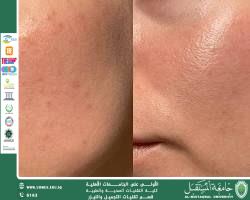
“A scientific article by lecturer Saja Falah Hassan entitled: The Role of Antioxidants in Skincare.”
Role of Antioxidants in Skin Care
Introduction
Antioxidants are considered among the most important biological components in maintaining skin health and protecting it from premature damage. The skin is continuously exposed to harmful environmental factors such as ultraviolet radiation, pollution, and oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Recent studies indicate that increased oxidative stress directly contributes to skin aging, chronic inflammation, and pigmentation disorders, making antioxidants an essential element in dermatology and modern cosmetic therapies.
Importance of Antioxidants for Skin Health
Antioxidants play a vital role in maintaining skin balance through several mechanisms:
Neutralization of Free Radicals:
Antioxidants inhibit unstable free radicals, thereby reducing cellular damage and protecting structural proteins such as collagen and elastin.
Preservation of Skin Structure:
They help protect supportive skin fibers, delaying the appearance of wrinkles and skin sagging.
Enhancement of the Skin Barrier Function:
Antioxidants contribute to strengthening the skin’s protective barrier, reducing transepidermal water loss and improving skin hydration.
Oxidative Stress and Its Impact on Skin Disorders
Oxidative stress occurs when the production of free radicals exceeds the body’s antioxidant defense capacity, leading to:
Accelerated photoaging
Increased skin inflammation such as acne and eczema
Pigmentation disorders and dark spot formation
Delayed skin healing following cosmetic or laser procedures
Studies have shown that reduced antioxidant levels in the skin are associated with a higher susceptibility to chronic skin diseases and deterioration of overall skin appearance.
Types of Antioxidants Used in Skin Care
Common antioxidants used topically or systemically include:
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid):
Stimulates collagen synthesis, improves skin tone, and reduces wrinkles.
Vitamin E (Tocopherol):
Protects cellular membranes from oxidative damage and enhances skin hydration.
Polyphenols:
Found in plant extracts such as green tea, and possess strong anti-inflammatory properties.
Antioxidant Enzymes:
Such as Superoxide Dismutase, which helps break down free radicals within skin cells.
Clinical and Cosmetic Role of Antioxidants
In clinical and cosmetic practice, antioxidants are used to:
Reduce side effects of laser and chemical peeling treatments
Accelerate skin healing after cosmetic procedures
Improve long-term skin care outcomes
Prevent ultraviolet-induced skin damage
Conclusion
Antioxidants are a fundamental component of modern skin care due to their effective role in protecting the skin from oxidative stress, delaying signs of aging, and enhancing skin health and physiological functions. A scientific understanding of antioxidant mechanisms and their proper application contributes to improved dermatological and cosmetic treatment outcomes and enhances the quality of healthcare services in dermatology and aesthetic medicine.
AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq