A scientific article by the teaching assistant (Ala Adel Rasmi) entitled "The Thyroid Gland"
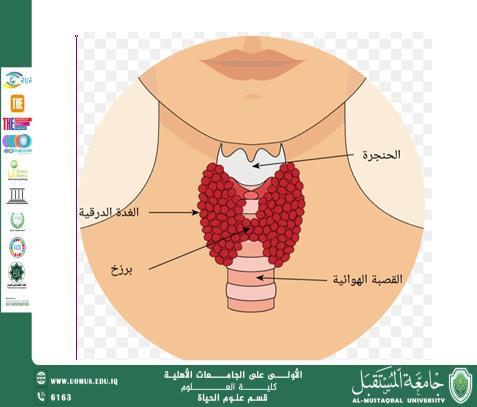
Thyroid gland:<br /><br />It is a small endocrine gland located in the front of the neck, specifically under the larynx, and is responsible for secreting important hormones that play a vital role in regulating many body functions. The main hormone secreted by the thyroid gland is "thyroxine" (T4) and "triiodothyronine" (T3), as they help control the speed of metabolism in the body. The thyroid gland also secretes the hormone calcitonin, which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.<br /><br />Thyroid gland functions:<br /><br />1. Regulating metabolism: Thyroid hormones affect how the body uses energy by increasing or decreasing the metabolic rate.<br /><br />2. Growth and development of the body: The thyroid gland plays an important role in physical and mental growth, especially during childhood.<br /><br />3. Regulating temperature: Thyroid hormones contribute to regulating body temperature, as they work to increase heat production when the body needs more energy.<br /><br />4. Heart and muscle functions: The thyroid gland helps regulate heart rate and muscle contraction force.<br /><br />Thyroid diseases:<br /><br />1. Hyperthyroidism: occurs when the thyroid gland secretes excessive amounts of its hormones, which leads to the acceleration of vital processes in the body. Hyperactivity can cause unexplained weight loss, increased heart rate, anxiety, and excessive sweating.<br /><br />2. Hypothyroidism: occurs when the thyroid gland is unable to produce enough hormones, which leads to the slowing down of vital processes. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and extreme cold.<br /><br />3. Goiter: is an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, often as a result of cell enlargement due to iodine deficiency or other disorders.<br /><br />4. Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis may occur as a result of infection or immune disorders, which may affect the secretion of hormones.<br /><br />Diagnosis and treatment of thyroid problems:<br /><br />-Diagnosis: Thyroid disorders are diagnosed through blood tests that measure the levels of the hormones TSH, T3, and T4. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI scans may also be performed.<br /><br />Treatment:<br />The treatment of the thyroid gland depends on the type of disease. Treatment may include medications to adjust hormone levels, radioactive iodine therapy in cases of hyperactivity, or surgery in some severe cases.<br /><br />In conclusion:<br />The thyroid gland is one of the vital organs that greatly affects human health. It is important to monitor the health of the thyroid gland periodically, especially if unexplained symptoms appear, in order to obtain appropriate treatment in a timely manner.<br /><br />Al-Mustaqbal University is the first university in Iraq