The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Accuracy of Brain Tumor Diagnosis Using MRI
Introduction
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most important medical imaging techniques used in diagnosing diseases of the nervous system, particularly brain tumors, due to its high accuracy and ability to reveal the anatomical and functional details of soft tissues without the use of ionizing radiation. With the tremendous advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, it has become possible to leverage these technologies to enhance the accuracy of brain tumor diagnosis and improve the quality of medical reports. This lecture aims to highlight the role of AI in improving the accuracy of brain tumor diagnosis using MRI.
The Concept of Artificial Intelligence and its Medical Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that focuses on designing systems capable of mimicking human intelligence in learning, reasoning, and decision-making. In the medical field, AI is used to analyze big data, including medical images, patient data, and electronic health records. These applications rely on advanced technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and artificial neural networks, which enable systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Its Importance in Diagnosing Brain Tumors
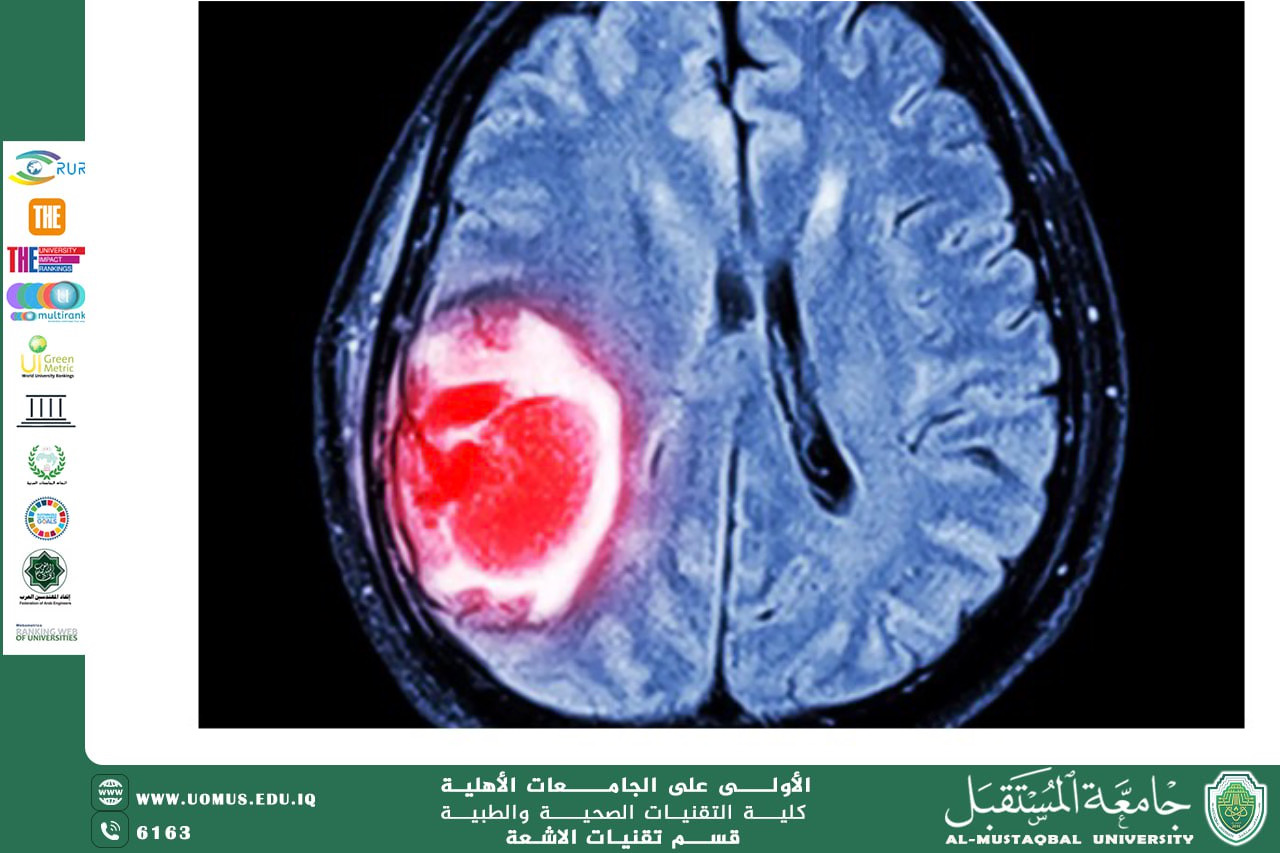
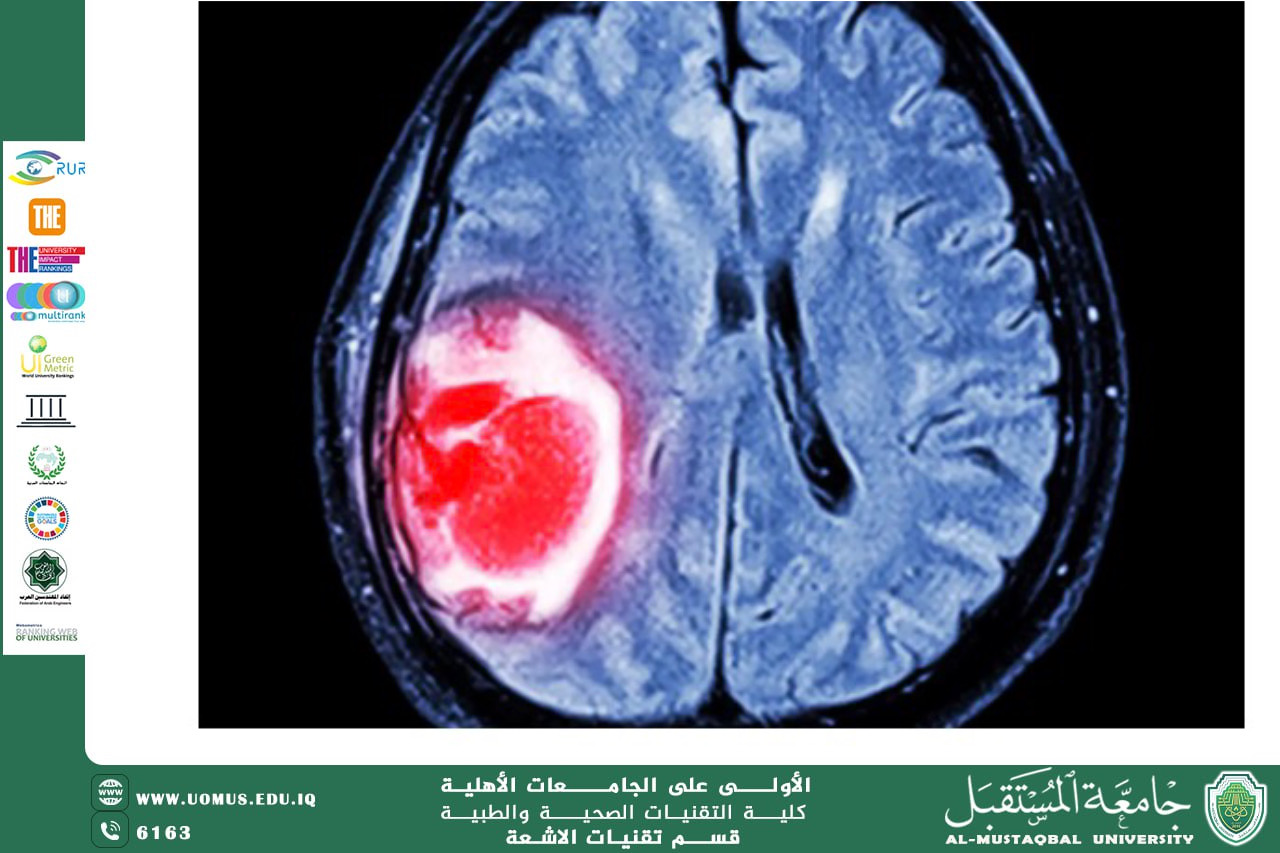
MRI is distinguished by its ability to produce high-contrast images of soft tissues, making it the ideal tool for diagnosing brain tumors. Various imaging sequences are used, such as T1, T2, FLAIR, diffusion, and perfusion, each providing different information that helps determine the tumor type, extent, and degree of malignancy. However, interpreting these images requires a high level of expertise and can be subject to variation among physicians.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in MRI Image Analysis
Artificial intelligence algorithms, particularly deep learning, contribute to the highly accurate analysis of MRI images by recognizing patterns invisible to the human eye. These algorithms can precisely determine the tumor's location, size, and boundaries, as well as classify it as benign or malignant. They also help differentiate between various types of brain tumors, such as gliomas and brain metastases.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy Using Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence contributes to reducing diagnostic errors resulting from human interpretation, especially in complex or early-stage cases. Intelligent systems act as a physician's assistant, providing accurate quantitative analyses and data-driven predictions. This integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with the physician's expertise leads to improved diagnostic accuracy and faster decision-making.
AI and Clinical Decision Support
AI's role extends beyond brain tumor diagnosis to include clinical decision support by suggesting appropriate treatment plans based on tumor characteristics and patient history. It can also be used to monitor tumor progression and assess treatment response, contributing to improved clinical outcomes.
Technical and Ethical Challenges
Despite the significant advantages of applying AI in brain tumor diagnosis using MRI, there are technical and ethical challenges that must be addressed. These challenges include protecting patient data privacy, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of algorithms, and the need to train medical personnel to use these technologies effectively.
The Future of AI in Brain Tumor Diagnosis with MRI
The future is expected to witness increasing development in the integration of AI with MRI technologies, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and more efficient healthcare. Artificial intelligence will become an integral part of the medical diagnostic system, working alongside physicians to achieve optimal treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: Artificial intelligence represents a significant leap forward in the diagnosis of brain tumors using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contributing to improved diagnostic accuracy, enhanced medical decision-making, and reduced errors. With continued technological advancements, these technologies are expected to play a pivotal role in the future of diagnostic medicine.