The skin microbiome
Introduction
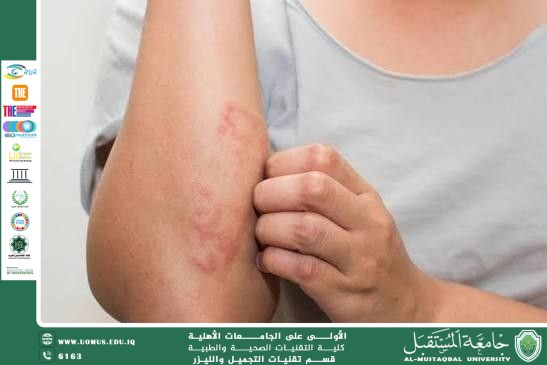
The skin microbiome is one of the most important elements of skin health, consisting of a diverse community of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Despite their small size, these microorganisms have a significant impact on skin function and protection against diseases. Recent studies indicate that imbalance in the skin microbiome may be associated with the development of chronic skin disorders, such as eczema (atopic dermatitis), making the understanding of microbiome composition and its roles essential in dermatology and cosmetic treatments.
---
Importance of the Skin Microbiome
The skin microbiome plays a dual role:
Skin protection: Beneficial bacteria and fungi prevent colonization by pathogenic organisms and maintain the natural skin barrier.
Immune regulation: Commensal microbes help train the immune system to recognize harmful microorganisms without triggering excessive inflammation.
When this balance is disrupted, the risk of chronic inflammatory skin conditions increases, making microbiome monitoring an important aspect of skin care.
---
Microbiome Dysbiosis and Its Impact on Chronic Skin Diseases
Microbiome imbalance (dysbiosis) occurs when microbial diversity decreases and harmful bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, increase. This imbalance leads to:
Enhanced skin inflammation: The immune system is stimulated to produce inflammatory cytokines that exacerbate eczema.
Weakened skin barrier: Skin becomes more susceptible to irritants and allergens.
Delayed wound healing: Lesions or scratches resulting from cosmetic procedures or laser treatments are more prone to infection.
Recent studies have shown that patients with eczema exhibit reduced microbial diversity and increased abundance of pathogenic bacteria compared to healthy individuals, demonstrating the direct relationship between the microbiome and chronic skin disorders.
---
Strategies for Microbiome Control
To reduce the risks associated with microbiome imbalance, the following scientific and therapeutic measures can be applied:
Topical probiotics: To restore the balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Hygiene and sterilization: Particularly before and after cosmetic or laser procedures, to minimize the transmission of harmful microorganisms.
Avoid excessive use of antibiotics or corticosteroids: Which may disrupt the skin microbiome.
---
Conclusion
The skin microbiome is a fundamental component of skin health, and its imbalance is clearly associated with the onset of chronic skin disorders such as eczema. Understanding the nature of this microbiome and methods to regulate it contributes to preventing chronic inflammation, improving recovery after cosmetic treatments, and enhancing the effectiveness of dermatological procedures. Increased scientific knowledge about the skin microbiome among professionals leads to higher quality care and better aesthetic outcomes for patients.
Al _ Mustaqbal University, the first university in Iraq