The Nagative Effect of LASER Radiation on human body Blood Viscosity BY PH.D Raad Shaker Alnayli
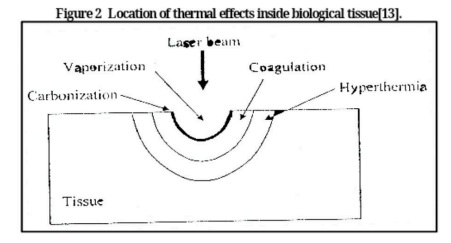
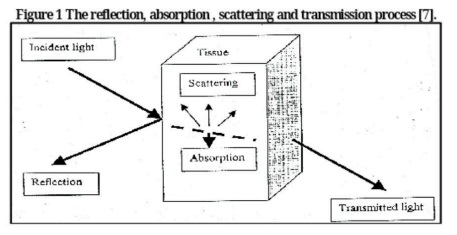
During the last three decades of the twentieth century, it has been found out useful<br />applications of laser rayin the elds of medicine, surgery, ophthalmology, industry, automatic<br />control, communications, chemistry andthe like. To this point, laser became a tool that is used<br />to treat the serious disease (cancer) by using photic-dynamictreatment, where a sensitive<br />substance of light is injected into the injured body and then laser with wave length of630 nm<br />can be used for the sake of making chemical reaction that produces poisonous substance to<br />kill tumors.Laser can also be used in sterilization of blood in blood bank which puries blood<br />from bacteria and virouses.[1-9]<br />The Action of Tissue on Laser<br />The Action of Tissue on Laser LightWhen a laser beam is an incident on a tissue, four basic<br />.physical phenomena can occur as shown in gure I<br />Reection and refraction, Absorption, Scattering and Transmission , and<br />The relative and absolut emagnitudes of these phenomenathe wavelength of the laser light<br />and the physical phenomenous drprnd on the eave length of the lasrrsnd the properties of the<br />. tusses<br />The Effect of Laser on Bio substance<br />When the laser light is absorbed by a bio substance ( a tissue, bacterial suspension, ...etc.) it<br />can result indifferent types of effects depending on the wavelength of the laser radiation, power<br />.density, pulse duration, andthe nature of the bio substance<br />Laser effects on the bio substance can be classied according to their wavelengthdependency<br />to wavelength dependent and wavelength independence<br />I.Photochemical interaction<br />At low laser intensities, irradiation of cells at certain wavelength can activate some of the native<br />componentsin bio substance. In this way specic biochemical reactions, as well as whole<br />cellular metabolism can be altered.This reaction is believed to form the basis of low power<br />laser effect (bio stimulation) Photochemical ablationinvolves photo dissociation or direct<br />breaking of intramolecular bonds in biopolymers, caused by absorption oncident photons and<br />subsequent release of bio substance[10]. This occur when the energy of the incident photonis<br />of the order of the bonding energy of a biomolecules then chemical decomposition occurs<br />leading to productsoccupying rapidly a volume larger than the initial one forming the ablation<br />.process[11, 12]<br />II Photo thermal interaction<br />The term thermal interaction refers for a large group of interaction type, where the increase<br />local temperatureis the signicant parameter change. Thermal effects can be induced by either<br />CW or pulsed laser radiation. At60oC, denaturation of proteins and collagen occurs which<br />leads to coagulation of tissue and necrosis of cell. At100oC, water molecules contained in<br />.most tissues start to vaporize<br />The large vaporization heat of water isadvantageous, since the vapor generated carries away<br />excess heat and helps to prevent any increase in thetemperature of adjacent tissue. Due to the<br />large increase in volume during this phase transition, gas bubbles arefound inducing<br />.mechanical ruptures and thermal decomposition of tissue fragments<br />At temperatures exceeding150oC, carbonization takes place which is observable by the<br />.blackening of adjacent tissue and the escape of smoke<br />.To avoid carbonization, the tissue is usually cooled with either water or gas<br /> Finally, beyond 300c, melting canoccur,[13,14] depending on the target materia