The Role of Multiparametric MRI (T1, T2, FLAIR, DWI, Perfusion) in Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Introduction
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone in brain tumor diagnosis due to its high soft tissue contrast and the multi-sequence imaging it offers, allowing for the evaluation of the tumor's anatomical and functional characteristics. With the increasing complexity of the data generated by these sequences, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as an effective tool for analyzing multiparametric images and improving diagnostic accuracy. This lecture aims to illustrate the integration of AI with different MRI sequences in brain tumor diagnosis.
AI in MRI Image Analysis
Artificial intelligence, particularly deep learning techniques, relies on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) capable of analyzing multidimensional medical images. These techniques enable the extraction of precise features from MRI images, such as signal intensity, texture, and irregular borders, contributing to improved tumor classification and grading.
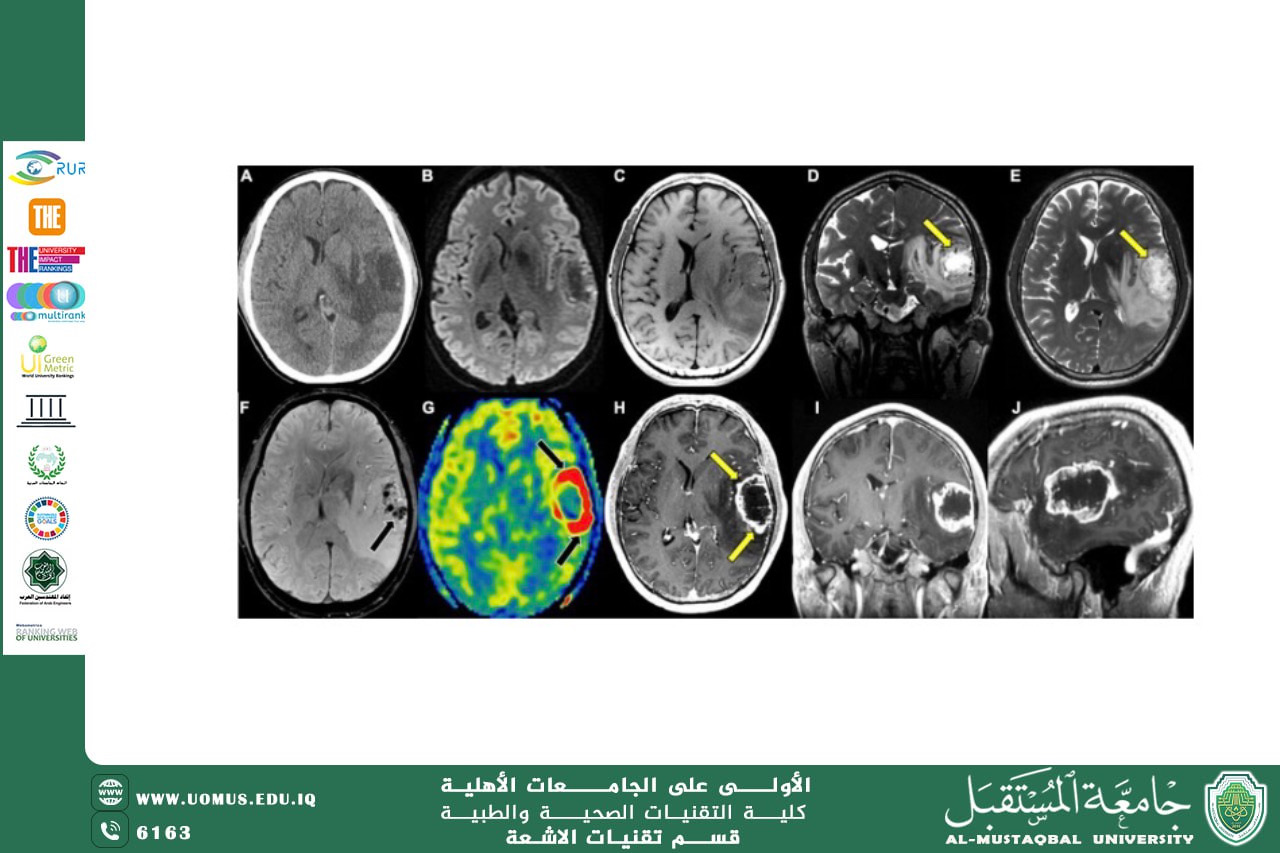
T1-weighted in brain tumor diagnosis
T1 sequencing provides detailed anatomical information about brain structure and is often used with gadolinium contrast medium to visualize tumor enhancement and boundaries. AI algorithms help analyze contrast-enhanced T1 images to accurately detect areas of abnormal enhancement, determine the extent of tumor infiltration, and differentiate between tumor and healthy tissue.
T2-weighted in edema and tumor extent assessment
T2 sequencing is highly sensitive to water content, making it ideal for detecting peritumoral edema. AI uses T2 images to determine the true extent of the tumor and analyze the relationship between tumor tissue and peritumor edema, which aids in therapeutic and surgical planning.
FLAIR in brain tumor diagnosis
FLAIR sequencing is important for suppressing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) signals, allowing for clearer visualization of lesions near the cerebral ventricles. AI algorithms combine FLAIR images with other sequencing methods to improve the detection of low-grade tumors and lesions overlapping with CSF.
DWI and ADC Maps in Histological Distinction
Diffusion sequencing (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps are used to assess the movement of water molecules within tissues. Artificial intelligence (AI) leverages this data to differentiate between high- and low-grade tumors, as well as to distinguish between a tumor and necrosis or abscess, by analyzing quantitative diffusion values.
The Importance of Perfusion MRI in Assessing Blood Visibility
Perfusion MRI provides functional information about intratumoral blood perfusion. AI algorithms use parameters such as CBV and CBF to analyze the degree of blood vascularization, which helps determine tumor malignancy and monitor response to radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Multiparametric MRI and AI Integration
The integration of different MRI sequences is one of the most significant advantages of AI, as intelligent models enable the simultaneous analysis of multiparameter data. This integration leads to improved tumor classification accuracy, more reliable prediction of tumor biological behavior, and more reliable clinical decision support.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its significant benefits, artificial intelligence (AI) applications face challenges related to standardizing imaging protocols and data quality. However, the continued advancement of AI and MRI technologies is expected to contribute to more accurate and personalized brain tumor diagnosis.
Conclusion
The integration of AI with various MRI sequences represents a fundamental advancement in brain tumor diagnosis, contributing to improved diagnostic accuracy, more precise tumor characterization, and support for comprehensive, multidimensional medical decision-making.
Prepared by: Dr. Mohannad Ahmed Sahib
Department of Radiology Technology