An article titled "3D Printing by Stereolithography (SLA) and its Applications in Biomedicine" by Lecturer M.M. Abdullah Qais Hashim
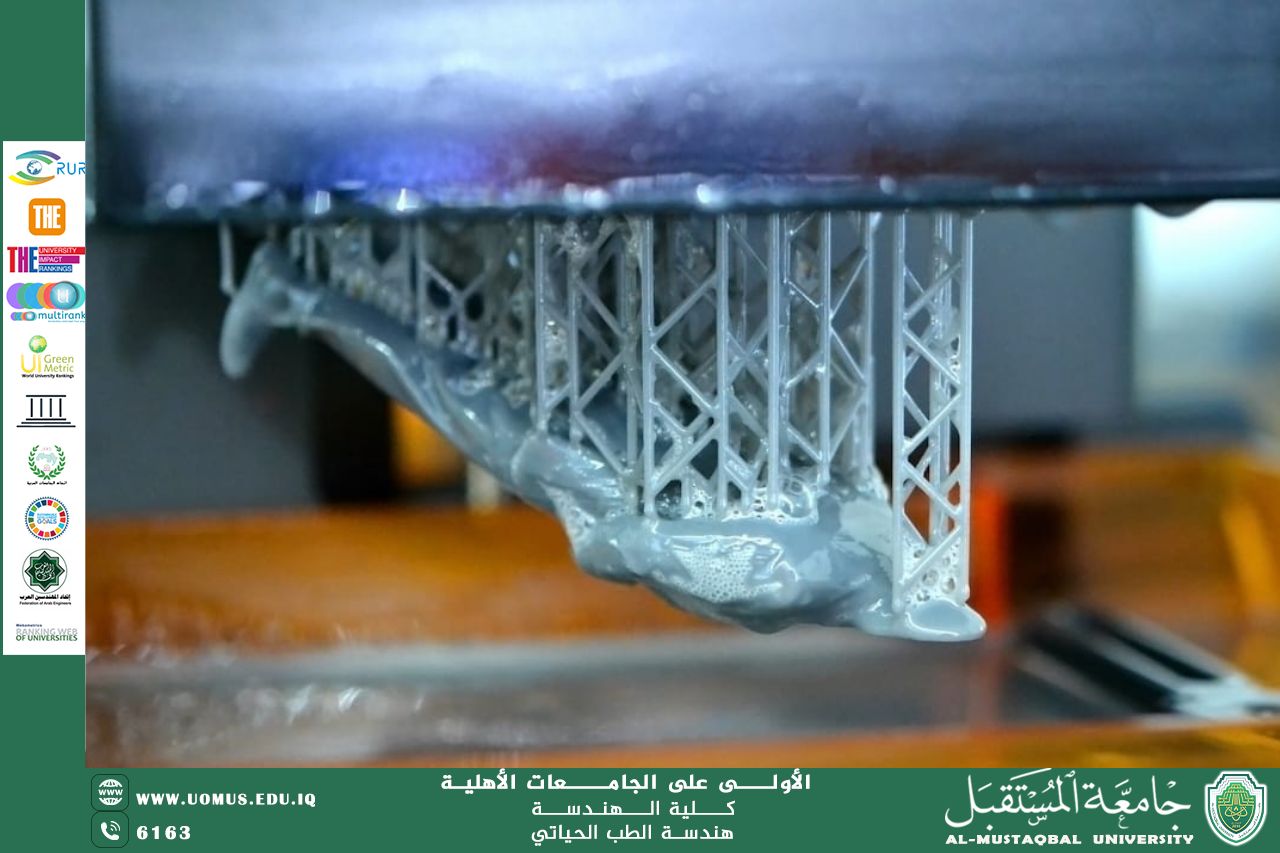
Photolithography (SLA) is one of the most precise 3D printing technologies and has found widespread use in biomedicine due to its ability to produce highly accurate models with excellent surface detail, which is crucial for delicate medical applications.
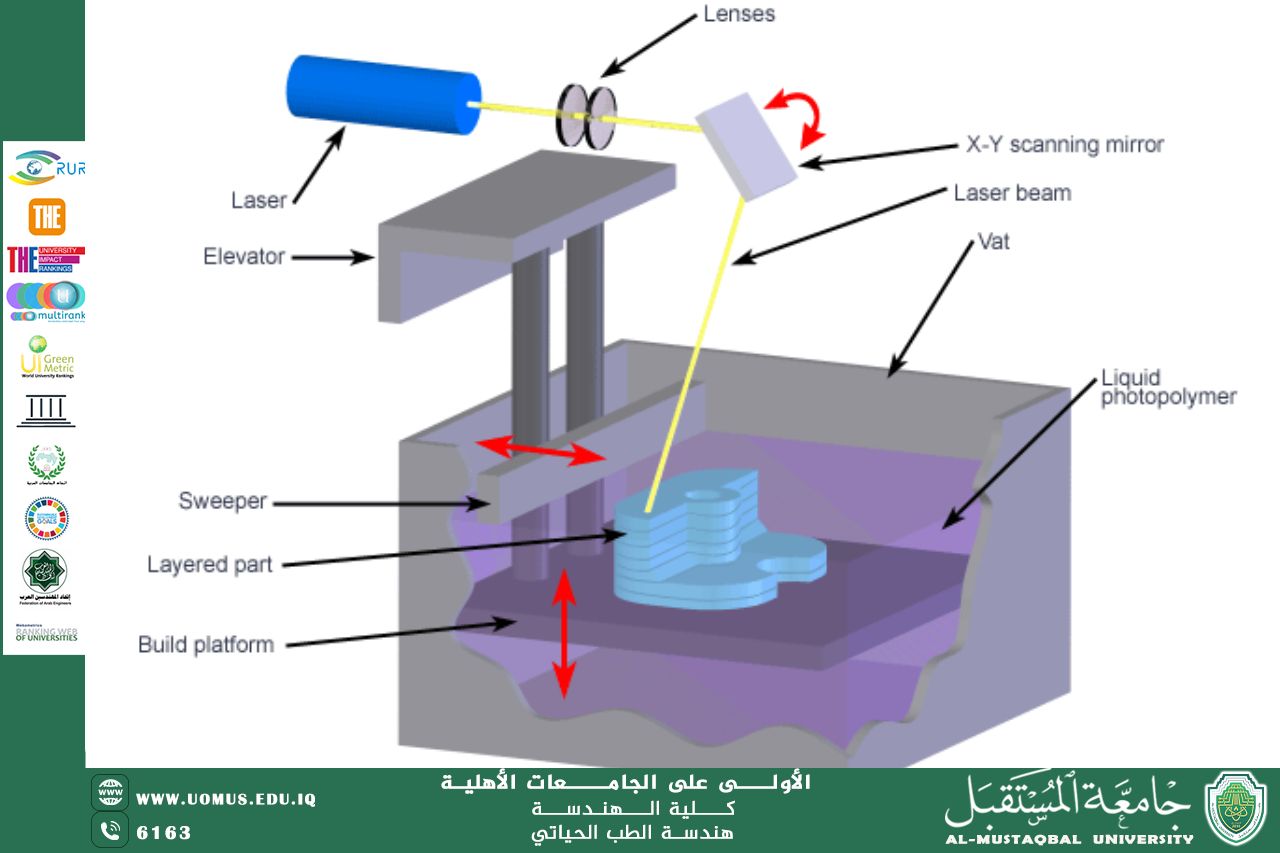
How it works: SLA technology uses lasers or ultraviolet light to harden photosensitive liquid resins layer by layer. This process allows for the production of microscopically accurate models suitable for precision medical applications.
Biomaterials Used
Materials used in medical applications include:
• Biocompatible medical resins
• Dental resins
• Transparent resins for bio-tissue simulation
• Flexible resins for vascular and soft tissue applications
Applications in Biomedicine
SLA technology is widely used in:
• Anatomical models for surgical planning and medical education
• Dental applications such as crowns and temporary molds
• Fabrication of high-precision micro-medical devices
• Prototyping of biomedical devices
Advantages in Medical Applications
• Very high geometric and surface accuracy
• Suitable for applications requiring fine detail
• Improved surgical planning and reduced operating time
Challenges
• Requirement for abutments and post-treatment
• Limited mechanical properties compared to SLS
• Requirement for careful handling of the resins
Conclusion
SLA technology is the ideal choice in biomedicine for applications requiring high precision and excellent surface quality, such as dentistry and anatomical models, making it a complementary tool to SLS technology in the biomedical field.