Celiac disease
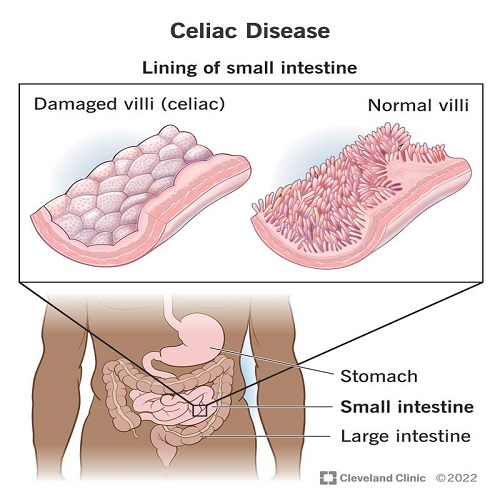
Celiac disease is an illness caused by an immune reaction to eating gluten. Gluten is a protein found in foods containing wheat, barley or rye.<br />If you have celiac disease, eating gluten triggers an immune response to the gluten protein in your small intestine. Over time, this reaction damages your small intestine's lining and prevents it from absorbing nutrients, a condition called malabsorption.<br />The intestinal damage often causes symptoms such as diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating or anemia. It also can lead to serious complications if it is not managed or treated. In children, malabsorption can affect growth and development in addition to gastrointestinal symptoms.<br />There's no definite cure for celiac disease. But for most people, following a strict gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms and help the intestines heal.<br /><br />Causes<br /><br />Your genes, combined with eating foods with gluten and other factors, can contribute to celiac disease. However, the precise cause isn't known. Infant-feeding practices, gastrointestinal infections and gut bacteria may contribute, but these causes have not been proved. Sometimes celiac disease becomes active after surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, viral infection or severe emotional stress.<br />When the body's immune system overreacts to gluten in food, the reaction damages the tiny, hairlike projections, called villi, that line the small intestine. Villi absorb vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from the food you eat. If your villi are damaged, you can't get enough nutrients, no matter how much you eat.<br /><br />Risk factors<br /><br />Celiac disease tends to be more common in people who have:<br />A family member with celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis.<br />Type 1 diabetes.<br />Down syndrome, William syndrome or Turner syndrome.<br />Autoimmune thyroid disease.<br />Microscopic colitis.<br />Addison's disease.<br /><br /><br /><br />Symptoms<br /><br />The symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly. They also may be different in children and adults. Digestive symptoms for adults include:<br />Diarrhea.<br />Fatigue.<br />Weight loss.<br />Bloating and gas.<br />Abdominal pain.<br />Nausea and vomiting.<br />Constipation.<br />However, more than half the adults with celiac disease have symptoms that are not related to the digestive system, including:<br />Anemia, usually from iron deficiency due to decreased iron absorption.<br />Loss of bone density, called osteoporosis, or softening of bones, called osteomalacia.<br />Itchy, blistery skin rash, called dermatitis herpetiformis.<br />Mouth ulcers.<br />Headaches and fatigue.<br />Nervous system injury, including numbness and tingling in the feet and hands, possible problems with balance, and cognitive impairment.<br />Joint pain.<br />Reduced functioning of the spleen, known as hyposplenism.<br />Elevated liver enzymes.<br /><br />Complications<br /><br />Celiac disease that is not treated can lead to:<br />Malnutrition. This occurs if your small intestine can't absorb enough nutrients. Malnutrition can lead to anemia and weight loss. In children, malnutrition can cause slow growth and short stature.<br />Bone weakening. In children, malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can lead to a softening of the bone, called osteomalacia or rickets. In adults, it can lead to a loss of bone density, called osteopenia or osteoporosis.<br />Infertility and miscarriage.Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can contribute to reproductive issues.<br />Lactose intolerance. Damage to your small intestine might cause you abdominal pain and diarrhea after eating or drinking dairy products that contain lactose. Once your intestine has healed, you might be able to tolerate dairy products again.<br />Cancer. People with celiac disease who don't maintain a gluten-free diet have a greater risk of developing several forms of cancer, including intestinal lymphoma and small bowel cancer.<br />Nervous system conditions. Some people with celiac disease can develop conditions such as seizures or a disease of the nerves to the hands and feet, called peripheral neuropathy.<br />Treatment :<br /><br />Coeliac disease is treated by excluding foods that contain gluten from your diet.<br />This prevents damage to the lining of your intestines and the associated symptoms, such as diarrhoea and stomach pain.<br />If you have coeliac disease, you must stop eating all sources of gluten for life. Your symptoms will return if you eat foods containing gluten, and it will cause long-term damage to your health.<br /><br />Gluten-free foods <br /><br />If you have coeliac disease, you can eat the following foods, which naturally do not contain gluten:<br />most dairy products, such as cheese, butter and milk<br />fruits and vegetables<br />meat and fish (although not breaded or battered)<br />potatoes<br />rice and rice noodles<br />gluten-free flours, including rice, corn, soy and potato flour<br />Dr. danyah adil baiee