" Automatic Recognition System of Body Activities in Smartphones Using Hybrid Deep Learning " hasan faez abdulhussein
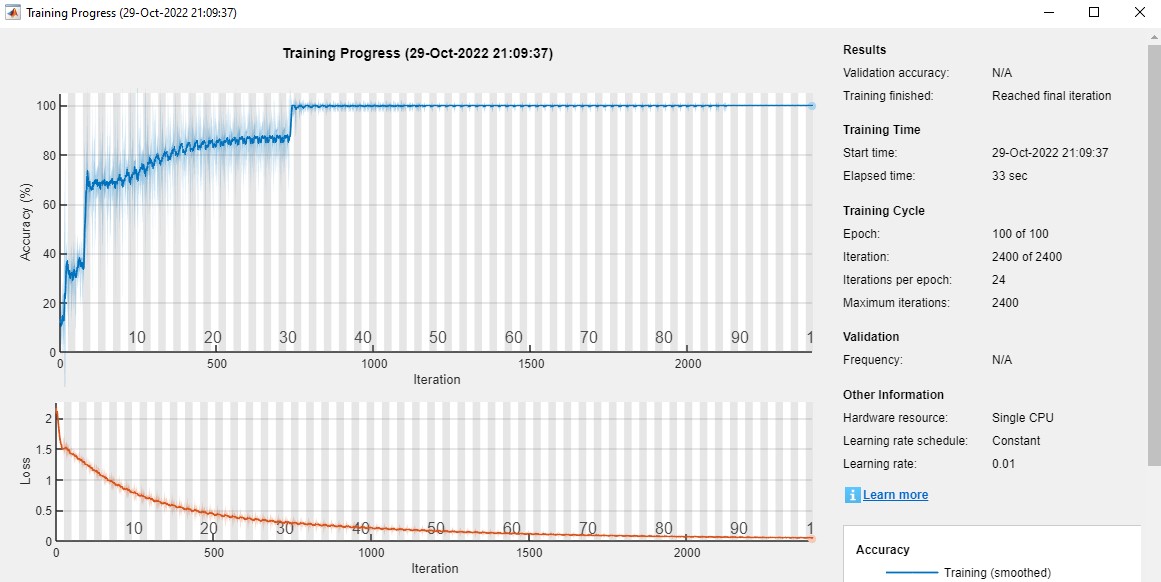
Human activity recognition from video frames or still images is a challenging task due to problems such as background clutter, <br />partial occlusion, change in scale, viewing angle, lighting, and appearance. Many applications, including video surveillance systems, <br />human-computer interaction, and robotics to describe human behavior, require a multiple activity recognition system. In this work, <br />we presented a classification scheme for five types of human activities based on hybrid deep learning. The data of this work was collected <br />from the sensors of users' smartphones. The NCA feature selection scheme was used to reduce the dimensions of the data, and further, CNN and <br />LSTM deep networks were used in series to learn spatial and temporal features and classify human activities. The proposed method achieved <br />an overall accuracy of 98.5% in detecting body activities for five different types of activities.<br /><br />Introduction<br /><br />Human Activity Recognition (HAR) employs computer systems to identify human activities using various sensors, such as image sensors, <br />sound sensors, and accelerometers. Its applications span healthcare for disabled individuals, sports analytics, smart homes, and <br />medical care. This thesis introduces a hybrid deep learning approach integrating CNN and LSTM for effective recognition of human <br />activities through smartphone sensors. With growing urbanization, HAR's role in smart cities for health monitoring and sustainable <br />living is becoming increasingly significant.<br />Deep Learning<br />Artificial neural networks are used in deep learning to perform complex calculations on huge amounts of data. Learning is a subset of machine learning that is based on how the human brain is organized and functions. <br />Deep learning techniques train computers using examples to learn. Deep learning is often used in sectors such as healthcare, e-commerce, leisure and advertising.<br /><br /><br /><br /><br />Proposed Methodology<br /><br />The proposed system utilizes smartphone sensor data to classify human activities using a hybrid deep learning model. Key steps include:<br />1. **Data Preprocessing**: Normalization and division into training and test sets.<br />2. **Feature Selection**: Using the Neighborhood Component Analysis (NCA) algorithm to enhance classification accuracy.<br />3. **Deep Learning Architecture**: Combining CNN layers for spatial features and LSTM layers for temporal sequences.<br />4. **Evaluation**: Testing on unseen data to achieve robust results.<br /><br /><br /><br />Results and Discussion<br /><br />The proposed method achieved an accuracy of 98.54% on test data. Simulation results demonstrated the effectiveness of the hybrid deep <br />network in accurately identifying five distinct human activities. Compared to baseline approaches, the CNN-LSTM model showed enhanced <br />performance in processing spatial and temporal features, validated by confusion matrices and evaluation metrics. <br /><br />Conclusion and Future Work<br /><br />This study presented a hybrid CNN-LSTM approach with NCA for feature selection, achieving high accuracy in human activity recognition. <br />Future work may involve extending the database, incorporating additional sensors, and optimizing neural network parameters using <br />meta-heuristic algorithms.<br /><br />Theoretical Background<br /><br />Deep learning has revolutionized human activity recognition by leveraging large datasets and powerful neural networks. <br />This study employs a hybrid model combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTMs). <br /><br />1. **CNNs**: These are designed to extract spatial features from data, such as patterns in accelerometer or gyroscope signals.<br />2. **LSTMs**: These recurrent neural networks are tailored for temporal data, enabling the system to understand sequences of human activities.<br />3. **Neighborhood Component Analysis (NCA)**: This algorithm reduces dimensionality by selecting the most relevant features, <br /> enhancing model performance and computational efficiency.<br /><br />By combining these techniques, the proposed method offers superior accuracy and robustness.<br /><br />Challenges and Limitations<br /><br />Despite its high performance, the proposed method faces several challenges:<br />1. **Sensor Variability**: Different smartphone models have varying sensor precision, affecting data consistency.<br />2. **Environmental Noise**: External factors like magnetic interference or inconsistent lighting can impact accuracy.<br />3. **Scalability**: Expanding the model to recognize more activities or integrate additional .<br />