Scientific Article by Dr. Nasser Abdul Hassan Nasser Title: Computational Chemistry and its Relationship with Biochemistry
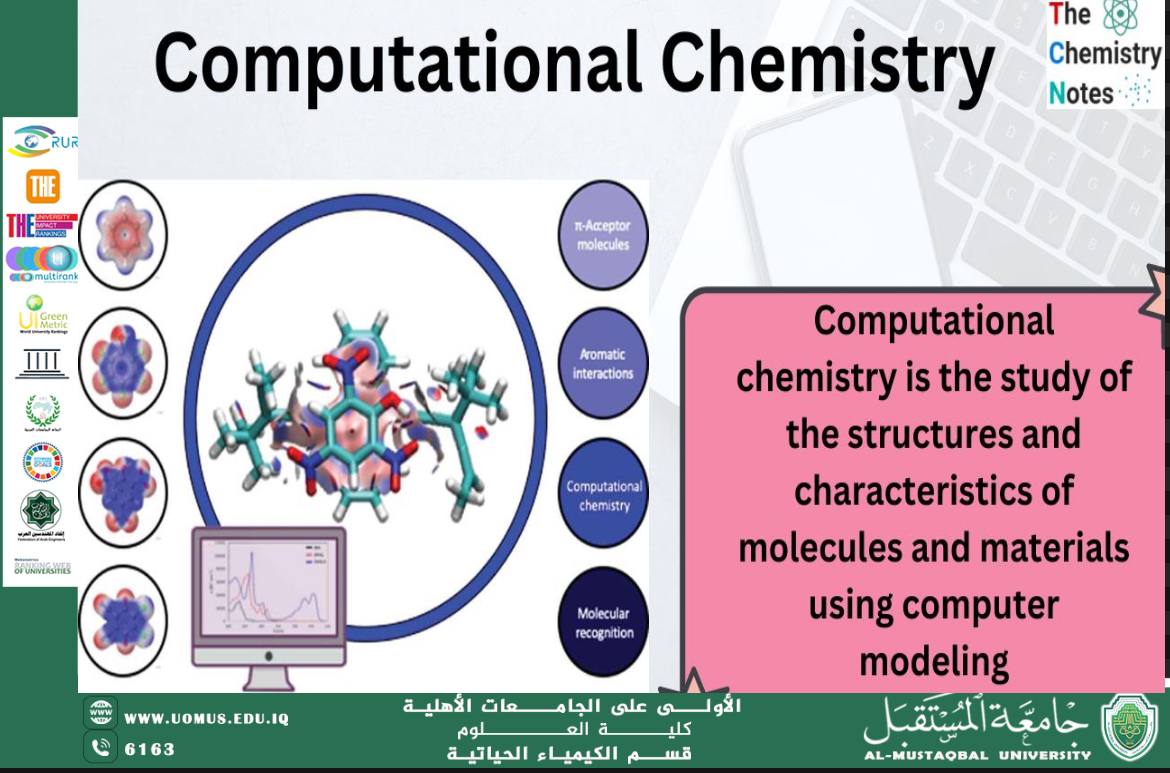
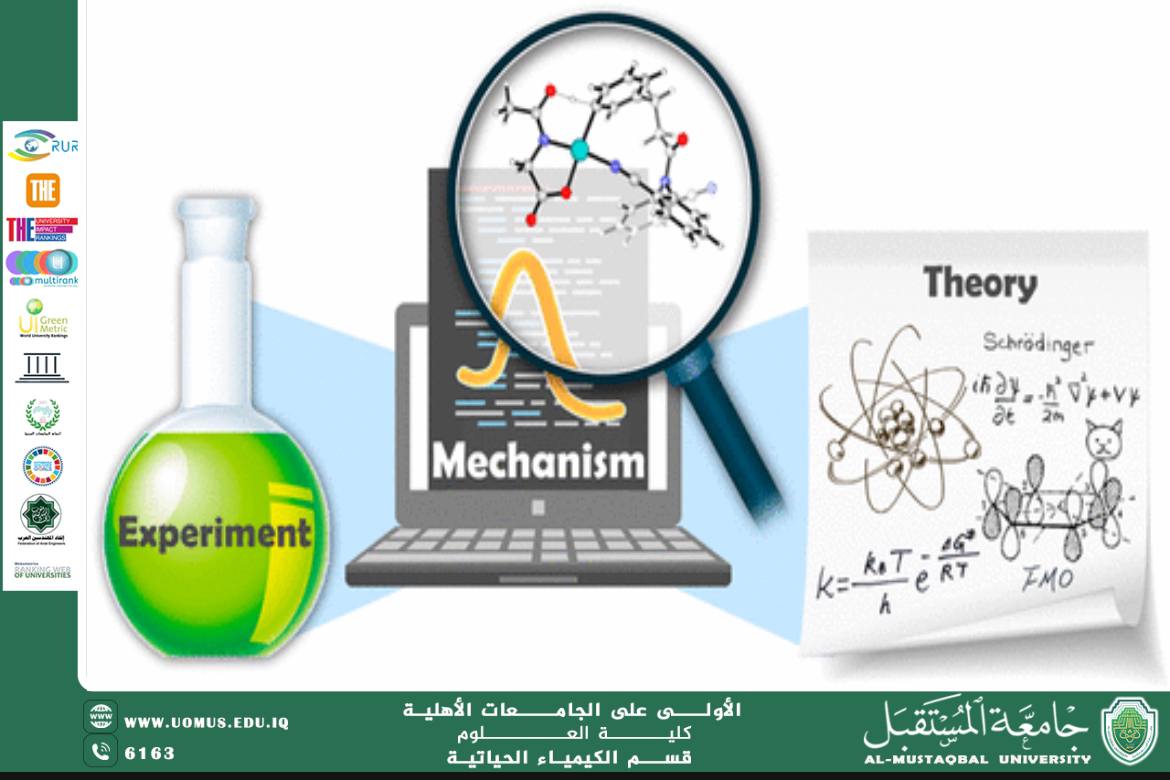
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computational techniques and mathematical models to understand chemical phenomena. By utilizing computers to simulate chemical reactions and calculate molecular properties, scientists can explore and explain chemical processes accurately and efficiently. On the other hand, biochemistry is the science that studies the chemical processes in living organisms. It relies on understanding the biochemical reactions occurring within cells and living organisms, serving as the foundation for understanding many life functions.<br />Concept of Computational Chemistry:<br />Computational chemistry deals with the use of advanced software and mathematical models to describe chemical reactions. It integrates mathematics, physics, and computer science to study chemical behavior at the molecular level. Computational methods such as Density Functional Theory (DFT), Hartree-Fock equations, and molecular simulations are used to provide deep insights into chemical compounds and their interactions.<br />The Interaction Between Computational Chemistry and Biochemistry:<br />In biochemistry, many complex chemical reactions occur within living organisms. By using computational tools, biochemists can simulate interactions between biological molecules such as proteins, enzymes, and DNA, enhancing our understanding of how these molecules function within cells.<br />By applying computational chemistry, it is possible to simulate interactions between proteins and enzymes during biochemical processes like metabolic reactions. Computational methods can also be used to study how drugs interact with cellular receptors or proteins, aiming to design more effective medicines.<br />The Role of Computational Chemistry in Biochemistry:<br />1. Studying Proteins and Enzymes: Proteins are large, complex molecules that play a vital role in living cells. Using computational chemistry, scientists can simulate protein folding and study their interactions with other molecules. For example, molecular simulations can help understand how enzymes interact with substrates in biochemical reactions.<br />2. Drug Design: Computational chemistry contributes to drug development by simulating how drugs interact with proteins or other molecules in the body. Using techniques like molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations, researchers can identify molecules that may interact effectively with specific therapeutic targets.<br />3. Studying Nucleic Acid Interactions: Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are essential biological molecules involved in storing and transmitting genetic information. Computational chemistry allows researchers to study the structure of these molecules and how they interact with other molecules, such as proteins, which aids in understanding the processes of transcription and translation of genetic information.<br />4. Analyzing Biological Networks: A modern application of computational chemistry is the analysis of complex biological networks, such as protein-protein interactions, gene interactions, and other cellular networks. This helps in understanding how biological processes are organized within cells and living organisms.<br />Challenges and Future Prospects:<br />Despite significant progress in the application of computational chemistry in biochemistry, many challenges remain. One of the primary challenges is simulating complex biological systems, as these systems are often large and highly intricate, making precise modeling computationally intensive. Additionally, there is still a need to develop more accurate and efficient methods for dealing with multi-molecular system interactions.<br />However, with continuous advancements in computing technology and increased computational power, the future holds great potential. Computational chemistry is expected to continue making significant contributions to understanding complex biological mechanisms and developing new drugs for disease treatment.<br />Computational chemistry is a powerful tool in studying biochemistry, providing a means to understand biological processes at the molecular level.<br />By combining computational science with biochemistry, it is possible to enhance drug design, examine biological interactions, and gain new insights into how biological systems operate. As computational techniques continue to advance, computational chemistry is likely to contribute even more to understanding and analyzing biological processes, opening new avenues for disease treatment and scientific progress in medicine and biology.<br /> Al-Mustaqbal University, the first university in Iraq.<br /><br />