Towards a Circular Economy: Reducing Waste and Promoting Sustainability
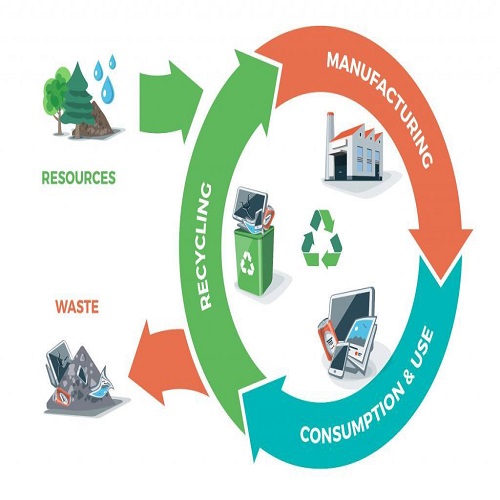
<br />Introduction<br />Our planet currently faces severe environmental challenges due to escalating pressure on natural resources, driven by excessive consumption and waste production. These pressures contribute to environmental degradation, impacting climate change, resource depletion, and ecosystem decline. This situation calls for adopting radical solutions. The circular economy presents a promising sustainable approach, founded on the principle of "reduce, reuse, and recycle" as an alternative to the traditional linear "use and dispose" model (Geissdoerfer et al., 2017). This article aims to offer a comprehensive overview of the circular economy's concept, importance, and strategies, alongside the challenges and benefits associated with its implementation to achieve a more sustainable economy.<br />The Concept and Importance of the Circular Economy<br />The circular economy is an innovative economic model designed to retain materials and resources within production cycles for as long as possible through the reuse of products and recycling of materials. This approach is based on principles that aim to reduce unsustainable consumption and production, including:<br />Reducing Resource Consumption: Preserving materials and recycling them limits the need for new resource extraction (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, 2019).<br />Minimizing Waste: Recycling enables a significant reduction in waste accumulation.<br />Supporting Sustainable Economic Growth: The circular economy enhances production efficiency and strengthens local economies, as waste can be reused as new resources rather than discarded.<br />Circular Economy Strategies for Reducing Waste<br />Several strategies can be applied within the circular economy framework to reduce waste, including:<br />1. Circular Design: Redesigning products to be recyclable and renewable, making them easier to disassemble and reuse, which helps reduce waste accumulation.<br />2. Industrial Recycling: Transforming waste into raw materials that can be reused across various production processes.<br />3. Extending Product Lifespan: Developing maintenance and repair techniques that reduce the need to continually manufacture new products.<br />4. Utilizing Renewable Resources: Focusing on renewable materials that can be innovatively and multiply recycled.<br />5. Cross-Sector Collaboration: The circular economy requires extensive cooperation among sectors, including both public and private sectors, to develop suitable recycling infrastructure and facilitate circular practices.<br />Global Applications of the Circular Economy<br />Many countries have adopted successful circular economy applications aimed at increasing efficiency and reducing waste. Among these applications are:<br />Electronic Waste Recycling: For instance, Apple reuses recycled metals in its modern devices to help reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste (Geissdoerfer et al., 2017).<br />Circular Fashion Industry: Some fashion brands have adopted the practice of reusing old fabrics to create new clothing, contributing to a reduction in the depletion of natural resources like cotton and water (Ghisellini, Cialani, & Ulgiati, 2016).<br />Agricultural Waste Management: In several countries, agricultural crop residues are used as raw materials for producing organic fertilizers or bioenergy, reducing waste and achieving multiple environmental benefits (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, 2019).<br />Benefits of the Circular Economy<br />The circular economy brings several environmental and economic benefits, including:<br />1. Reducing Carbon Emissions: The circular economy reduces the need for new resource extraction, which decreases emissions contributing to climate change.<br />2. Supporting Local Economies: The circular economy creates new job opportunities in recycling, maintenance, and remanufacturing fields, and can also reduce raw material costs, enhancing local companies' competitiveness.<br />3. Ensuring Environmental Security: Adopting a circular economy makes resources more sustainable, ensuring the protection and sustainability of ecosystems for future generations.<br />Challenges Facing the Circular Economy<br />Despite its many benefits, the circular economy faces challenges that may hinder its widespread implementation. Key challenges include:<br />High Initial Costs: The transition to a circular economy may require significant investments in developing technology and adjusting production lines to meet new standards.<br />Need for Regulatory and Policy Development: Circular economy initiatives need government support through suitable policies and regulations to encourage organizations to adopt circular practices.<br />Limited Awareness: In some communities, limited awareness may act as a barrier to embracing circular economy principles, necessitating greater efforts to shift traditional consumption patterns.<br />Conclusion<br />The circular economy represents a crucial approach for balancing economic growth and environmental sustainability. By adopting practices that prioritize reuse and reduce consumption, we can move toward a more sustainable economic system that conserves resources and limits pollution. The success of this transition relies on the commitment of individuals, companies, and governments to implement circular economy principles, with a focus on education, raising awareness, and enhancing necessary infrastructure.<br /><br /> م.م عمار بدري يونس خضير<br /><br />References<br />Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2019). Circular Economy: A vision for a circular economy for plastic.<br />Ghisellini, P., Cialani, C., & Ulgiati, S. (2016). A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. Journal of Cleaner Production.<br />Geissdoerfer, M., et al. (2017). The circular economy – A new sustainability paradigm? Journal of Cleaner Production.<br /> <br />