Glass Manufacturing: A Step-by-Step Guide
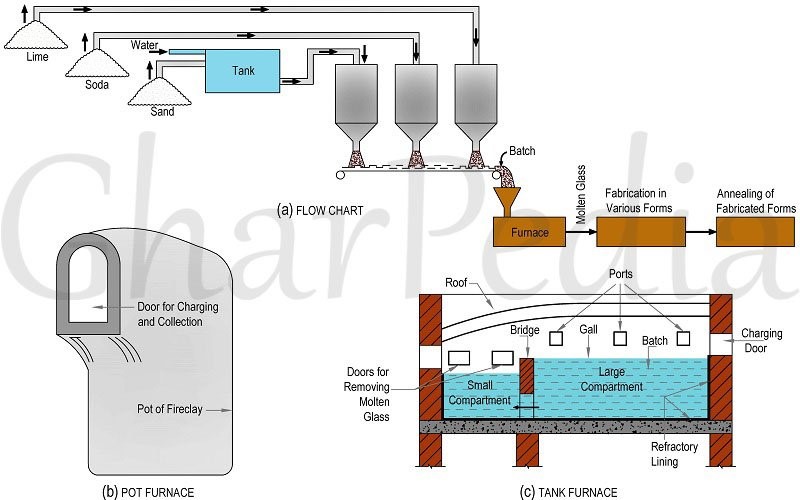
Malik Mustafa Mohammed, Head of the department.<br />Glass Manufacturing: A Step-by-Step Guide<br />Glass manufacturing is a fundamental industry with applications spanning construction, automotive, electronics, and household items. To understand how glass is produced, let's delve into its manufacturing stages:<br />1. Raw Material Preparation: The process begins with preparing the essential raw materials:<br />o Sand (silica): The primary component of glass. Higher purity leads to better quality glass.<br />o Sodium carbonate (soda ash): Reduces the melting point of sand, saving energy during the melting process.<br />o Calcium carbonate (lime): Enhances the chemical and physical properties of glass, such as durability and scratch resistance. These materials are weighed and mixed in specific proportions to create the desired glass mixture. Purity is crucial for a high-quality end product.<br />2. Melting Process: This is a critical stage where the glass mixture is heated in special furnaces to approximately 1700 degrees Celsius. The mixture melts and undergoes chemical reactions, forming molten glass.<br />3. Shaping: Once molten, the glass is shaped into desired forms using various techniques such as blowing, drawing, and molding. The temperature of the molten glass must be carefully controlled to ensure easy shaping without solidification.<br />4. Cooling (Annealing): To prevent cracks and internal stress, the shaped glass is cooled gradually in annealing furnaces. This process ensures even heat distribution and improves the glass's quality and durability.<br />5. Quality Control and Analysis: Rigorous testing is conducted to assess the glass's transparency, mechanical strength, heat resistance, and other properties. Any defects are analyzed to improve future production processes.<br />Analysis and Additional Insights<br />• Key raw materials: Sand, soda ash, and lime form the foundation of glass.<br />• High-temperature process: The melting process requires extremely high temperatures.<br />• Diverse shaping techniques: Glass can be transformed into a wide range of products using various techniques.<br />• Importance of annealing: Controlled cooling is essential for preventing defects.<br />• Quality control: Testing ensures the final product meets specific standards.<br />Potential Areas for Further Exploration<br />• Types of glass: Different types of glass (e.g., soda-lime glass, borosilicate glass) have varying compositions and properties, suitable for different applications.<br />• Glass recycling: The environmental impact of glass production and the importance of recycling glass.<br />• Historical development: The evolution of glassmaking techniques and the historical significance of glass in various cultures.<br />• Advanced glass technologies: Modern advancements in glass manufacturing, such as tempered glass, laminated glass, and specialty glasses for specific applications.<br />Dhirar Salim Mohammed. Chemical engineer.<br />