The Benefits And Harms Of Bacterial Resistance To Antibiotics
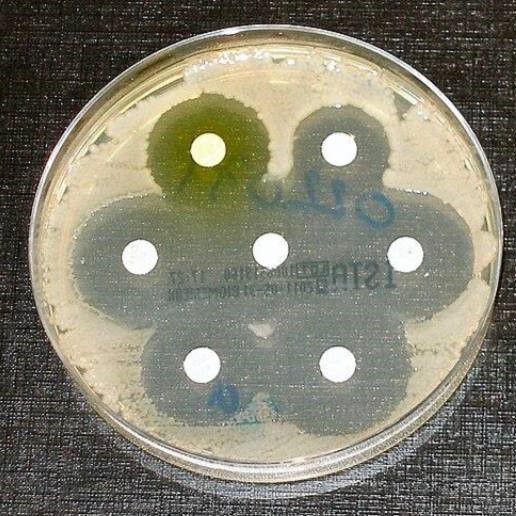
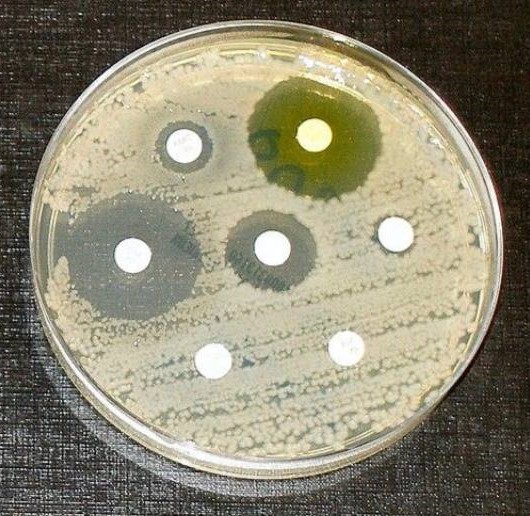
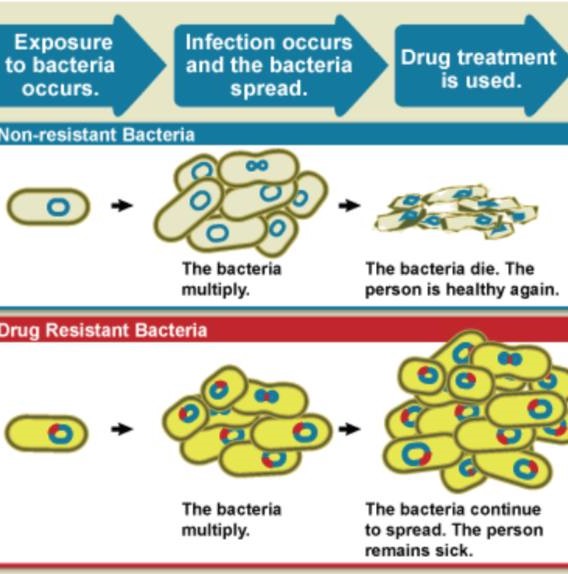
1.1.Introduction<br /> Antibiotic Resistance is the ability of bacteria to expand mechanisms that allow them to resist the effects of antibiotics. Antibiotic resistant microorganisms are characterized by the fact that they are hard to handle, want better doses, or are willing to move on to alternative treatments that may be more toxic and more expensive. Antibiotic-resistant microorganisms are called multi-resistant because all types of microorganisms expand this ability to resist. Fungi expand resistance to antifungal<br /> agents, viruses grow resistance to antiviral agents and protozoa grow resistance against protozoa and in the same way microorganisms increase resistance to antibiotics. Resistance arises either as a result of genetic mutations or as a result of transmission from one gender that has acquired resistance to another that has not received it. Resistance may appear immediately due to genetic mutations, but long- term use of antibiotics appears to stimulate the emergence of mutations specifically in resistance-inducing genes. Therefore, there is an urgent need to reduce misuse of antibiotics by using them most effectively when they are most needed.[1] Slighter-spectrum antibiotics are preferred over extensive-spectrum because the earlier target of the microorganism responsible for the disease is more effective, not to mention the fewer facet results. For sufferers who are taking these drugs at home without consulting a doctor, it is very important to teach them the proper way to use them. Health workers can help reduce this burden by following standard hygienic<br /> and medical sterilization procedures, the most important of which is to carry out routine hand washing and encourage sufferers, their family and friends to do the same. Bacteria can also be engineered by applying evolutionary stress on a group of microorganisms. A new gene is shaped and bacteria are able to transfer genetic information in a horizontal manner (between microorganisms), via plasmid alternative (circular DNA) to other microorganisms. If a bacterium has multiple<br /><br /> resistance genes, it is known as a multidrug resistant bacterium or in every language as a superior bacterium.<br /><br />Bacteria, are streaked on dishes with, white disks, each impregnated with a distinct antibiotic. Clear jewelry, which include those at the left, display that micro organism have now not grown<br />1.2.Definition<br />The World Health Organization defines antimicrobial resistance because the resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics, that can deal with infections resulting from those microorganisms. [2] Neither men nor women can expand immunity to antibiotics. Resistance is a assets of microorganisms, no longer of human beings or other organisms they infect. All sorts of microorganisms can increase drug resistance. Therefore, there's resistance to antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals and antiparasitics. Antibiotic, resistance is a subset of antimicrobial resistance. Since this extra particular resistance is associated with bacteria, it's also divided into subgroups: microbiological, resistance and medical resistance. Microbial resistance is the maximum commonplace phenomenon and results from mutations or inherited<br /> <br /> genes that permit microorganisms, to face up to the microbial killing mechanisms associated with a few antibiotics. Clinical resistance manifests itself within the failure of numerous therapeutic techniques, with bacteria at hazard from remedy usually growing resistance after surviving the results of remedy. In both instances of acquired resistance, microorganisms can bypass the genetic trigger for resistance through horizontal genetic switches for conjugation, transduction, or transformation. This can result in the spread of resistance to the equal form of pathogen, or perhaps similar bacterial pathogens.<br /><br />1.3.The benefits and harms of bacterial resistance to antibiotics. <br />1. Survival advantage: Bacteria that develop resistance to antibiotics have a survival gain over non-resistant bacteria. They are much more likely to<br /> <br />survive and multiply within the presence of antibiotics, allowing them to continue causing infections.[6]<br />2. Natural defense mechanism: Resistance is a herbal defense mechanism of micro organism in opposition to antibiotics. Bacteria can increase resistance via genetic mutations or through obtaining resistance genes from different micro organism via horizontal gene switch. This mechanism helps bacteria live on in challenging environments.<br />1.3.2. Harms of bacterial resistance to antibiotics:<br />1. Limited treatment alternatives: The maximum sizeable harm of bacterial resistance is that it limits the effectiveness of antibiotics. As bacteria end up proof against multiple antibiotics, it will become more hard to treat infections due to these resistant strains. This can result in longer and extra extreme infections, extended mortality prices, and higher healthcare prices.<br />2. Increasedmorbidityandmortality:Bacterialresistancecanbringaboutextended illness, multiplied severity of [9] infections, and higher charges of remedy disasters. In some cases, there can be no appropriate antibiotics to be had to deal with certain infections, which could cause higher morbidity and mortality quotes.<br />3. Complications in scientific strategies: Bacterial resistance can pose complications in various scientific methods that require the prevention or remedy of infections. For example, resistant micro organism can result in surgical website online infections, pneumonia, or urinary tract infections in hospitalized patients, making it greater challenging to perform approaches properly.<br /><br />4. Spread of resistance genes: Bacteria can transfer resistance genes to different micro organism, even the ones belonging to extraordinary species, through horizontal gene transfer. This spread of resistance genes contributes to the fast unfold of resistance within bacterial populations, making it harder to govern and deal with infections.<br />5. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics: The improvement and unfold of bacterial resistance are greatly prompted through the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. Inappropriate or pointless antibiotic use, along with while prescribed for viral infections, promotes the choice and proliferation of resistant micro organism.<br /><br />1.4.Causes<br />Antibiotic resistance is caused specifically by the overuse or misuse of antibiotics. This is due to the development of defense mechanisms against the capsules that microorganisms fight against and the fact that certain signatures of microorganisms that are naturally resistant to antimicrobials are more widespread than microorganisms that can be easily treated with drugs. It leads to the existence of. fought. Although antimicrobial resistance has clearly been emerging for many years, the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance is increasing due to its use by antimicrobial marketers within healthcare organizations and other growing environments.<br />1.4.1.Natural occurrence<br />The constant promotion of antibiotics clearly has the potential for antibiotic resistance to develop. Natural ,choice manner, that organisms that can adapt to their environment live to tell their own story and preserve it for their offspring. As a result, with the help of some antibiotic marketers , the types of microorganisms ,that can survive over, time ,even under sustained attack are increasing in the environment and ,among non-resistant populations. It is clear that it is becoming more and more popular. <br /><br />