The Mallampati Test: A Tool for Predicting Difficult Intubation
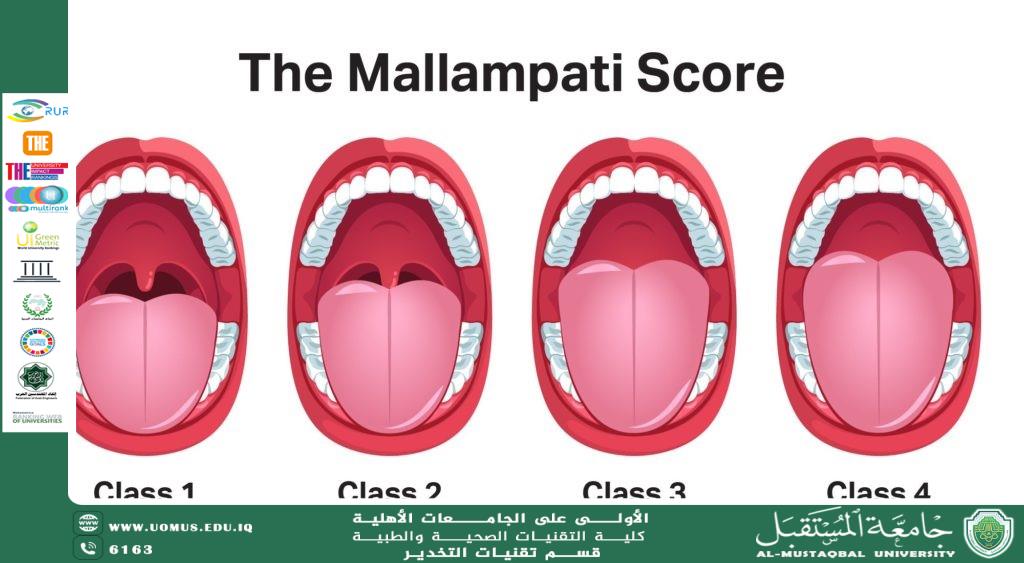
The Mallampati test is a quick and simple bedside assessment used by healthcare professionals to evaluate a patient's airway and predict potential difficulties with intubation. It involves visually assessing the structures in the oropharynx, specifically the visibility of the base of the uvula, faucial pillars, and soft palate. <br />How the Mallampati Test Works<br />The test is performed with the patient sitting upright, head in a neutral position, mouth wide open, and tongue protruded without phonation. Based on the visibility of the structures mentioned above, the patient is assigned a Mallampati class: <br />• Class I: Soft palate, fauces, uvula, and pillars are visible. <br />• Class II: Soft palate, fauces, and uvula are visible.<br />• Class III: Soft palate and base of uvula are visible. <br />• Class IV: Only the hard palate is visible. <br /><br /> <br /> <br />Effectiveness of the Mallampati Test<br />The Mallampati test has been widely used for over 30 years and is considered a valuable tool in airway assessment. However, it is important to note that it is not a perfect predictor of difficult intubation.<br />• Sensitivity: The Mallampati test has a moderate sensitivity, meaning it can correctly identify some but not all patients who will have difficult intubation. <br />• Specificity: The test has a high specificity, meaning it is good at identifying patients who are unlikely to have difficult intubation.<br />Limitations of the Mallampati Test<br />The Mallampati test has some limitations:<br />• It is a subjective assessment and can be influenced by factors such as patient cooperation and examiner experience. <br />• It only assesses the anatomical structures of the oropharynx and does not take into account other factors that can contribute to difficult intubation, such as obesity, neck mobility, and previous airway surgery.<br />Approach to Predicting Difficult Intubation<br />The Mallampati test, while a valuable tool in airway assessment, is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to predicting difficult intubation. Healthcare professionals utilize a variety of factors and assessments to get a comprehensive picture of a patient's airway and anticipate potential challenges.<br /><br />Factors Beyond the Mallampati<br />Several factors beyond the Mallampati score can contribute to difficult intubation:<br />• Patient characteristics: Obesity, a large tongue, a short or thick neck, and a receding mandible can all make intubation more challenging.<br />• Medical history: Previous airway surgery, radiation therapy to the neck, and certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can affect airway anatomy and function.<br />• Clinical assessment: Assessing neck mobility, mouth opening, and the ability to protrude the tongue can provide additional clues about potential difficulties.<br />Other Assessment Tools<br />In addition to the Mallampati test, healthcare professionals may use other assessment tools, such as:<br />1-Thyromental distance: Measuring the distance between the thyroid cartilage and the mentum (chin) can help assess the space available for intubation.<br />2-Cormack-Lehane grading: This system evaluates the view of the larynx during direct laryngoscopy, providing a more objective assessment of airway difficulty.<br />The Importance of Clinical Judgment<br />Ultimately, predicting difficult intubation relies heavily on the clinical judgment of experienced healthcare professionals. They take into account all available information, including the Mallampati score, other assessment tools, patient characteristics, and medical history, to make an informed decision about the best approach to airway management.<br /><br /><br />Conclusion<br />The Mallampati test is a useful tool for predicting difficult intubation, but it is most effective when used as part of a comprehensive airway assessment. And should not be used in isolation. It is most effective when used in conjunction with other airway assessment tools and clinical judgment. By considering a variety of factors and utilizing other assessment tools, healthcare professionals can better anticipate potential challenges and ensure patient safety during intubation. <br />م.م نهى نوماس <br /><br />AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq<br /><br />