An Article Titled: “The Future of Cybersecurity in the Era of the Internet of Things (IoT)” By Programmer Sara Faeq Ali
The world is undergoing an unprecedented digital transformation driven by the Internet of Things (IoT), as smart devices have become an integral part of daily life and modern work environments. This massive expansion of digital connectivity brings complex security challenges, making cybersecurity a critical component for ensuring system continuity and data protection.
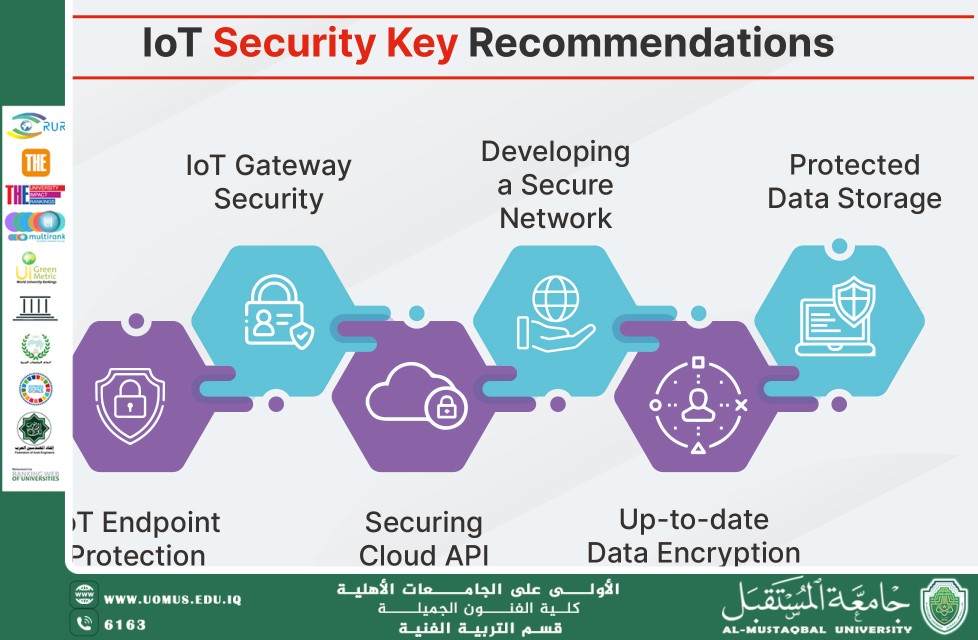
The Rapid Expansion of IoT and Its Security Impact
The number of IoT devices is expected to exceed tens of billions in the coming years. This enormous growth leads to a significant increase in data exchange and, consequently, more opportunities for cyberattacks. Attacks are no longer limited to data theft; they now aim to disrupt services, conduct industrial espionage, and even impact critical infrastructure such as energy, water, and transportation systems.
Types of Cyberattacks Associated with IoT
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: Exploiting compromised IoT devices to form large botnets.
Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting manufacturers or software providers to gain access to devices.
Cyber-Physical Attacks: Manipulating smart devices to cause real-world damage.
Data Espionage and Surveillance: Exploiting devices to monitor users without their knowledge.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Securing IoT Environments
As attacks become more sophisticated, artificial intelligence has become a key tool in cyber defense by:
Analyzing device behavior and detecting abnormal patterns
Predicting attacks before they occur
Enabling automated incident response
Reducing reliance on human intervention
Cybersecurity from a Design and Regulatory Perspective
One of the most important future trends is integrating cybersecurity into IoT device design from the outset rather than adding it later. Laws and regulations also play a crucial role in requiring companies to implement clear security standards and protect user privacy, especially in sensitive sectors such as healthcare and smart cities.
Future Challenges
Despite continuous advancements, several challenges remain, including:
A shortage of skilled professionals in IoT security
Inconsistent security standards among manufacturers
Difficulty managing and securing large, complex systems
Balancing ease of use with strong security measures
Future Outlook
The future of cybersecurity in IoT environments is moving toward:
Unified security platforms for managing thousands of devices
Wider adoption of advanced encryption techniques
International cooperation to combat cross-border cyber threats
Increased cybersecurity awareness among individuals and organizations
Conclusion
The Internet of Things represents a powerful technological revolution, but it also carries significant responsibilities. Investing in cybersecurity is no longer optional—it is a fundamental necessity for ensuring a safe and sustainable digital future....Almustaqbal University, The First University in Iraq.