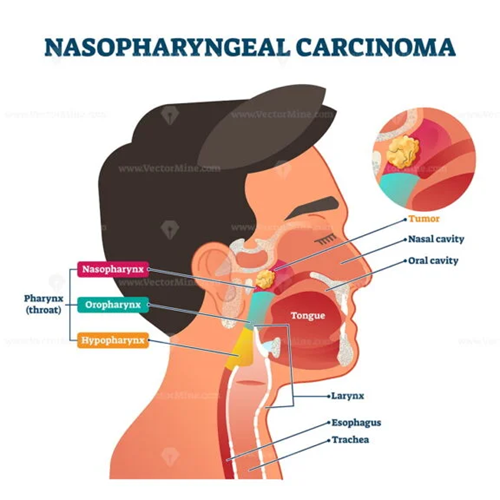
Scientific article by Dr. Ali Hussein Hamza Al-Nasrawi Otorhinolaryngologist and laser specialist entitled (Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma)
Based on recent research and guidelines published after 2023, the treatment landscape for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) in the Middle East continues to evolve. Here's an updated overview of causes and treatment options:<br />Causes of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma<br />The etiology of NPC remains multifactorial, with key risk factors including:<br />- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, which remains a significant risk factor, particularly in endemic regions[1].<br />- Genetic predisposition, especially in populations with higher incidence rates[1].<br />- Environmental factors, including exposure to certain chemicals and consumption of preserved foods[1].<br />Current Treatment Approaches:<br />A- Radiotherapy and Chemoradiotherapy<br />Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) continues to be the cornerstone of treatment for NPC, especially for early-stage disease[1]. For more advanced cases,, concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) is the standard of care, with platinum-based regimens being the most common[1].<br />B-Chemotherapy<br />For advanced stages:<br />- Induction chemotherapy may be used before CCRT to shrink tumors[1].<br />- Adjuvant chemotherapy following CCRT is sometimes employed, though its use is becoming more selective based on risk factors[1].<br />C-Immunotherapy<br />Recent advancements include:<br />- The approval of toripalimab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, for recurrent or metastatic NPC. When combined with chemotherapy, it has shown promise in extending progression-free survival[3].<br />- Ongoing trials are exploring the use of immunotherapies like pembrolizumab and nivolumab in various treatment settings for NPC[3].<br />Surgery<br />While not typically a first-line treatment, surgery may be considered for:<br />1-- Resectable local recurrences<br />2-- Removal of cancerous lymph nodes in the neck[4]<br />Personalized Treatment Approaches Emerging trends include:<br />- Risk classification based on plasma EBV-DNA levels to guide treatment decisions[1].<br />- Development of personalized treatment strategies, considering individual patient factors and tumor characteristics[1].<br />Conclusion:<br />Treatment for NPC in the Middle East continues to advance, with a focus on combining established modalities like chemoradiotherapy with newer approaches such as immunotherapy. Ongoing research and clinical trials are likely to further refine treatment strategies, potentially improving outcomes for patients with this challenging disease.<br /><br />Citations:<br />[1] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9480178/<br />[2] https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/ear-nose-and-throat-disorders/tumors-of-the-head-and-neck/nasopharyngeal-cancer<br />[3] https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/head-and-neck-cancer/types/nasopharyngeal-cancer<br />[4] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nasopharyngeal-carcinoma/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20375535<br />[5] https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/nasopharyngeal-cancer/treatment/decisions<br />[6] https://actchealth.com/blogs/a-comprehensive-guide-to-nasopharyngeal-cancer-symptoms-and-treatment<br />[7] https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2024/fda-toripalimab-nasopharyngeal-cancer<br />[8] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/nasopharyngeal-cancer/<br />