An article titled "Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Printing and its Applications in Biomedical Engineering" by Lecturer M.M. Abdullah Qais Hashim
Selective laser 3D printing (SLS) is an advanced technology in additive manufacturing that has played a significant role in the development of biomedical engineering. This technology is characterized by its ability to produce robust and functional parts, making it suitable for medical applications that require high durability and engineering precision.
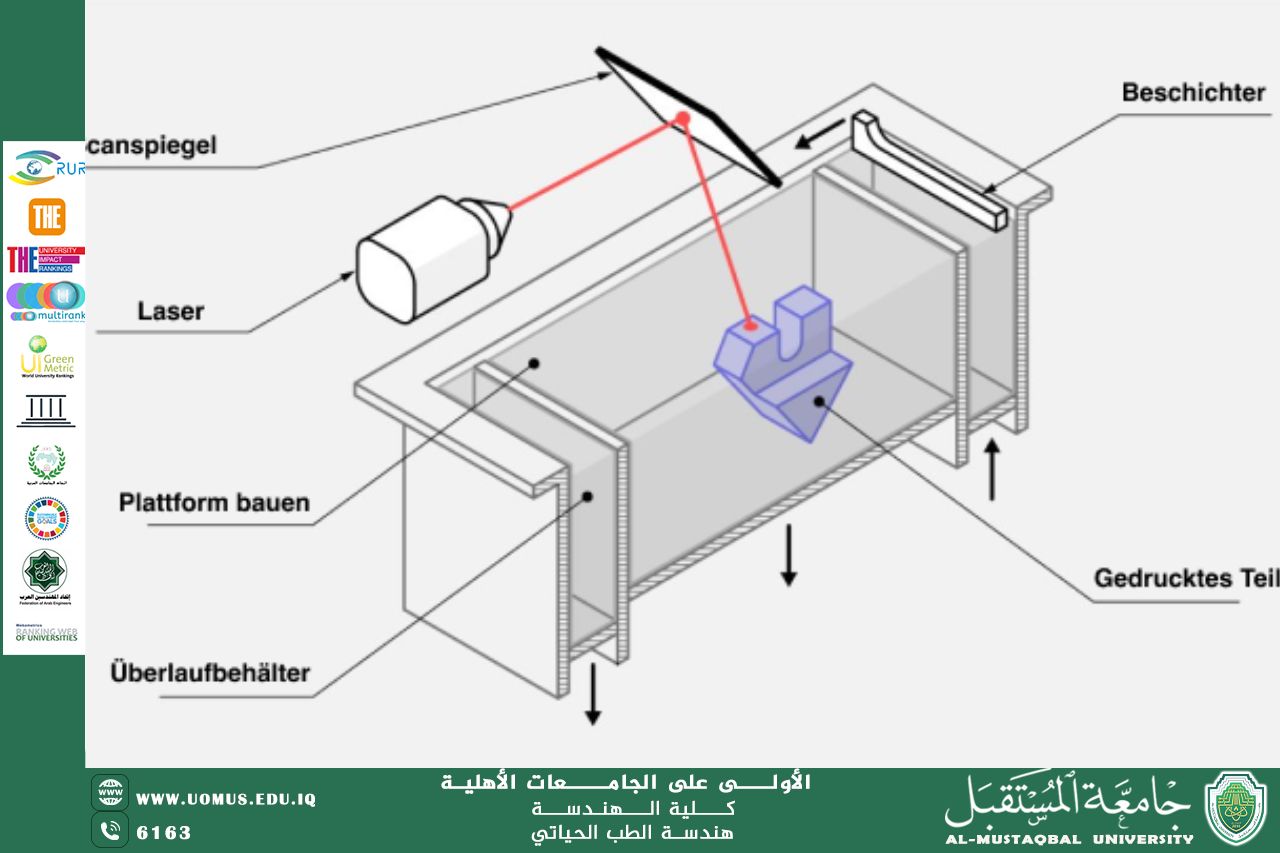
How it works: SLS technology utilizes a high-powered laser to selectively sinter powder materials layer by layer according to a digital (CAD) model. This results in a cohesive 3D structure without the need for external supports, as the unsintered powder acts as a natural support during printing.
Biomaterials Used
In biomedical applications, biocompatible materials such as:
• Medical-grade nylon polymers (Nylon 11, Nylon 12)
• Fiber-reinforced polymers for increased durability
• Sterilizable biocomposite powders
Applications in Biomedicine
SLS technology is widely used in:
• Manufacturing custom prosthetics to patient measurements
• Producing surgical guides
• Creating educational and schematic bone models for surgical procedures
• Manufacturing scaffolds for tissue engineering
Advantages in Medical Applications
• High mechanical strength suitable for functional medical components
• Patient-specific design
• No need for internal supports
• Sterilizable and suitable for clinical use
Challenges
• High cost of equipment and materials
• Requirement for precise control of printing conditions to ensure biocompatibility
Conclusion
SLS technology is an ideal choice in biomedical engineering, especially in applications requiring high strength, durability, and customization, such as prosthetics and surgical guides.