Oral Lichen Planus: A Chronic Inflammatory Condition by Ghadeer talib
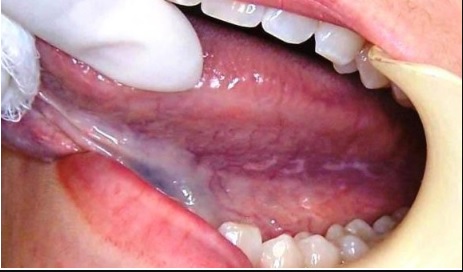
Introduction Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth. It is an immune-mediated condition that leads to painful, erosive, or ulcerative lesions in the oral cavity. While OLP is not contagious, it can significantly impact a patient's quality of life due to discomfort and potential complications.<br /><br />Causes and Risk Factors The exact cause of OLP remains unclear, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the mucous membranes. Several factors may contribute to its development, including:<br /><br />Genetic predisposition<br /><br />Psychological stress<br /><br />Allergic reactions<br /><br />Medications (such as NSAIDs, beta-blockers, and oral hypoglycemic agents)<br /><br />Hepatitis C virus infection<br /><br /><br />Symptoms OLP presents in various forms, including:<br /><br />Reticular Form: Characterized by white, lace-like patches on the oral mucosa, usually painless.<br /><br />Erosive Form: Painful red patches or ulcerations, often causing significant discomfort.<br /><br />Atrophic Form: Thinning of the mucosa with increased sensitivity and pain.<br /><br />Plaque-like Form: White, raised patches that may resemble leukoplakia. Common sites affected include the inner cheeks, tongue, gums, and lips. Some patients may also experience a burning sensation, sensitivity to spicy foods, and dry mouth.<br /><br /><br />Diagnosis Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic appearance of lesions. However, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm OLP and rule out other conditions, such as oral cancer or fungal infections. Histopathological examination reveals characteristic changes, including basal cell degeneration and lymphocytic infiltration.<br /><br />Treatment and Management While there is no cure for OLP, treatment aims to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. Common management strategies include:<br /><br />Topical Corticosteroids: First-line treatment to reduce inflammation and discomfort.<br /><br />Immunosuppressive Agents: Tacrolimus and cyclosporine may be used in severe cases.<br /><br />Pain Relievers: Analgesic mouthwashes or systemic pain relievers can help manage discomfort.<br /><br />Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding spicy foods, tobacco, and alcohol to prevent irritation.<br /><br />Regular Monitoring: Long-term follow-up is necessary, as OLP carries a small risk of malignant transformation into oral squamous cell carcinoma.<br /><br /><br />Conclusion Oral Lichen Planus is a chronic inflammatory condition requiring long-term management. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can improve patient outcomes and prevent complications. Regular dental check-ups and lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in managing this condition effectively<br />