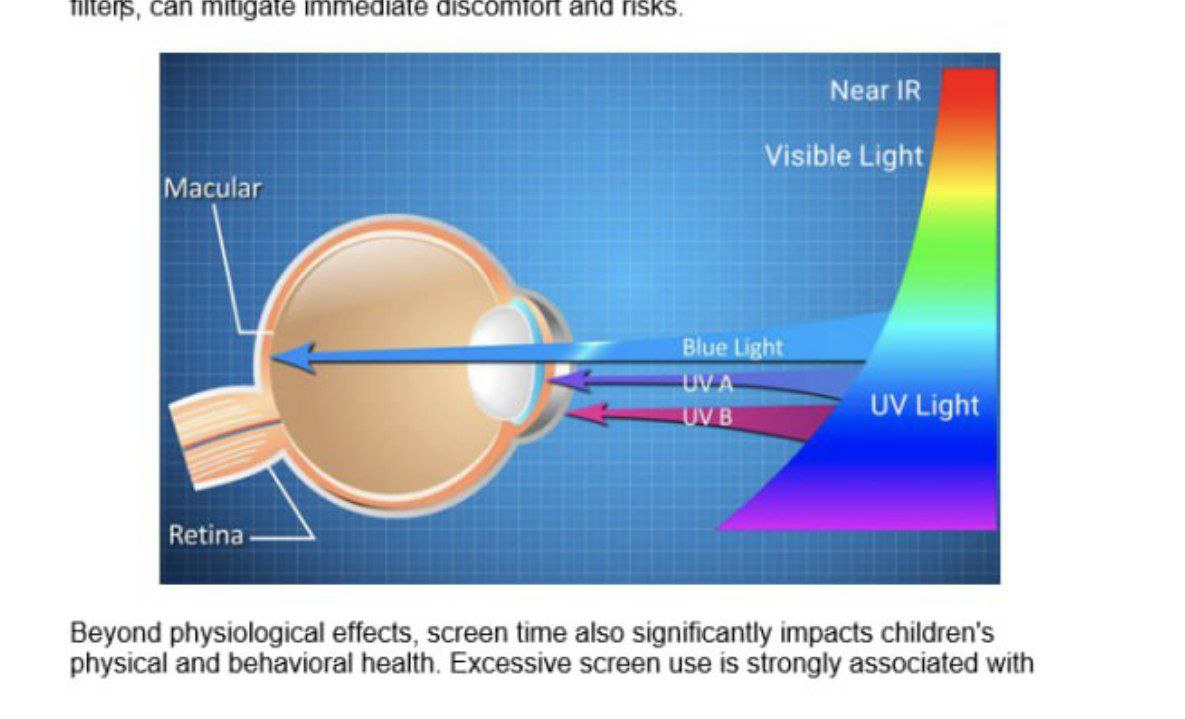
Screen Time: The Effects of Blue Light Exposure and Broader Impacts
The pervasive use of screens in modern life has raised concerns about their impact on physical and mental health. With the advent of smartphones, tablets, computers, and televisions, screen time has become a dominant activity for people of all ages. While these technologies bring many conveniences and benefits, excessive screen use poses significant health risks, particularly concerning blue light exposure, sleep patterns, eye health, and its broader implications for children, such as obesity and behavioral issues.<br /><br />One of the most studied effects of prolonged screen time is the impact of blue light exposure on sleep patterns. Blue light, a high-energy visible (HEV) light emitted by digital screens, interferes with melatonin production, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep. When exposed to blue light, especially in the evening, the body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, is disrupted. This delay in melatonin secretion can result in difficulty falling asleep, reduced sleep quality, and shorter sleep duration. Over time, poor sleep patterns contribute to a range of health issues, including fatigue, cognitive impairment, and mood disorders. For children and adolescents, whose circadian systems are more sensitive, blue light exposure at night is particularly detrimental, as it coincides with critical periods of growth and brain development.<br /><br />childhood obesity, a growing global concern. When children spend extended periods on sedentary activities like watching TV or playing video games, their physical activity levels decline, contributing to weight gain. This sedentary behavior is often compounded by snacking on high-calorie, low-nutrient foods during screen time. Furthermore, the marketing of unhealthy foods and beverages on television and online platforms reinforces poor dietary choices among children, exacerbating the risk of obesity. Reduced physical activity during screen time also leads to poorer cardiovascular health and lower overall fitness levels, which can persist into adulthood if habits are not corrected.<br /><br />Behavioral issues are another critical concern linked to excessive screen time in children. Prolonged exposure to screens, particularly unsupervised or unregulated content, can contribute to problems such as attention deficits, hyperactivity, and emotional dysregulation. Children who spend excessive time on screens may have fewer opportunities to engage in creative, unstructured play or interact with peers and family members, which are crucial for social and emotional development. Moreover, the instant gratification provided by digital media can affect children’s ability to focus and delay gratification in other areas of life, contributing to academic challenges and difficulties in forming healthy relationships. Screen addiction, characterized by compulsive use and difficulty disengaging from digital devices, further exacerbates these issues, highlighting the need for parental supervision and guidelines.<br /><br />