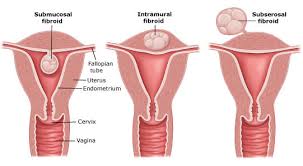
Relation between fibroid and infertility
Infertility is a disease of the reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse. Uterine fibroids are the most common tumor in women, and their prevalence is high in patients with infertility. Fibroids may be the sole cause of infertility in 2-3% of women. Depending on their location in the uterus, fibroids have been implicated in recurrent pregnancy loss as well as infertility. Pregnancy and live birth rates appear to be low in women with submucosal fibroids; their resection has been shown to improve pregnancy rates. In contrast, subserosal fibroids do not affect fertility outcomes and their removal does not confer any benefit. Intramural fibroids appear to reduce fertility, but recommendations concerning their treatment remain unclear. Myomectomy should be discussed individually with the patient; other potential symptoms such as dysmenorrhea or bleeding disorders should be included in the indication for surgery.<br />Understanding Fibroids<br />Fibroids are benign tumors on the smooth muscle of the uterus and are common among women of reproductive age, particularly those over 35 years old.Fibroids may not only impact your fertility but can cause various symptoms such as: <br />Painful cramps <br />Heavy bleeding <br />Anemia <br />Bloating <br />Constipation<br />Incontinence <br />Types of Fibroids<br />The three most common types of fibroids are:<br />1- Subserosal fibroids grow on the uterus’s outer wall into the pelvic or abdominal cavity. They are more likely to cause symptoms impacting the bladder, rectum, or intestines.<br />2- Intramural fibroids develop within the muscular layers of the uterine wall, and smaller-sized ones typically cause mild symptoms. <br />3- Submucosal fibroids grow in the innermost lining of the uterus or endometrium. They are the most likely to cause heavy menstrual bleeding. <br />Since different types of fibroids grow in various locations in or around the uterus, knowing which kind you have provides a better idea of their impact on fertility.<br /><br />The link between uterine fibroids and infertility depends on their location and growth pattern within the uterine walls. <br />Some of the ways fibroids may cause infertility include:<br />Changing the shape of your cervix so fewer sperm can enter.<br />Changing the shape of the uterus to block sperm or embryo movement.<br />Blocking your fallopian tubes.<br />Impacting the size of your uterine cavity lining.<br />Reducing blood flow to the uterine cavity so an embryo cannot be implanted.<br />Exploring treatment options, crafting a tailored birth plan, and working with medical professionals are necessary when handling uterine fibroids and infertility. <br />Can Fibroids Prevent Pregnancy?<br />Fibroids can grow during pregnancy as there is an increase in estrogen and progesterone levels in your body. In terms of conceiving, fibroids rarely prevent women from getting pregnant. <br />Typically, you cannot treat fibroids while pregnant, but there may be options available to relieve symptoms temporarily. Also, some fibroid symptoms can be signs of pregnancy complications, so talk to a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis.<br />How Do You know if Fibroids are Causing Infertility?<br />If you are struggling to conceive and think you may have fibroids, you might be wondering if there is a connection between the two. The best way to find out if fibroids are causing infertility is by consulting a fibroid specialist, especially if you are experiencing symptoms. Our symptom checker can also provide further insight into whether fibroids cause the symptoms you are experiencing and if you should consult a doctor for an official diagnosis.<br />Which Fibroids Cause Infertility?<br />Each type of fibroid is associated with causing specific symptoms. When it comes to infertility or pregnancy complications, submucosal fibroids are most likely to cause issues. Submucosal fibroids and infertility are firmly linked, as they can disrupt implantation and embryo growth. <br />What Size of Fibroids Can Cause Infertility?<br />There are three different size classifications for fibroids: small (between 20 mm and 5 cm), medium (Between 20 and 60 mm), and large (More than 60 mm). <br />Smaller fibroids tend to cause mild symptoms, while larger fibroids are more likely to have relatively severe symptoms, such as infertility.<br /><br />Treatment Options for Fibroids and Fertility<br />1- Hysterectomy: This surgical procedure removes the uterus, resulting in a woman being unable to conceive or be pregnant. It’s a permanent solution with significant drawbacks. Hysterectomies entail immediate sterility but also necessitate a prolonged recovery period along with risks of early menopause due to hormonal imbalances. <br />2- Myomectomy: Unlike a hysterectomy, this surgical procedure preserves the uterus. A myomectomy removes fibroids from the uterine walls, leaving the uterus intact. However, there is potential for scarring and fibroid recurrence after a myomectomy. According to research studies, myomectomy postoperative adhesions significantly impact the ability to conceive. Therefore, when surgery is performed as infertility treatment, attention should be paid to whether the benefits outweigh the risks .<br />3- Acessa™ Procedure: This emerging technique offers minimally invasive alternatives to traditional surgical approaches, utilizing radiofrequency ablation to target fibroid tissue. The main concern with Acessa™ is that the research about its impact on fertility is currently inconclusive. <br />4- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE): UFE is a minimally invasive procedure, and with its high success rate, the National Institute of Health reports it’s clear that UFE is one of the most promising methods for preserving fertility while addressing fibroids. UFE introduces tiny particles into the uterine artery, cutting off the fibroid’s blood supply so they shrink and wither away. The procedure ultimately alleviates fibroids symptoms without resorting to surgery. Most importantly, UFE leaves the uterus intact, allowing for conception and pregnancy post-treatment. <br />The choice of fibroid treatment ultimately depends on the size, number, and location of fibroids, age, and fertility goals. It is important to consult your doctor to understand the different treatments, the risks of fibroid surgery, and their impact on fertility. <br /><br />د. فرقد صالح<br /><br /><br />The first university in Iraq