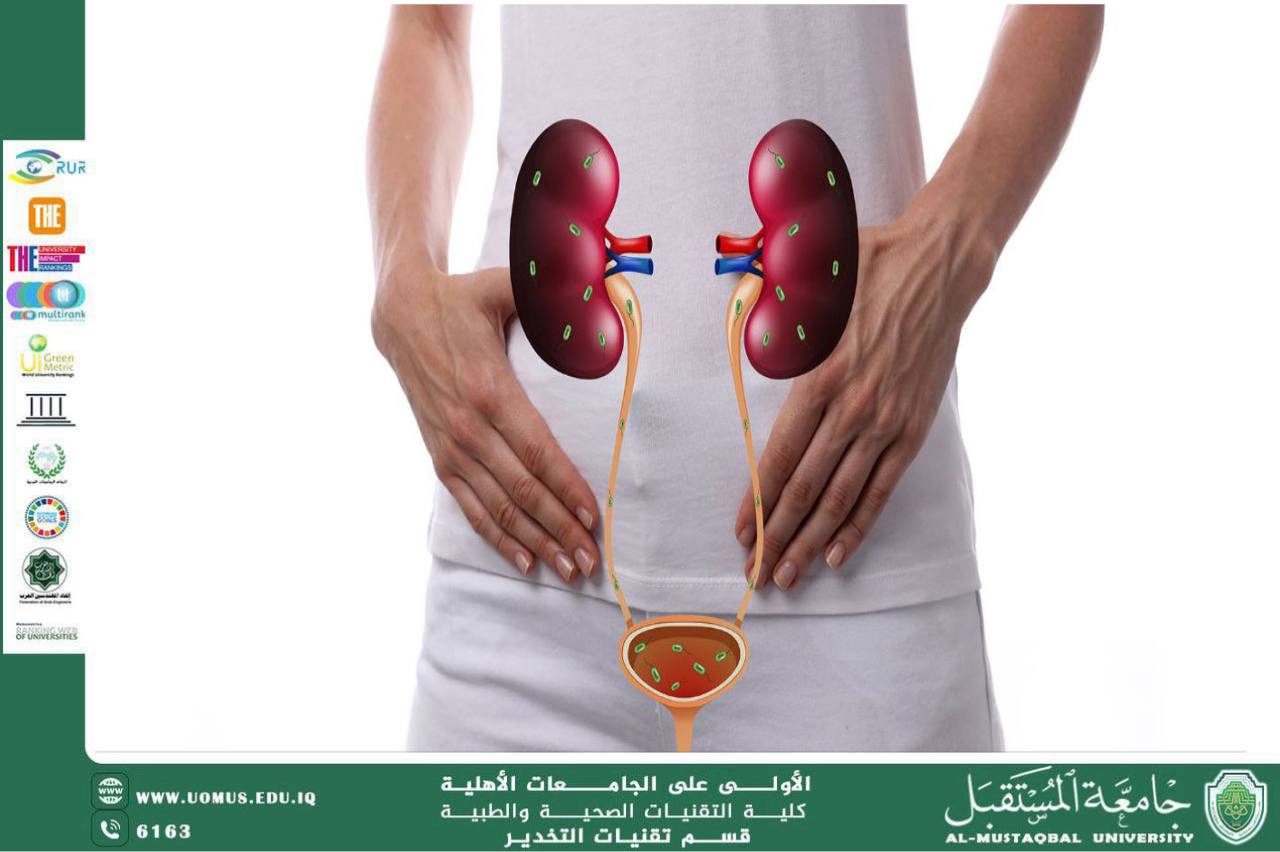
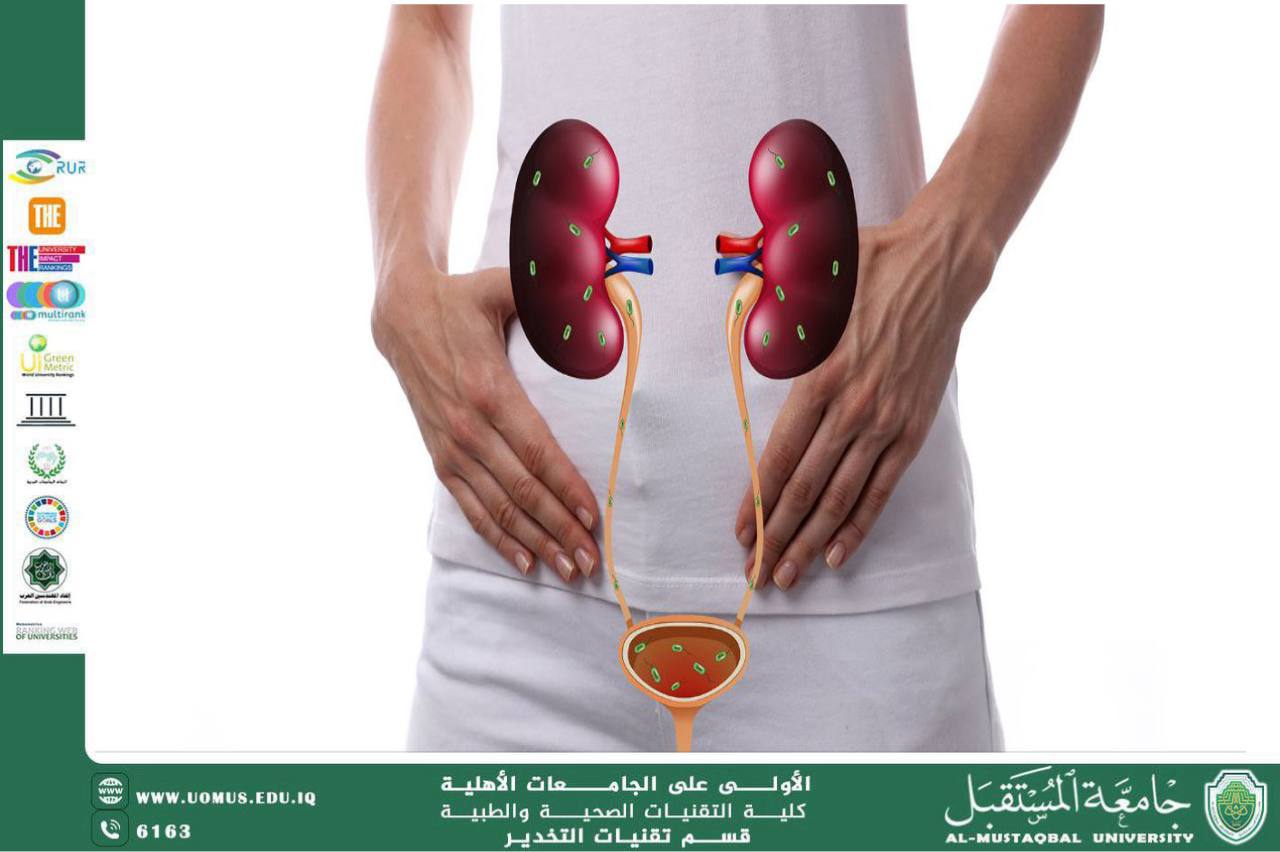
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
These are the most common urinary tract conditions and are usually caused by bacterial infections.
Symptoms:
• Burning sensation during urination
• Frequent urination
• Lower abdominal pain
• Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
Treatment:
• Antibiotics according to the type of bacteria
• Increased fluid intake
• Analgesics when needed
2. Kidney and Urinary Stones
These occur due to the deposition of salts and minerals in the urine.
Symptoms:
• Severe flank pain
• Blood in the urine
• Nausea and vomiting
Treatment:
• Adequate water intake
• Medications to help dissolve or pass stones
• Shock wave lithotripsy
• Surgical intervention when necessary
3. Cystitis
Cystitis may be bacterial or non-bacterial in origin.
Treatment:
• Antibiotics in bacterial cases
• Pain relievers
• Avoidance of irritants such as caffeine
4. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
This condition commonly affects men over the age of 50.
Symptoms:
• Weak urine stream
• Difficulty initiating urination
• Frequent nighttime urination
Treatment:
• Alpha-blocker medications
• 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
• Surgical intervention when required
5. Kidney Failure
This condition may result from chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
Treatment:
• Control of the underlying disease
• Supportive medications
• Dialysis or kidney transplantation
Diagnostic Methods
• Urinalysis
• Kidney function tests
• Ultrasound imaging
• Computed tomography (CT scan)
• Urine culture
Prevention
• Regular water intake
• Maintaining personal hygiene
• Avoiding prolonged urine retention
• Early treatment of infections
• Regular medical check-ups for patients with diabetes and hypertension
Conclusion
Urinary tract diseases require early diagnosis and appropriate treatment to prevent serious complications. Adherence to medical advice and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential for effective prevention and management.
Hasan Najeh
Al-Mustaqbal University
The First University in Iraq.