A Scientific Article by Ms. Zahraa Ubais entitled: Candida albicans as an Opportunistic Pathogenic Fungus
Candida albicans
Introduction
Candida albicans is a type of yeast (fungus) that normally lives in small amounts on the human body, such as in the mouth, gut, and skin. Under certain conditions, it can grow excessively and cause infections known as candidiasis.
Classification
• Kingdom: Fungi
• Phylum: Ascomycota
• Genus: Candida
• Species: Candida albicans
Characteristics
Candida albicans has several important characteristics:
• It is a unicellular yeast
• Reproduces by budding
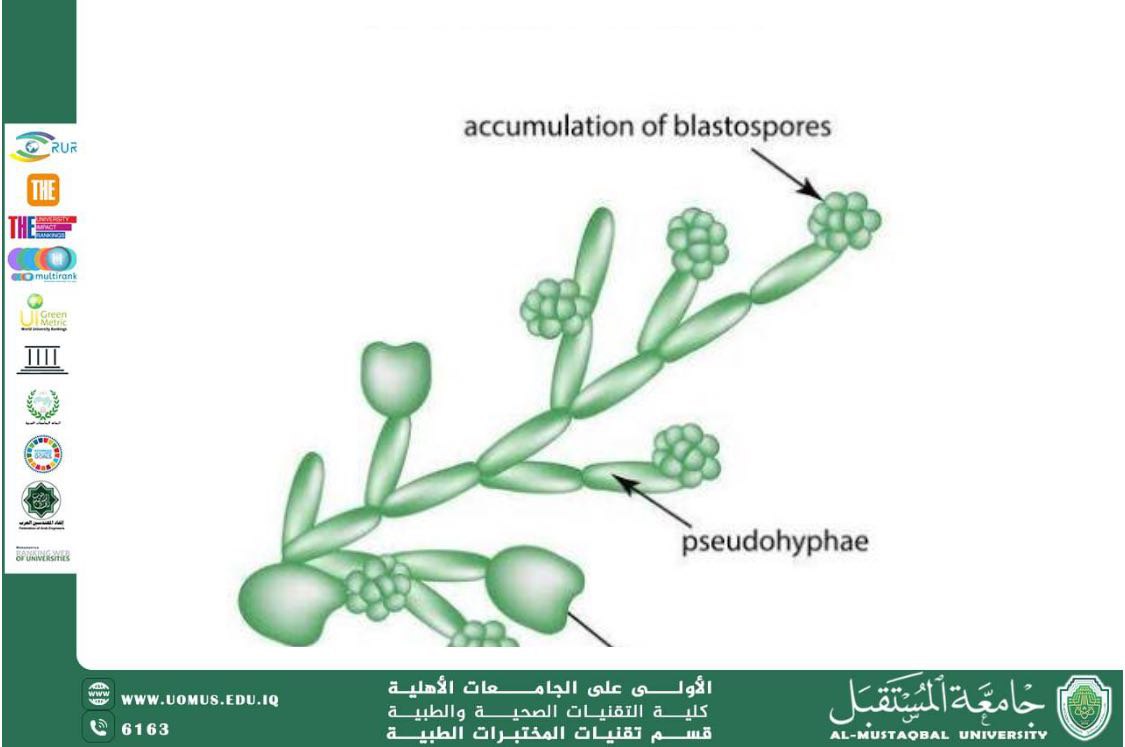
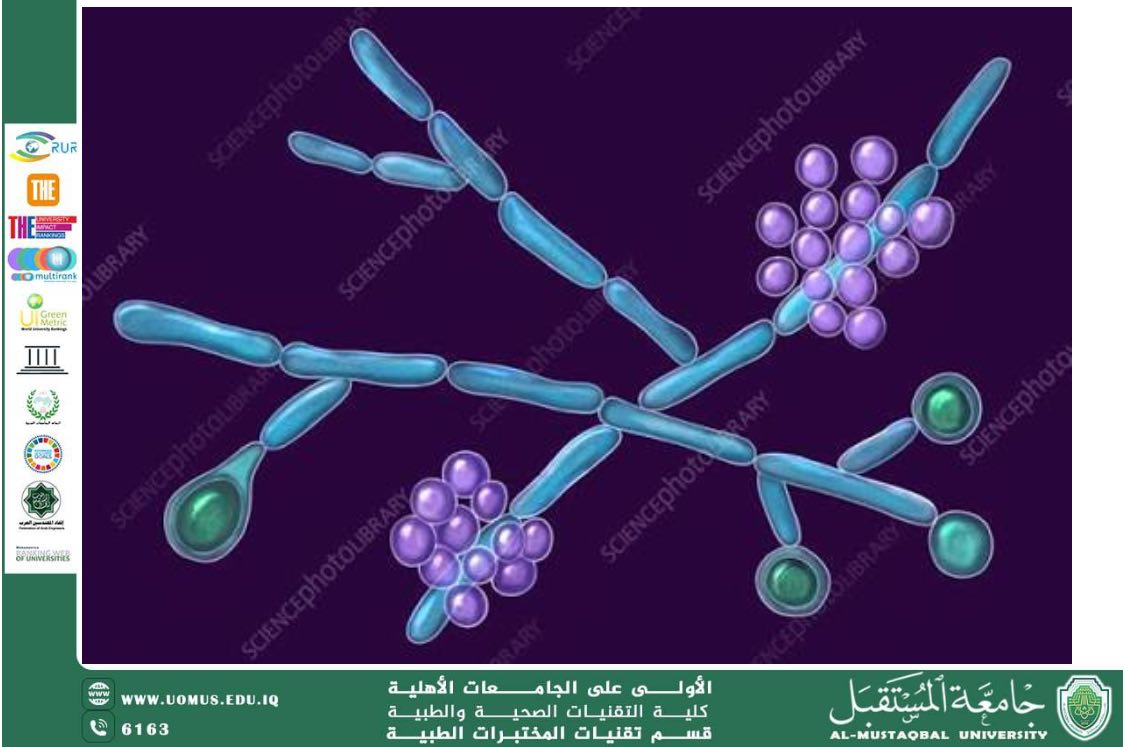
• Can form pseudohyphae and true hyphae
• Grows well in warm, moist environments
• Appears as smooth, creamy colonies on culture media
Habitat
This fungus is commonly found as part of the normal human microbiota, especially in the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and vagina.
Medical Importance
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogen. Overgrowth may occur due to:
• Weakened immune system
• Prolonged use of antibiotics
• Diabetes mellitus
• Poor hygiene
It can cause oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections, and systemic infections in severe cases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on:
• Microscopic examination
• Culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar
• Germ tube test (positive for Candida albicans)
Treatment
Treatment includes antifungal drugs such as:
• Nystatin
• Fluconazole
• Clotrimazole
Conclusion
Candida albicans is a common fungus with both harmless and harmful roles. Proper hygiene and medical care help prevent serious infections caused by this organism.
Al-Mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq
Department of Medical Laboratory Techniques – First in the Iraqi National Ranking.