A Scientific Article by the Lecturer Wafa Ghaleb Jawad (The Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency)
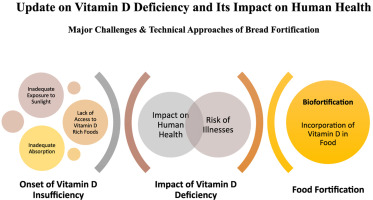
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a crucial role in <br />maintaining overall health. It is primarily obtained through sunlight exposure, certain <br />foods, and supplements. However, a deficiency in vitamin D is a common global <br />health issue that can lead to various health problems. This article explores the <br />effects of vitamin D deficiency on the human body.<br />1. Bone Health and Muscle Function<br />Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption in the gut, which is necessary for <br />strong bones and teeth. A deficiency can result in weakened bones, increasing the <br />risk of fractures and conditions such as osteoporosis. In children, it can cause <br />rickets, a condition characterized by bone deformities. Additionally, low vitamin D <br />levels may lead to muscle weakness and pain, making everyday activities more <br />challenging.<br />2. Immune System Dysfunction<br />Vitamin D plays a significant role in supporting the immune system. A deficiency <br />can weaken the body’s ability to fight infections and illnesses, making individuals <br />more susceptible to colds, flu, and other infections. Recent studies also suggest a <br />possible link between vitamin D levels and the severity of autoimmune diseases <br />such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.<br />3. Mental Health<br />Emerging research indicates that vitamin D deficiency may contribute to mental <br />health issues, including depression and anxiety. Vitamin D receptors are present in <br />areas of the brain associated with mood regulation, and insufficient levels may <br />disrupt this balance. This connection highlights the importance of maintaining <br />adequate vitamin D levels for emotional well-being.<br />4. Chronic Diseases<br />Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to several chronic diseases, including <br />cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. For example, low <br />levels of vitamin D may increase the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease. <br />Additionally, some studies suggest that maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels may <br />reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.<br />5. Risk Factors for Deficiency<br />Certain factors increase the risk of vitamin D deficiency, such as limited sun <br />exposure, darker skin pigmentation, aging, obesity, and dietary restrictions. <br />Individuals living in regions with limited sunlight or those who wear clothing that <br />covers most of their skin are particularly vulnerable.<br />6. Addressing Vitamin D Deficiency<br />To prevent and address vitamin D deficiency, individuals should aim to include <br />vitamin D-rich foods in their diets, such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and <br />egg yolks. Sun exposure, even for a few minutes a day, can significantly help <br />increase vitamin D levels. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend <br />supplements to meet daily requirements.<br />Conclusion<br />Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread but preventable health issue. By ensuring <br />adequate intake and sunlight exposure, individuals can reduce the risk of numerous <br />health problems and improve overall well-being. Public health measures and <br />awareness campaigns can further contribute to addressing this deficiency on a <br />global scale