An article titled "Electricity in the Service of Medicine" by Engineer Hassanein Hadi Hussein
The relationship between electricity and medicine is no longer merely an operational one for devices; it has become an organic relationship deeply rooted in the core of healthcare. The human body is fundamentally an "electrobiological system," where nerve cells and muscles communicate via precise electrical impulses. Hence, biomedical engineering has emerged as a tool to utilize "electrical systems" to understand these impulses, diagnose diseases, and even treat them.
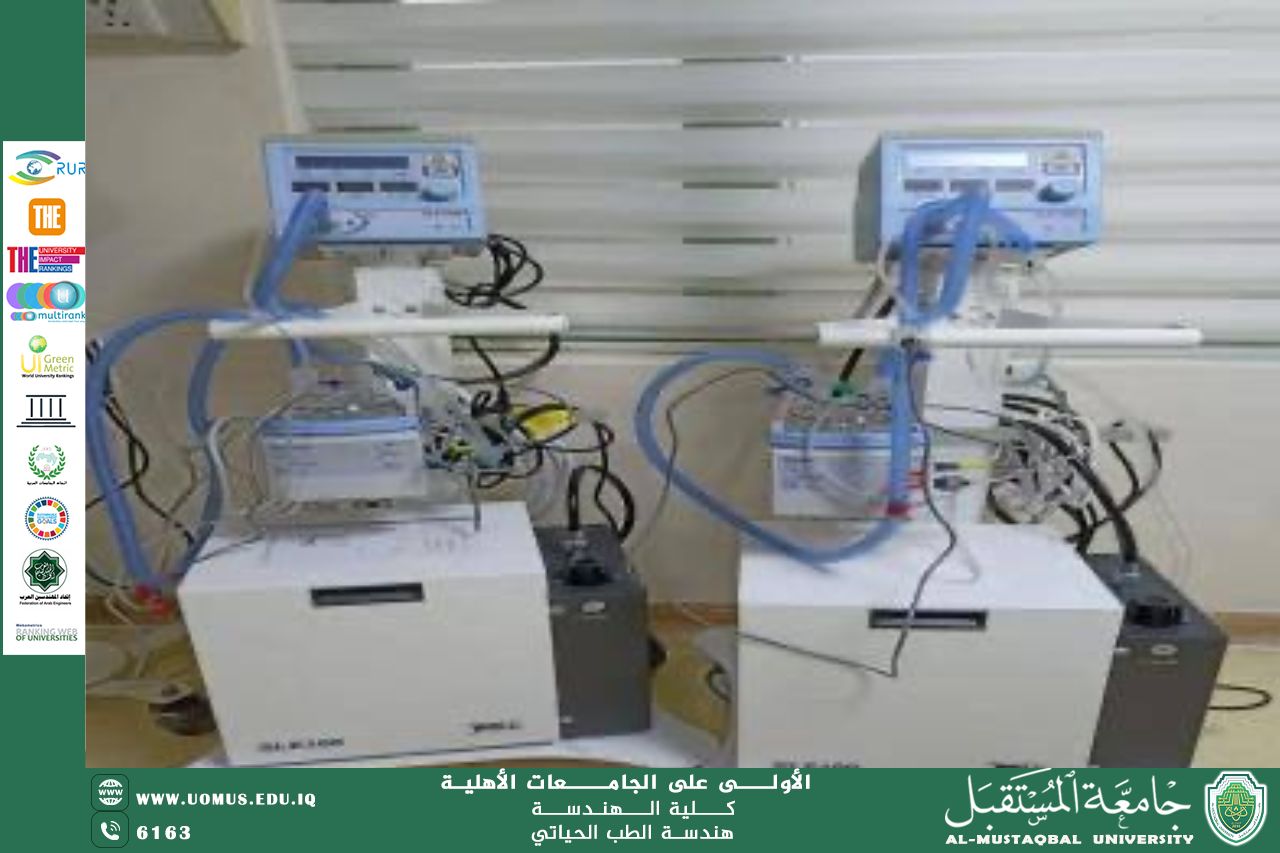
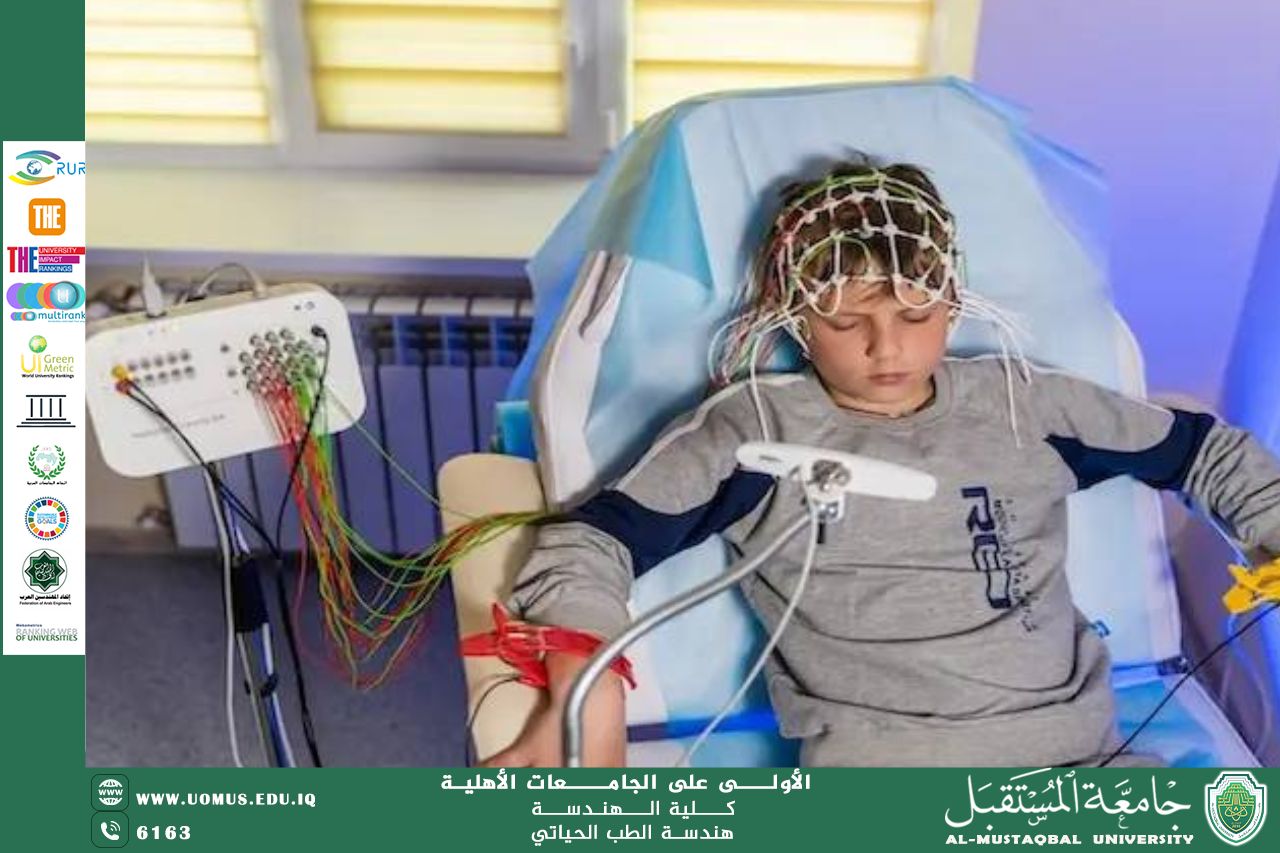
1. Bio-signal Sensing
Sensors and electronic circuits are the first line of defense in medical diagnosis.
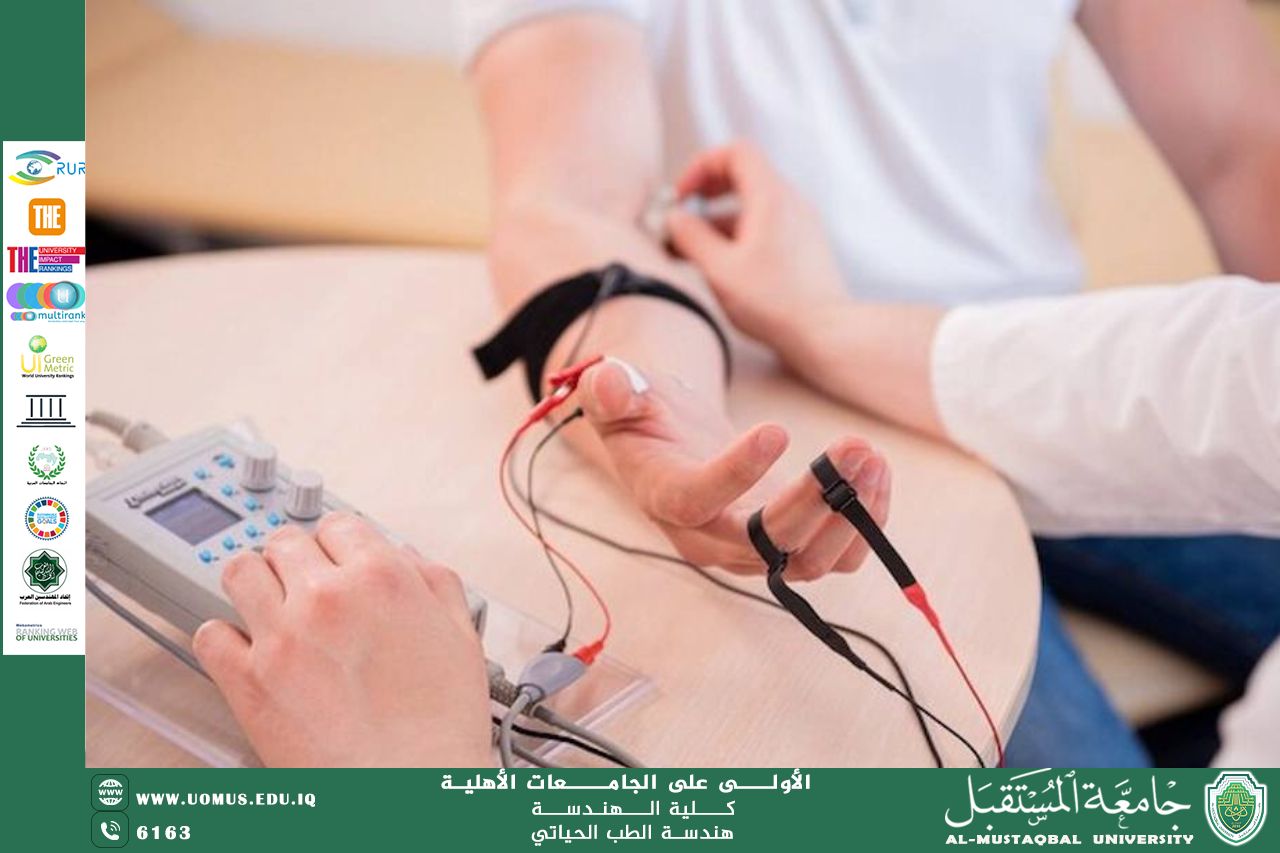
• Electrocardiogram (ECG) and Electroencephalogram (EEG): Electrical engineers design electrodes that act as software interfaces, capturing the electrical potential difference generated by biological activities.
• Signal Amplification: Because the body's signals are very weak and affected by ambient noise, "medical signal amplifiers" are used to refine and amplify these impulses without distortion, allowing physicians to visualize health conditions with high accuracy.
2. Electricity as a Diagnostic Tool
Major diagnostic devices rely on advanced electrical engineering principles:
• Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This uses powerful magnetic fields and pulses of radio waves to excite the body's atoms and create detailed tissue maps.
• Ultrasound Imaging: This uses the phenomenon of piezoelectricity, where electrical impulses are converted into sound vibrations that penetrate the body and then return, converting back into electrical signals to create an image of the fetus or organs.
3. Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is not limited to monitoring; it also intervenes as a direct treatment in critical cases:
• Pacemaker: This is a small computer and electrical circuit implanted under the skin. It sends precisely measured electrical impulses to stimulate the heart muscle if its natural rhythm is disrupted.
• Defibrillator: This device delivers a sudden, high-voltage electrical charge to restore the heart's electrical activity in cases of sudden cardiac arrest, saving thousands of lives daily.
4. Electrical Safety in the Medical Environment
One of the most important aspects of electricity in medicine is ensuring patient safety. Biomedical engineers design complex electrical isolation circuits to prevent any current leakage from devices into the patient's body, as even very small currents can cause this. (In microamperes) can cause cardiac arrest if applied directly during surgery.
Conclusion
The title "Electricity in the Service of Medicine" encapsulates a technological revolution that has made the impossible possible. Through electrical engineering, the human body has been transformed from a mysterious black box into an open system that can be read, understood, and repaired. The integration of electronic circuits with biological sciences is the primary driver of future medical innovations, such as artificial organs and diagnostic artificial intelligence.