A scientific article by Ms. Ala Adel Rasmi entitled "skin cells "
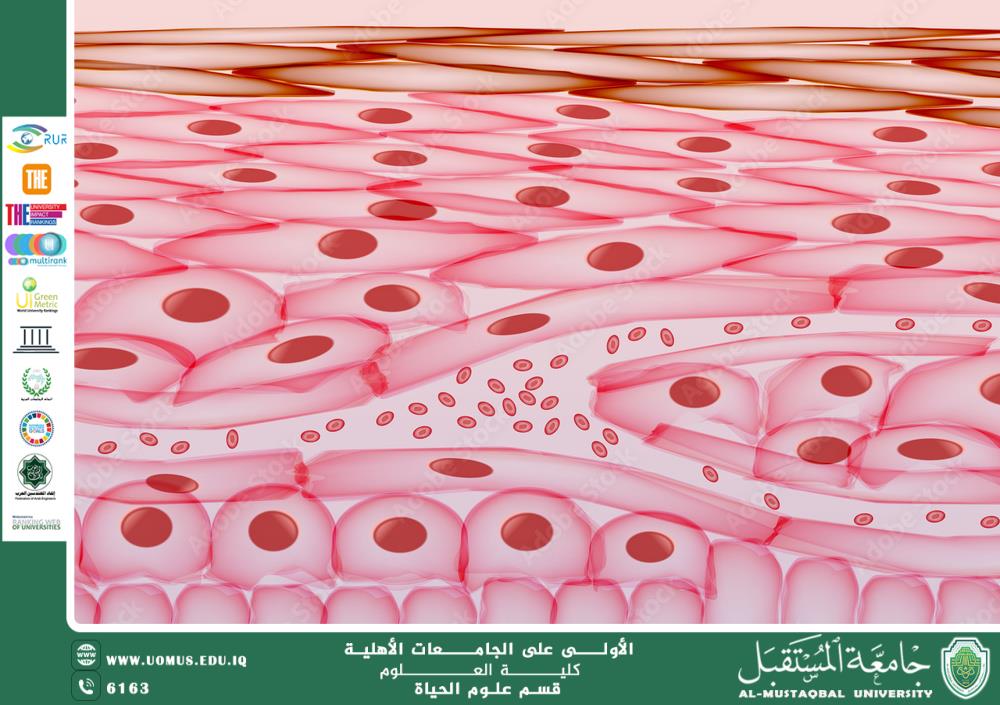
Skin cells are the cells that form skin tissue and play an important role in protecting the body from external factors, such as bacteria, viruses, and climate changes. The skin is the largest organ in the body and acts as a protective shield, and includes several types of cells that perform multiple functions.<br /><br />1. Main types of skin cells:<br />1.1 Keratinocytes:<br />Definition: Keratinocytes are the most common type in the skin, making up about 90% of the cells in the upper layer of the skin (dermis).<br />Function: Produces the protein keratin, which provides strength and durability to the skin, hair, and nails. It also plays an important role in protecting the skin from environmental factors such as microbes and exposure to ultraviolet rays.<br />Layer: Found in the outer layer of the epidermis, it gradually moves from the basal layer to the upper layers where it dies and turns into dead cells that form the stratum corneum.<br />1.2 Melanocytes:<br />Definition: They are cells found in the basal layer of the epidermis.<br />Function: Produces melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Melanin helps protect the skin from damage caused by ultraviolet rays.<br />Layer: Found in the basal layer of the epidermis, produces melanin that is transferred to keratinocytes.<br />1.3 Langerhans Cells:<br />Definition: These are immune cells found in the epidermis.<br />Function: They act as part of the immune system and help defend the skin against microbes and foreign bodies.<br />Layer: They are found mainly in the spinous layer of the epidermis.<br />1.4 Merkel Cells:<br />Definition: These are sensory cells found in the epidermis.<br />Function: They act as pressure sensors and aid in sensory perception, enhancing the skin's ability to sense external stimuli.<br />Layer: They are found in the basal layer of the epidermis, near nerve endings.<br />2. Main layers of the skin:<br />The skin consists of three main layers, each of which contains different types of cells:<br /><br />2.1 Epidermis:<br />It is the outer layer of the skin, which contains keratinocytes.<br />Sub-layers of the skin:<br />Stratum Basale: It contains stem cells that divide to form new cells. This is where melanin cells and Langerhans cells are found.<br />Stratum Spinosum: It contains keratinocytes that begin to form connections between cells.<br />Stratum Granulosum: It contains keratinocytes that produce protein granules that contribute to the formation of the skin's protective barrier.<br />Stratum Corneum: It contains dead cells containing keratin, and it is the layer that constantly gets rid of dead skin cells.<br />2.2 Dermis:<br />It is the layer that lies beneath the epidermis, and contains collagen and elastin fibers that provide elasticity and strength to the skin. The dermis contains blood vessels, nerves, and sweat glands.<br />Other types of cells in the dermis:<br />Fibroblasts: produce collagen and elastin.<br />Immune cells: such as mast cells and macrophages.<br />2.3 Hypodermis:<br />It is the deepest layer of the skin, containing fat and connective tissue. It plays a role in thermal insulation and energy storage.<br />3. Functions of skin cells:<br />Protection: Keratinocytes form a barrier that protects the body from microbes, wounds, and dehydration.<br />Melanin production: Melanocytes protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet rays.<br />Thermoregulation: Sweat glands help cool the body.<br />Sensation: Merkel cells and neurons in the dermis send sensory signals to the brain.<br />Regeneration: The skin's ability to renew itself thanks to stem cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis.<br />4. Diseases related to skin cells:<br />Skin cancer: such as melanoma, a type of cancer that begins in melanocytes.<br />Immune diseases: such as psoriasis and eczema, where an abnormal reaction occurs in the immune cells in the skin.<br />Skin ulcers: can occur as a result of poor cell renewal or wounds that did not heal properly.<br />5. Factors affecting skin cells:<br />Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays: leads to damage to melanocytes and increases the risk of cancer.<br />Aging: The process of cell renewal slows down with age, leading to wrinkles and dry skin.<br />Nutrition and environment: Environmental factors such as pollution and nutrition affect the health of skin cells.<br />Skin cells are an essential part of the body's natural barrier, and play a major role in maintaining the body's overall health, and protecting it from many environmental and pathological factors.<br /><br /><br /><br />AL_mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq<br /><br />