م.م دعاء ساهي حسونEsophagus
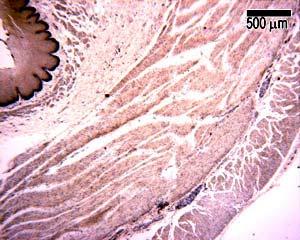
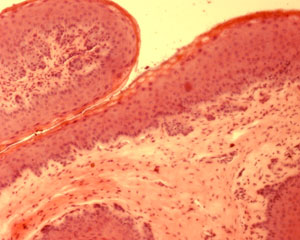
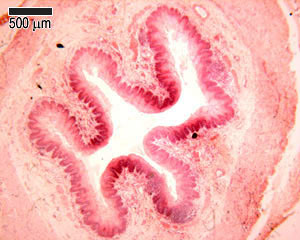
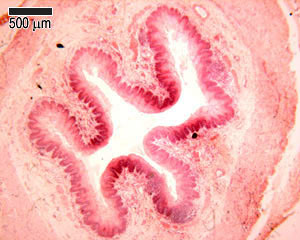
Function of the Esophagus<br />The esophagus is a muscular tube through which food is carried from the pharynx to the stomach. Like the rest of the lining of the GI tract, it has to be protective, as it is open to the outside. The esophagus also has to accommodate a wide variety of food and drink (hot, cold, spicy etc).<br />Swallowing if voluntary, and involves the skeletal muscles of the oropharynx. After this a strong peristaltic reflex coveys the food or drink to the stomach. This usually only takes a few seconds.<br />At the junction with the stomach (esophago -gastric junction), there is a sphincter, which usually prevents reflux or regurgitationThis photograph shows a transverse section of the esophagus at low power, so you can see almost all of the whole esophagus,<br /> including its four layers: - mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and adventitia. these four layers, and the lumen of the esophagus.<br />The esophagus has a folded appearance. When swallowing food, it is able to distend, and accommodate the food being swallowed on its way to the stomach.This photograph shows the lining epithelium of the esophagus at high power<br />Just like the epithelium lining the skin, the basal layer is a layer of dividing cells, which proliferate and constantly move upwards, continuously replacing the lining of the epithelium.<br />Make sure you can identify pyknotic cells at the lumen, and the layer of dividing cells in the photograph on the left hand sidethe mucosa consists of the epithelium, underlying lamina propria and muscularis mucosa.<br />The lamina propria contains lymphatic capillaries, blood capilaries, and loose connective tissue. The darkly staining cells in the lamina propria are lymphoid aggregations (see the topic on lymphoid tissue to know more).<br />The muscularis mucosa is a thin, double layer of smooth muscle, more substantial in the lower part of the esophagus.The submucosa is highly vascular, and contains loose connective tissue. It contains esophageal glands, that secrete mucus to help ease the passage of swallowed food.<br />The muscularis externa layer in the top third of the esophagus contains skeletal muscle, in the middle, it is a mixture of smooth and skeletal muscle, and in the bottom third it is entirely smooth.<br /><br /><br /><br /><br />